“前視圖”投影
為了將激光雷達傳感器的“前視圖”展平為2D圖像,必須將3D空間中的點投影到可以展開的圓柱形表面上,以形成平面。

問題在于這樣做會將圖像的接縫直接放在汽車的右側。將接縫定位在汽車的最后部更有意義,因此前部和側部更重要的區域是不間斷的。讓這些重要區域不間斷將使卷積神經網絡更容易識別那些重要區域中的整個對象。
以下代碼解決了這個問題。

沿每個軸配置刻度
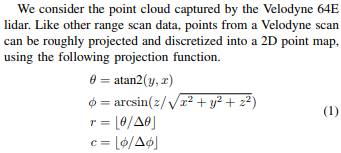
變量h r e s h_{res}和v r e s v_{res}非常依賴于所使用的LIDAR傳感器。在KTTI數據集中,使用的傳感器是Velodyne HDL 64E。根據Velodyne HDL 64E的規格表,它具有以下重要特征:
垂直視野為26.9度,分辨率為0.4度,垂直視野被分為傳感器上方+2度,傳感器下方-24.9度
360度的水平視野,分辨率為0.08-0.35(取決于旋轉速度)
旋轉速率可以選擇在5-20Hz之間
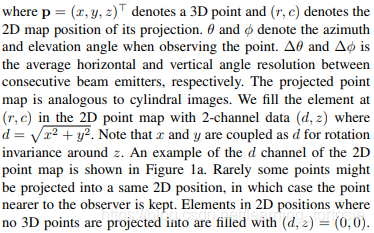
可以按以下方式更新代碼:
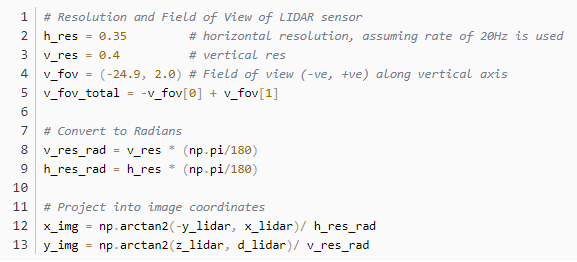
然而,這導致大約一半的點在x軸負方向上,并且大多數在y軸負方向上。為了投影到2D圖像,需要將最小值設置為(0,0),所以需要做一些改變:

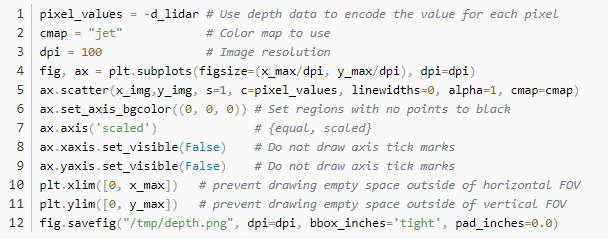
繪制二維圖像
將3D點投影到2D坐標點,最小值為(0,0),可以將這些點數據繪制成2D圖像。
完整代碼
把上面所有的代碼放在一個函數中。
def lidar_to_2d_front_view(points, v_res, h_res, v_fov, val=“depth”, cmap=“jet”, saveto=None, y_fudge=0.0 ): “”“ Takes points in 3D space from LIDAR data and projects them to a 2D ”front view“ image, and saves that image.
Args: points: (np array) The numpy array containing the lidar points. The shape should be Nx4 - Where N is the number of points, and - each point is specified by 4 values (x, y, z, reflectance) v_res: (float) vertical resolution of the lidar sensor used. h_res: (float) horizontal resolution of the lidar sensor used. v_fov: (tuple of two floats) (minimum_negative_angle, max_positive_angle) val: (str) What value to use to encode the points that get plotted. One of {”depth“, ”height“, ”reflectance“} cmap: (str) Color map to use to color code the `val` values. NOTE: Must be a value accepted by matplotlib‘s scatter function Examples: ”jet“, ”gray“ saveto: (str or None) If a string is provided, it saves the image as this filename. If None, then it just shows the image. y_fudge: (float) A hacky fudge factor to use if the theoretical calculations of vertical range do not match the actual data.
For a Velodyne HDL 64E, set this value to 5. ”“”
# DUMMY PROOFING assert len(v_fov) ==2, “v_fov must be list/tuple of length 2” assert v_fov[0] 《= 0, “first element in v_fov must be 0 or negative” assert val in {“depth”, “height”, “reflectance”}, ’val must be one of {“depth”, “height”, “reflectance”}‘
x_lidar = points[:, 0] y_lidar = points[:, 1] z_lidar = points[:, 2] r_lidar = points[:, 3] # Reflectance # Distance relative to origin when looked from top d_lidar = np.sqrt(x_lidar ** 2 + y_lidar ** 2) # Absolute distance relative to origin # d_lidar = np.sqrt(x_lidar ** 2 + y_lidar ** 2, z_lidar ** 2)
v_fov_total = -v_fov[0] + v_fov[1]
# Convert to Radians v_res_rad = v_res * (np.pi/180) h_res_rad = h_res * (np.pi/180)
# PROJECT INTO IMAGE COORDINATES x_img = np.arctan2(-y_lidar, x_lidar)/ h_res_rad y_img = np.arctan2(z_lidar, d_lidar)/ v_res_rad
# SHIFT COORDINATES TO MAKE 0,0 THE MINIMUM x_min = -360.0 / h_res / 2 # Theoretical min x value based on sensor specs x_img -= x_min # Shift x_max = 360.0 / h_res # Theoretical max x value after shifting
y_min = v_fov[0] / v_res # theoretical min y value based on sensor specs y_img -= y_min # Shift y_max = v_fov_total / v_res # Theoretical max x value after shifting
y_max += y_fudge # Fudge factor if the calculations based on # spec sheet do not match the range of # angles collected by in the data.
# WHAT DATA TO USE TO ENCODE THE VALUE FOR EACH PIXEL if val == “reflectance”: pixel_values = r_lidar elif val == “height”: pixel_values = z_lidar else: pixel_values = -d_lidar
# PLOT THE IMAGE cmap = “jet” # Color map to use dpi = 100 # Image resolution fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(x_max/dpi, y_max/dpi), dpi=dpi) ax.scatter(x_img,y_img, s=1, c=pixel_values, linewidths=0, alpha=1, cmap=cmap) ax.set_axis_bgcolor((0, 0, 0)) # Set regions with no points to black ax.axis(’scaled‘) # {equal, scaled} ax.xaxis.set_visible(False) # Do not draw axis tick marks ax.yaxis.set_visible(False) # Do not draw axis tick marks plt.xlim([0, x_max]) # prevent drawing empty space outside of horizontal FOV plt.ylim([0, y_max]) # prevent drawing empty space outside of vertical FOV
if saveto is not None: fig.savefig(saveto, dpi=dpi, bbox_inches=’tight‘, pad_inches=0.0) else: fig.show()
以下是一些用例:
import matplotlib.pyplot as pltimport numpy as np
HRES = 0.35 # horizontal resolution (assuming 20Hz setting)VRES = 0.4 # vertical resVFOV = (-24.9, 2.0) # Field of view (-ve, +ve) along vertical axisY_FUDGE = 5 # y fudge factor for velodyne HDL 64E
lidar_to_2d_front_view(lidar, v_res=VRES, h_res=HRES, v_fov=VFOV, val=“depth”, saveto=“/tmp/lidar_depth.png”, y_fudge=Y_FUDGE)
lidar_to_2d_front_view(lidar, v_res=VRES, h_res=HRES, v_fov=VFOV, val=“height”, saveto=“/tmp/lidar_height.png”, y_fudge=Y_FUDGE)
lidar_to_2d_front_view(lidar, v_res=VRES, h_res=HRES, v_fov=VFOV, val=“reflectance”, saveto=“/tmp/lidar_reflectance.png”, y_fudge=Y_FUDGE)
產生以下三個圖像:
Depth

Height

Reflectance

后續操作步驟
目前創建每個圖像非常慢,可能是因為matplotlib,它不能很好地處理大量的散點。
因此需要創建一個使用numpy或PIL的實現。
測試
需要安裝python-pcl,加載PCD文件。
sudo apt-get install python-pip
sudo apt-get install python-dev
sudo pip install Cython==0.25.2
sudo pip install numpy
sudo apt-get install git
git clone https://github.com/strawlab/python-pcl.git
cd python-pcl/
python setup.py build_ext -i
python setup.py install
可惜,sudo pip install Cython==0.25.2這步報錯:
“Cannot uninstall ‘Cython’。 It is a distutils installed project and thus we cannot accurately determine which files belong to it which would lead to only a partial uninstall.”
換個方法,安裝pypcd:
pip install pypcd
查看 https://pypi.org/project/pypcd/ ,用例如下:
Example-------
。. code:: python
import pypcd# also can read from file handles.pc = pypcd.PointCloud.from_path(’foo.pcd‘)# pc.pc_data has the data as a structured array# pc.fields, pc.count, etc have the metadata
# center the x fieldpc.pc_data[’x‘] -= pc.pc_data[’x‘].mean()
# save as binary compressedpc.save_pcd(’bar.pcd‘, compression=’binary_compressed‘)
測試數據結構:
“ 》》》 lidar = pypcd.PointCloud.from_path(‘~/pointcloud-processing/000000.pcd’)
》》》 lidar.pc_data
array([(18.323999404907227, 0.04899999871850014, 0.8289999961853027, 0.0),
(18.3439998626709, 0.10599999874830246, 0.8289999961853027, 0.0),
(51.29899978637695, 0.5049999952316284, 1.944000005722046, 0.0),
…,
(3.7139999866485596, -1.3910000324249268, -1.7330000400543213, 0.4099999964237213),
(3.9670000076293945, -1.4739999771118164, -1.8569999933242798, 0.0),
(0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0)],
dtype=[(‘x’, ‘《f4’), (‘y’, ‘《f4’), (‘z’, ‘《f4’), (‘intensity’, ‘《f4’)])
》》》 lidar.pc_data[‘x’]
array([ 18.3239994 , 18.34399986, 51.29899979, …, 3.71399999,
3.96700001, 0. ], dtype=float32) ”
加載PCD:
import pypcd
lidar = pypcd.PointCloud.from_path(’000000.pcd‘)
x_lidar:
x_lidar = points[’x‘]
結果:
Depth

Height

Reflectance

編輯:lyn
-
傳感器
+關注
關注
2552文章
51228瀏覽量
754651 -
投影
+關注
關注
0文章
143瀏覽量
24715 -
激光雷達
+關注
關注
968文章
3989瀏覽量
190074
原文標題:點云處理——將激光雷達數據投影到二維圖像
文章出處:【微信號:vision263com,微信公眾號:新機器視覺】歡迎添加關注!文章轉載請注明出處。
發布評論請先 登錄
相關推薦
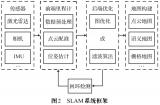
激光雷達在SLAM算法中的應用綜述
激光雷達技術的基于深度學習的進步
激光雷達與其他傳感器的比較
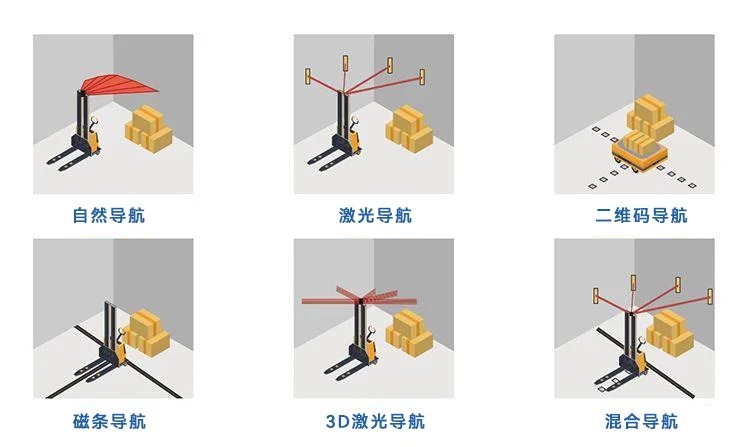
agv叉車激光導航和二維碼導航有什么區別?適用什么場景?選哪種比較好?
二維力傳感器怎么安裝,在安裝二維力傳感器的安裝步驟

lidar傳感器和激光測距傳感器的區別
半導體激光雷達及傳感器件產業化項目落地德州
瑞識科技推出用于激光雷達的二維可尋址VCSEL芯片并獲量產訂單
Phlux推出一種新型傳感器以進軍汽車激光雷達(LiDAR)市場
華為詳細解讀激光雷達
SolidVue為激光雷達傳感器設計SoC,可評估周圍物體的形狀和距離
現代汽車和起亞汽車宣布開發片上激光雷達傳感器




 關于激光雷達傳感器如何投影成二維圖像
關于激光雷達傳感器如何投影成二維圖像












評論