一、數(shù)組
開發(fā)環(huán)境:
虛擬機(jī)+Linux操作系統(tǒng)。
虛擬機(jī):虛擬一臺電腦。
Linux操作系統(tǒng):redhat、ubuntu系統(tǒng)、紅旗系統(tǒng)。
Linux基本指令、C語言數(shù)據(jù)結(jié)構(gòu)、C語言語句、C語言運(yùn)算符、數(shù)組。
數(shù)組:多個同類型數(shù)據(jù)的集合。
一維數(shù)組的定義語法:int data[10]; <數(shù)據(jù)類型> <數(shù)據(jù)名稱>[常量-整數(shù)-數(shù)據(jù)數(shù)量];
定義一個int類型的數(shù)組,數(shù)組的名稱是data,長度是10,所占空間大小:4*10字節(jié)。
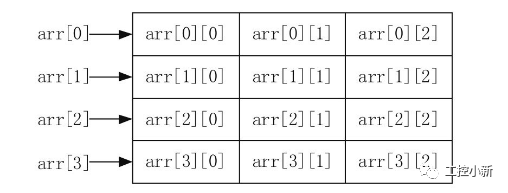
二維數(shù)組的定義語法:int data[10][5];
|
int data[3][5]= { {1,2,3,4,5}, {1,2,3,4,5}, {1,2,3,4,5}, }; #include int main() { int data[3][5]= { {1,2,3,4,5}, {11,12,13,14,15}, {21,22,23,24,25}, }; printf("%d\n",data[1][1]); return 0; } |
多維數(shù)組的定義語法:int data[][][]…
特點(diǎn):
- 訪問數(shù)組成員的時候:下標(biāo)是從0開始的。int data[10]; 下標(biāo) (0~9)
- 數(shù)組只是支持在定義的時候進(jìn)行整體賦值。
- 數(shù)組定義的時候,[]里只能填常量。數(shù)組在定義之后就無法更改大小。
- 數(shù)組的空間是連續(xù)的—內(nèi)存。
- 數(shù)組的名稱就是數(shù)組空間的首地址。
- 數(shù)組初始化時,如果沒有賦值,那么數(shù)組空間里的數(shù)據(jù)是未知的---局部變量。
- 數(shù)組初始化時,只要給一個空間賦值,剩余空間都自動初始化為0---局部變量。
示例1:
|
#include int main() { char i; int data[10]={12,13,14,15}; //下標(biāo) int a[5]; for(i=0;i<10;i++) //0~9 { printf("data[%d]=%d\n",i,data[i]); } for(i=0;i<5;i++) //0~4 { printf("a[%d]=%d\n",i,a[i]); } return 0; } |
示例2:
|
#include int main() { int i; int data[5]={0}; //下標(biāo) //從鍵盤上讀取5個數(shù)據(jù)存放到數(shù)組里 printf("請輸入5個數(shù)據(jù):"); for(i=0;i<5;i++) { scanf("%d",&data[i]); //兩種:空格 、 回車-換行 }
for(i=0;i<5;i++) { printf("data[%d]=%d\n",i,data[i]); }
for(i=4;i>=0;i--) { printf("data[%d]=%d\n",i,data[i]); } return 0; } |
配置VIM編輯器:在命令行上運(yùn)行命令: vim /etc/vimrc
打開文件之后,在文件結(jié)尾加上兩行代碼保存退出。
|
set number set tabstop=4 |
作業(yè):
- 定義數(shù)組,從鍵盤上錄入5個浮點(diǎn)類型數(shù)據(jù)存放到數(shù)組,計(jì)算平均值和最大、最小值,輸出到屏幕上。
|
#include int main() { int i; float sum=0; float data[5]; float max=0; float min=100; printf("請輸入5個數(shù)據(jù):"); /*1. 輸入數(shù)據(jù)*/ for(i=0;i<5;i++) { scanf("%f",&data[i]); } /*2. 處理數(shù)據(jù)*/ for(i=0;i<5;i++) { sum+=data[i]; //累加 if(data[i]>max)max=data[i]; if(data[i])min=data[i];<> } printf("平均值:%.1f\n",sum/5.0); printf("最大值:%.1f\n",max); printf("最小值:%.1f\n",min); return 0; } |
- 定義數(shù)組,從鍵盤上錄入5個整數(shù)數(shù)據(jù),求和,輸出結(jié)果。
|
#include int main() { int i; int sum=0; int data[5]; printf("請輸入5個數(shù)據(jù):"); /*1. 輸入數(shù)據(jù)*/ for(i=0;i<5;i++) { scanf("%d",&data[i]); } /*2. 處理數(shù)據(jù)*/ for(i=0;i<5;i++) { sum+=data[i]; //累加 } printf("和:%d\n",sum); return 0; } |
- 定義數(shù)組,從鍵盤上錄入10個整數(shù)數(shù)據(jù),計(jì)算里面大于5、大于10數(shù)據(jù)的數(shù)量,輸出結(jié)果。
|
#include int main() { int i; int data[10]; int cnt_10=0,cnt_5=0; printf("請輸入10個數(shù)據(jù):"); for(i=0;i<10;i++) { scanf("%d",&data[i]); } //處理數(shù)據(jù) for(i=0;i<10;i++) { if(data[i]>5)cnt_5++; if(data[i]>10)cnt_10++; } printf("cnt_5=%d\n",cnt_5); printf("cnt_10=%d\n",cnt_10); return 0; } |
作業(yè):
- 數(shù)組數(shù)據(jù)的替換:從鍵盤上輸入10個整數(shù)數(shù)據(jù)之后,再將數(shù)組里等于5的數(shù)據(jù)替換成8.
|
#include int main() { int data[10]; int i; for(i=0;i<10;i++) { scanf("%d",&data[i]); } for(i=0;i<10;i++) { if(data[i]==5)data[i]=8; } for(i=0;i<10;i++) { printf("%d ",data[i]); } return 0; } |
- 數(shù)組數(shù)據(jù)的排序:從鍵盤上輸入10個整數(shù)數(shù)據(jù),按照從大到小和小到大的兩種方式排序再輸出。--冒泡排序
|
#include int main() { int data[]={9,8,7,6,5,4,3,2,1}; int i,j; int tmp; for(i=0;i<9-1;i++) { for(j=0;j<9-1;j++) { if(data[j]>data[j+1]) { tmp=data[j]; data[j]=data[j+1]; data[j+1]=tmp; } } } for(i=0;i<9;i++) { printf("%d ",data[i]); } printf("\n"); return 0; }
/* 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 冒泡排序:相鄰的兩個數(shù)做比較,進(jìn)行位置交換 第一輪排序: 8 9 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 8 7 9 6 5 4 3 2 1 8 7 6 9 5 4 3 2 1 8 7 6 5 9 4 3 2 1 8 7 6 5 4 9 3 2 1 8 7 6 5 4 3 9 2 1 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 9 1 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 9
第二輪排序: 7 8 6 5 4 3 2 1 9 7 6 8 5 4 3 2 1 9 7 6 5 8 4 3 2 1 9 */
#include int main() { int data[]={1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9}; int i,j; int tmp; int flag=0; for(i=0;i<9-1;i++) { for(j=0;j<9-1-i;j++) { if(data[j]>data[j+1]) { tmp=data[j]; data[j]=data[j+1]; data[j+1]=tmp; flag=1; } } if(flag)flag=0; else break; }
for(i=0;i<9;i++) { printf("%d ",data[i]); } printf("\n"); return 0; }
/* 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 冒泡排序:相鄰的兩個數(shù)做比較,進(jìn)行位置交換 第一輪排序: 8 9 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 8 7 9 6 5 4 3 2 1 8 7 6 9 5 4 3 2 1 8 7 6 5 9 4 3 2 1 8 7 6 5 4 9 3 2 1 8 7 6 5 4 3 9 2 1 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 9 1 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 9
第二輪排序: 7 8 6 5 4 3 2 1 9 7 6 8 5 4 3 2 1 9 7 6 5 8 4 3 2 1 9 */ |
- 數(shù)組數(shù)據(jù)的拼接:定義A,B,C 3個數(shù)組,分別從鍵盤上給A,B,數(shù)組錄入數(shù)據(jù),再將A,B兩個數(shù)組的數(shù)據(jù)拷貝到C數(shù)組里,再打印出C數(shù)組的值。
|
#include int main() { int A[5]={1,2,3,4,5}; int B[5]={11,12,13,14,15}; int C[10]; int i=0,j=0; for(i=0;i<5;i++)C[i]=A[i]; //將A數(shù)組的數(shù)據(jù)拷貝到C數(shù)組 for(j=i;j+5;j++)c[j]=b[j-i];> for(i=0;i<10;i++) { printf("%d ",C[i]); } return 0; } |
- 數(shù)組數(shù)據(jù)的刪除(不是真正意思的刪除,這里相當(dāng)于覆蓋)。---數(shù)據(jù)庫
先從鍵盤上錄入10個整數(shù)數(shù)據(jù):比如:12 34 56 78 12 34 12 5 12 77
比如:刪除數(shù)組里所有的12這個數(shù)據(jù):得到最終結(jié)果:34 56 78 34 5 77 其他后面空間清0
|
#include int main() { int data[10]={1,2,2,2,5,2,7,2,9,2}; int a; int i,j; int cnt=9; //數(shù)組最后一個下標(biāo)位置 printf("原數(shù)組里的值:"); for(i=0;i<10;i++) { printf("%d ",data[i]); } printf("\n");
printf("請輸入要刪除的數(shù)字:"); scanf("%d",&a);
for(i=0;i<10;i++) { if(data[i]==a) { //實(shí)現(xiàn)數(shù)據(jù)覆蓋 for(j=i;j<10-1;j++) { data[j]=data[j+1]; } data[cnt--]=0; i--; } } printf("現(xiàn)在數(shù)組里的值:"); for(i=0;i<10;i++) { printf("%d ",data[i]); } printf("\n"); return 0; } |
- 數(shù)組數(shù)據(jù)的插入(整數(shù)數(shù)組)
比如:12 ,45,89,12,77
在第2個位置后面插入一個888
結(jié)果:12,45,888,89,12,77
|
#include int main() { int data[11]={1,2,2,2,5,2,7,2,9,2};//10個數(shù)據(jù) int a,b; int i,j; printf("原數(shù)組里的值:"); for(i=0;i<11;i++) { printf("%d ",data[i]); } printf("\n");
printf("請輸入要插入的數(shù)字值:"); scanf("%d",&a); printf("請輸入要插入的位置(數(shù)組的下標(biāo)位置):"); scanf("%d",&b);
for(i=10-1;i>=b;i--) { data[i+1]=data[i]; } data[b]=a; //插入數(shù)字
printf("現(xiàn)在數(shù)組里的值:"); for(i=0;i<11;i++) { printf("%d ",data[i]); } return 0; } |
6.從鍵盤上輸入一串整數(shù),使用中文大寫打印出來。--開具發(fā)票的時候就會用到
比如中文:壹、貳、叁、肆、伍、陸、柒、捌、玖、拾、佰、仟、萬、億、元、角、分、零、整
數(shù)位分離
任務(wù)2
- 給普通用戶增加sudo命令權(quán)限
- gedit文本編輯器命令。
vim 基于命令行編輯器。 (1)修改代碼-改錯
任務(wù)3:語句章節(jié)作業(yè)
1. 計(jì)算一個unsigned int類型數(shù)據(jù)中有多少個1(練習(xí)位運(yùn)算、if語句、循環(huán)語句)
|
#include int main() { unsigned int data=0x1234; int i; int cnt=0; //計(jì)數(shù)器--計(jì)數(shù) for(i=0;i<32;i++) { if(data&0x1) // 0與任何數(shù)相&,結(jié)果是0 { cnt++; } data>>=1;//data=data>>1; } printf("data=%d\n",data); return 0; } /* 00000000 00000000 00000000 00000010 ---0x2 00000000 00000000 00000000 00000001 00000000 00000000 00000000 00000000 */ |
1.求100之內(nèi)自然數(shù)中最大的能被17整除的數(shù)。(保存數(shù)據(jù))
|
#include int main() { int i; for(i=100;i>17;i--) { if(i%17==0) { printf("i=%d\n",i); break; } } return 0; }
//for循環(huán): 已知循環(huán) //while循環(huán):未知循環(huán) while(cnt--) |
3.計(jì)算并輸出200—400之間不能被3整除的整數(shù)的和。
|
#include int main() { int i; int sum=0; for(i=200;i<=400;i++) { if(i%3!=0) { sum+=i; } } printf("sum=%d\n",sum); return 0; } |
3.輸出所有200-400以內(nèi)能被3整除且個位數(shù)字為6的整數(shù)。
|
#include int main() { int i; for(i=200;i<=400;i++) { if(i%3==0) { //126 if(i%10==6)printf("個位數(shù)為6:%d\n",i); } } return 0; } |
4,打印所有水仙花數(shù)。所謂水仙花是指一個三位數(shù),其各位數(shù)字的立方和等于該數(shù)。
|
#include int main() { int i; int a,b,c; for(i=100;i<=999;i++) { //123 a=i/100; //百位 b=i%100/10; c=i%10/1; if((a*a*a+b*b*b+c*c*c)==i) { printf("%d\n",i); } } return 0; } |
5,判斷某一年是否是閏年(條件是:1、能整除4且不能整除1002、能整除400)。
|
#include int main() { int year; printf("請輸入年份:"); scanf("%d",&year);
if((year%4==0&&year%100!=0) || (year%400==0)) { printf("%d是閏年.\n",year); } else { printf("%d是平年.\n",year); } return 0; } |
6.輸入一個不多于5位的正整數(shù),判斷他是幾位數(shù),并逆序輸出。--不需要循環(huán)
|
#include int main() { int data; printf("輸入不多于5位數(shù)的整數(shù):"); scanf("%d",&data);
//12345 if(data/10000)printf("5位數(shù)\n"); else if(data/1000)printf("4位數(shù)\n"); else if(data/100)printf("3位數(shù)\n"); else if(data/10)printf("2位數(shù)\n"); else if(data/1)printf("1位數(shù)\n"); return 0; } |
7.輸入一個華氏溫度,輸出攝氏溫度,計(jì)算公式為(華氏度-32)×5÷9要求結(jié)果保留兩位小數(shù)。printf("%.2f",data); * / // \n 12*3
任務(wù)4:字符串
4.1數(shù)組的知識點(diǎn)
1.一維數(shù)組、二維數(shù)組、多維數(shù)組
2.數(shù)組:基本數(shù)據(jù)類型數(shù)組(int、float、char類型)、結(jié)構(gòu)體數(shù)組…..
3.字符數(shù)組、字符串?dāng)?shù)組(學(xué)習(xí)很多字符串操作函數(shù))
4.2字符串?dāng)?shù)組
字符數(shù)組和字符串?dāng)?shù)組的區(qū)別?
字符串?dāng)?shù)組結(jié)尾有一個特殊的結(jié)束符:'\0'
|
#include int main() { int a[]={10,20,30}; //整數(shù)類型數(shù)組 char b[]={'A','B','C','D'}; //字符數(shù)組 char c[]="ABCD"; //字符串?dāng)?shù)組 '\0'
printf("a數(shù)組的大小:%d\n",sizeof(a));//12 %d %c %f %s %x printf("b數(shù)組的大小:%d\n",sizeof(b));//4 printf("c數(shù)組的大小:%d\n",sizeof(c));//5 printf("long的大小:%d\n",sizeof(long)); //4 printf("int的大小:%d\n",sizeof(int)); //4 //long int return 0; } |
字符串是字符數(shù)組嗎?是
字符數(shù)組是字符串嗎?不一定
字符串的輸入輸出有哪些?
|
#include int main() { char str[100]; scanf("%s",str); //從鍵盤上輸入字符串 printf("str=%s\n",str); //輸出字符串 return 0; }
#include #include int main() { char str[100]="12345"; //scanf("%s",str); //從鍵盤上輸入字符串 //printf("str=%s\n",str); //輸出字符串
//char *gets(char *); //獲取字符串 //功能:多了一個獲取空格的功能,回車 //gets(str);//從鍵盤上輸入字符串 //printf("你輸入的字符串是:"); //puts(str);//輸出字符串 printf("字符串的長度:%d\n",strlen(str)); //5 return 0; } |
字符串常見的處理函數(shù)有哪些?
|
#include #include int main() { char str[200]; //常量:不可修改 "中文字符串" //字符串拼接 //strcat(str,"歡迎學(xué)習(xí)嵌入式開發(fā)"); //strcat(str," 學(xué)習(xí)單片機(jī)"); //strcat(str," 學(xué)習(xí)Linux"); //printf("str=%s,%d\n",str,strlen(str));
//字符串比較 如果相等返回0 //printf("比較結(jié)果:%d\n",strcmp("1234","123"));
//字符串拷貝 //strcpy(str,"1123435gffbgfb"); //printf("結(jié)果:%s\n",str);
//字符串查找函數(shù) printf("查找結(jié)果:%s\n",strstr("dscdscdsc123ksdhsd","123"));
return 0; }
/* const 聲明常量---聲明只讀變量
//字符串拼接 char *strcat(char *restrict, const char *restrict); //字符串比較 int strcmp(const char *, const char *); //字符串拷貝 char *strcpy(char *restrict, const char *restrict); //計(jì)算字符串長度 size_t strlen(const char *); //字符串查找函數(shù) char *strstr(const char *, const char *); */ |
實(shí)現(xiàn)計(jì)算字符串長度的功能?
|
#include int main() { char str[200]; int i=0; printf("請輸入字符串:"); gets(str); while(str[i]!='\0') { i++; } printf("字符串長度:%d\n",i); return 0; } |
練習(xí)題目: 從鍵盤上輸入一串字符串,計(jì)算字符串里的空格、大寫字母、小寫字母、數(shù)字個數(shù)?
|
#include int main() { char str[200]; int i=0; int cnt1=0,cnt2=0,cnt3=0,cnt4=0; printf("請輸入字符串:"); gets(str); //從鍵盤上錄入數(shù)據(jù) while(str[i]!='\0') { if(str[i]==' ') //判斷空格 { cnt1++; } else if(str[i]>='0'&&str[i]<='9') { cnt2++; } else if(str[i]>='a'&&str[i]<='z') { cnt3++; } else if(str[i]>='A'&&str[i]<='Z') { cnt4++; } i++; } printf("空格數(shù)量:%d\n",cnt1); printf("數(shù)字?jǐn)?shù)量:%d\n",cnt2); printf("小寫數(shù)量:%d\n",cnt3); printf("大寫數(shù)量:%d\n",cnt4); return 0; } |
4.3字符的輸入
解決字符不能連續(xù)輸入的問題:
|
#include int main() { char a; char b; char c; printf("請輸入字符1:"); scanf("%c",&a); //A\n printf("請輸入字符2:"); scanf(" %c",&b); printf("請輸入字符3:"); scanf(" %c",&c);
printf("輸入字符:%c,%c,%c\n",a,b,c); return 0; }
方式2: #include int main() { // int getchar(void); // int putchar(int); char a; char b; char c; printf("請輸入字符1:"); scanf("%c",&a); //\n while(getchar()!='\n'){}
printf("請輸入字符2:"); scanf("%c",&b); while(getchar()!='\n'){}
printf("請輸入字符3:"); scanf("%c",&c); while(getchar()!='\n'){}
printf("輸入字符:%c,%c,%c\n",a,b,c); return 0; } |
從鍵盤上輸入字符的方式:常用的兩種
|
#include int main() { // int getchar(void); // int putchar(int); char a; //scanf("%c",&a); //printf("%c",a);
a=getchar(); //從標(biāo)準(zhǔn)輸入獲取一個字符 putchar(a); //輸出字符
return 0; } |
輸入字符串的常見方式:
|
#include int main() { // int getchar(void); // int putchar(int); char str1[100]; char str2[100]; printf("請輸入字符串1:"); //scanf("%s",str1); gets(str1); printf("請輸入字符串2:"); //scanf("%s",str2); gets(str2); printf("結(jié)果:%s,%s\n",str1,str2); return 0; } |
使用字符獲取函數(shù)充當(dāng)字符串輸入功能:
|
#include int main() { // int getchar(void); // int putchar(int); char str[100]; int i=0; char a; while(1) { a=getchar(); //讀取一個字符 if(a=='#') { str[i]='\0'; break; } str[i++]=a; } printf("%s",str); return 0; } |
4.4字符串作業(yè)
1.從鍵盤上輸入一串字符串,計(jì)算字符串里的空格、大寫字母、小寫字母、數(shù)字個數(shù)
2.字符串比較:從鍵盤上錄入2個字符串,判斷是否相等。
3.字符串刪除:從鍵盤上錄入一個字符串,刪除字符串里指定的單詞,輸出結(jié)果。
比如:原字符串”akjbcds123dfjvbf123fdvbfd123”
刪除單詞:“123”
輸出的結(jié)果:”akjbcdsdfjvbffdvbfd”
4.字符串查找:從鍵盤上錄入一個字符串,查找字符串里有幾個特定的單詞。再輸出結(jié)果。
比如:原字符串”akjbcds123dfjvbf123fdvbfd123”
查找的單詞:“123”
輸出結(jié)果:3
5.字符串排序:從鍵盤上錄入一個字符串,按照小到大的順序排序。
6.字符串的插入:從鍵盤上錄入一個字符串,從指定位置插入一個字符串,再輸出結(jié)果。
比如:原字符串“1234567890”
(1).從指定位置插入新的單詞。 比如 從第2個下標(biāo)插入一個“ABC”字符串。
結(jié)果:“123ABC4567890”
(2).從指定單詞后面插入新的單詞。 比如 從”123”這個單詞后插入一個“ABC”字符串。
結(jié)果:“123ABC4567890”
7.字符串替換: 從鍵盤上錄入一個字符串,將指定單詞替換成想要的單詞。
比如:原字符串“123jfvfdj123dkfvbfdvdf”
想要將“123”替換成“888”或者“8888”或者“88”
8.從鍵盤上輸入一個整數(shù):將整數(shù)轉(zhuǎn)為字符串輸出。
比如:int a; scanf(“%d”,&a);使用字符串形式打印出a的值。
9.從鍵盤上輸入一個字符串,轉(zhuǎn)為整數(shù)輸出。
審核編輯:符乾江
-
C語言
+關(guān)注
關(guān)注
180文章
7604瀏覽量
136813 -
數(shù)組
+關(guān)注
關(guān)注
1文章
417瀏覽量
25945
發(fā)布評論請先 登錄
相關(guān)推薦
C語言中的數(shù)組詳解
C語言中數(shù)組的用法
c語言二維數(shù)組定義及其規(guī)則詳解
c語言之字符數(shù)組詳解
C語言數(shù)組詳解





 C語言—數(shù)組詳解
C語言—數(shù)組詳解










評論