我們推薦以生命周期感知方式在 Android 上收集數(shù)據(jù)流。如果您正在用 Jetpack Compose 構(gòu)建 Android 應(yīng)用,請使用 collectAsStateWithLifecycle API 以生命周期感知方式從用戶界面收集數(shù)據(jù)流。
-
使用界面狀態(tài)
https://developer.android.google.cn/topic/architecture/ui-layer#consume-ui-state
借助 collectAsStateWithLifecycle,您可以在不需要應(yīng)用資源時釋放它們,例如當(dāng)應(yīng)用處于后臺時。此類資源可能包括 Firebase 查詢、位置或網(wǎng)絡(luò)更新及數(shù)據(jù)庫連接等,在不需要它們的情況下讓其處于活躍狀態(tài)會影響用戶設(shè)備的運行健康狀況。 請繼續(xù)閱讀本文,以詳細(xì)了解此 API、以生命周期感知方式收集數(shù)據(jù)流的理由,以及此 API 與 collectAsState API 的差異。
collectAsStateWithLifecycle
collectAsStateWithLifecycle 是一個可組合函數(shù),可從數(shù)據(jù)流中收集值,并以生命周期感知方式將最新值表示為 Compose State。每當(dāng)數(shù)據(jù)流發(fā)出新值時,此 State 對象的值都會更新,從而讓組合 (Composition) 中每個使用 State.value 的對象進行重新組合。
-
State
https://developer.android.google.cn/reference/kotlin/androidx/compose/runtime/State
默認(rèn)情況下,collectAsStateWithLifecycle 使用 Lifecycle.State.STARTED 從數(shù)據(jù)流中開始和結(jié)束收集值。這些動作會在生命周期 (Lifecycle) 移入和移出目標(biāo)狀態(tài)時發(fā)生。您可以通過 minActiveState 參數(shù)配置此生命周期狀態(tài)。
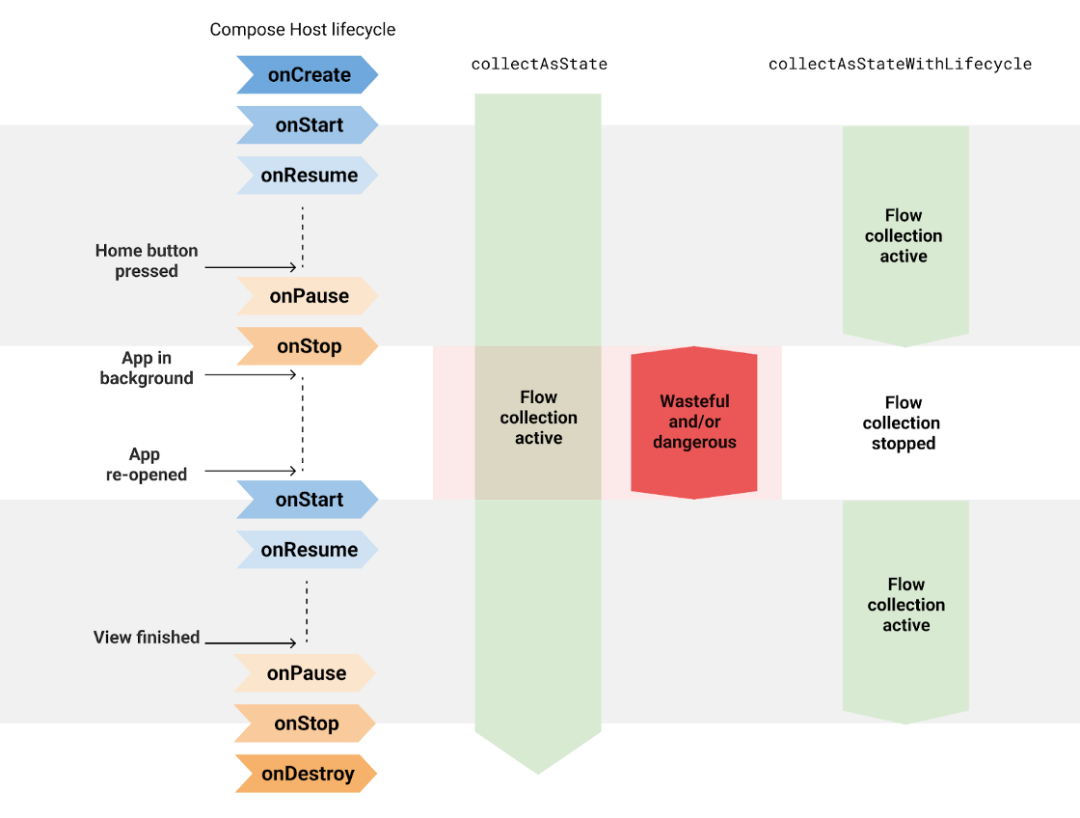
△ 默認(rèn)情況下,當(dāng)應(yīng)用處于后臺時 collectAsStateWithLifecycle 會取消收集數(shù)據(jù)流
-
Lifecycle.State.STARTED
https://developer.android.google.cn/reference/android/arch/lifecycle/Lifecycle.State#started
以下代碼片段展示了如何使用 collectAsStateWithLifecycle 來收集可組合函數(shù)中的 ViewModel 所公開的 StateFlow 的 uiState 字段:
/* Copyright 2022 Google LLC.SPDX-License-Identifier: Apache-2.0 */fun AuthorRoute(onBackClick: () -> Unit,modifier: Modifier = Modifier,viewModel: AuthorViewModel = hiltViewModel()) {val uiState: AuthorScreenUiState by viewModel.uiState.collectAsStateWithLifecycle()AuthorScreen(authorState = uiState.authorState,newsState = uiState.newsState,modifier = modifier,onBackClick = onBackClick,onFollowClick = viewModel::followAuthorToggle,)}
每當(dāng) AuthorViewModel 的 uiState 發(fā)出新的 AuthorScreenUiState 值時,都會重新組合 AuthorRoute。有關(guān) collectAsStateWithLifecycle 的更多用法,請參考 "Now in Android" 應(yīng)用及相關(guān)遷移 PR。
-
AuthorViewModel
https://github.com/android/nowinandroid/blob/main/feature-author/src/main/java/com/google/samples/apps/nowinandroid/feature/author/AuthorViewModel.kt -
AuthorRoute
https://github.com/android/nowinandroid/blob/main/feature-author/src/main/java/com/google/samples/apps/nowinandroid/feature/author/AuthorScreen.kt -
Now in Android
https://github.com/android/nowinandroid/search?q=collectAsStateWithLifecycle -
遷移 PR
https://github.com/android/nowinandroid/pull/166
如果您要在項目中使用 collectAsStateWithLifecycle API,請將 androidx.lifecycle.lifecycle-runtime-compose 工件添加到項目中。
/* Copyright 2022 Google LLC.SPDX-License-Identifier: Apache-2.0 */// app/build.gradle filedependencies {implementation "androidx.lifecycle2.6.0-alpha01"}
注意: 這是一個尚處于 Alpha 版的全新 API,且該 API 還要求您使用ExperimentalLifecycleComposeApi 注釋。
-
版本 2.6.0-alpha01
https://developer.android.google.cn/jetpack/androidx/releases/lifecycle#version_26_2 -
ExperimentalLifecycleComposeApi
https://developer.android.google.cn/reference/kotlin/androidx/lifecycle/compose/ExperimentalLifecycleComposeApi
collectAsStateWithLifecycle 在實現(xiàn)機制上使用了 repeatOnLifecycle API,我們也推薦大家在 Android 視圖 (View) 系統(tǒng)中收集數(shù)據(jù)流的 API。
-
collectAsStateWithLifecycle 的實現(xiàn)機制
https://cs.android.com/androidx/platform/frameworks/support/+/androidx-main:lifecycle/lifecycle-runtime-compose/src/main/java/androidx/lifecycle/compose/FlowExt.kt;l=168 -
repeatOnLifecycle
https://developer.android.google.cn/reference/kotlin/androidx/lifecycle/package-summary#(androidx.lifecycle.Lifecycle).repeatOnLifecycle(androidx.lifecycle.Lifecycle.State,kotlin.coroutines.SuspendFunction1)
借助 collectAsStateWithLifecycle,您無需輸入下方的樣板代碼,這些代碼同樣以生命周期感知的方式從可組合函數(shù)收集數(shù)據(jù)流:
/*Copyright2022GoogleLLC.SPDX-License-Identifier: Apache-2.0 */funAuthorRoute(...){vallifecycle=LocalLifecycleOwner.current.lifecyclevaluiStatebyproduceState( initialValue=viewModel.uiState.valuekey1=lifecyclekey2=viewModel){lifecycle.repeatOnLifecycle(state=STARTED){viewModel.uiState.collect{value=it}}}AuthorScreen(...)}
在架構(gòu)中收集數(shù)據(jù)流
應(yīng)用架構(gòu)中的類型不應(yīng)該知道其他類型的實現(xiàn)細(xì)節(jié)。界面不應(yīng)該知道 ViewModel 如何產(chǎn)生界面狀態(tài)。如果界面在屏幕上不可見,則應(yīng)停止收集數(shù)據(jù)流,以釋放應(yīng)用資源 (如果可行的話)。
界面可以通過使用 collectAsStateWithLifecycle 收集界面狀態(tài)來幫助釋放資源。ViewModel 可以通過以收集器感知的方式生成界面狀態(tài)來完成相同的操作。如果沒有收集器,例如當(dāng)界面在屏幕上不可見時,則停止收集來自數(shù)據(jù)層的上游數(shù)據(jù)流。您可以在生成界面狀態(tài)時使用 .stateIn(WhileSubscribed) 數(shù)據(jù)流 API 來執(zhí)行此操作。如需了解更多信息,請觀看 "Kotlin Flows 實戰(zhàn)" 講座的這一部分。如要測試以這種方法生成界面狀態(tài)的 ViewModel,請查看測試指南。

△ 在界面層中,使用 collectAsStateWithLifecycle 收集界面狀態(tài),并在數(shù)據(jù)層公開響應(yīng)式數(shù)據(jù)流時使用 .stateIn(WhileSubscribed) 生成界面狀態(tài)。這樣一來應(yīng)用的其余部分便能在不需要的時候釋放資源
-
.stateIn(WhileSubscribed)
https://github.com/android/nowinandroid/blob/main/feature-author/src/main/java/com/google/samples/apps/nowinandroid/feature/author/AuthorViewModel.kt#L104 -
Kotlin Flows 實戰(zhàn)
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=fSB6_KE95bU&t=1009s -
測試 StateFlow
https://developer.android.google.cn/kotlin/flow/test#statein
數(shù)據(jù)流的使用者和生產(chǎn)者不需要知道彼此的實現(xiàn)方式。在具備多個環(huán)境、變體、代碼庫和功能的大型應(yīng)用中找出實現(xiàn)細(xì)節(jié)是非常耗時的。更糟糕的是,依賴于實現(xiàn)細(xì)節(jié)的代碼維護起來非常困難。
讓資源在后臺保持活躍狀態(tài)
Android 應(yīng)用可以在海量 Android 設(shè)備上運行。但遺憾的是,所有設(shè)備和用戶擁有的資源都是有限的,因此應(yīng)用通常在受限環(huán)境中運行。運行 Android 應(yīng)用時,有一些重要因素會影響用戶體驗和設(shè)備系統(tǒng)健康:-
CPU 使用: 在所有設(shè)備組件中,CPU 的耗電量最高。而電池續(xù)航時間一直是用戶關(guān)注的重點,因此如果發(fā)生 CPU 濫用的情況,用戶可能會卸載您的應(yīng)用;
-
流量消耗: 在未連接 Wi-Fi 時減少應(yīng)用的網(wǎng)絡(luò)流量,可以幫助用戶節(jié)省流量費用;
-
內(nèi)存用量: 應(yīng)用對內(nèi)存的使用方式也會對設(shè)備的整體穩(wěn)定性和性能產(chǎn)生非常大的影響。
-
為數(shù)十億用戶打造產(chǎn)品
https://developer.android.google.cn/docs/quality-guidelines/build-for-billions
與 collectAsState 的差異
開發(fā)者們經(jīng)常會問道: 如果 collectAsStateWithLifecycle 是從 Android 可組合函數(shù)中收集數(shù)據(jù)流最安全的方法,那現(xiàn)在為什么還需要 collectAsState API?為什么不將生命周期感知功能添加到 collectAsState 中,而是創(chuàng)建新的 API?可組合函數(shù)的生命周期與 Compose 運行的平臺無關(guān)。正如 "可組合項的生命周期" 頁面中所述,可組合函數(shù)的實例進入組合,執(zhí)行 0 次或多次重組,然后離開組合:
https://developer.android.google.cn/jetpack/compose/lifecycle
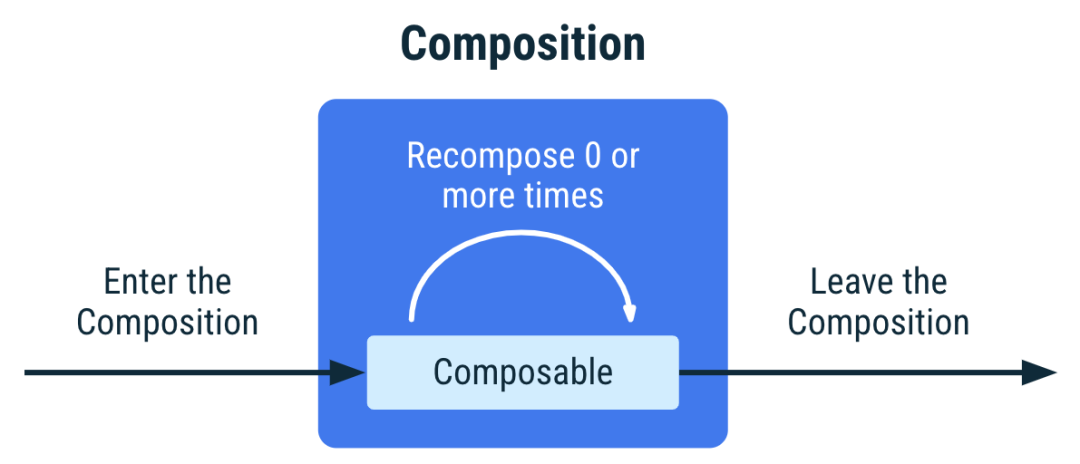
△ 組合中可組合函數(shù)實例的生命周期
collectAsState API 遵循組合的生命周期。此 API 在可組合項進入組合時開始收集數(shù)據(jù)流,并在可組合項離開組合時停止收集。collectAsState 是用于收集數(shù)據(jù)流且與平臺無關(guān)的 API。
但是,在 Android 應(yīng)用中使用 Compose 時,Android 生命周期也會對資源的管理方式產(chǎn)生非常大的影響。即使 Compose 在 Android 應(yīng)用處于后臺時停止重組,collectAsState 也會繼續(xù)收集數(shù)據(jù)流。這使得層次結(jié)構(gòu)的其余部分無法釋放資源。
collectAsState 和 collectAsStateWithLifecycle 在 Compose 中各有用途。后者用于開發(fā) Android 應(yīng)用,前者用于在其他平臺進行開發(fā)。
從 collectAsState 遷移到 collectAsStateWithLifecycle 非常容易:
/* Copyright 2022 Google LLC.SPDX-License-Identifier: Apache-2.0 */fun AuthorRoute(...) {val lifecycle = LocalLifecycleOwner.current.lifecycleval uiState by produceState( initialValue = viewModel.uiState.valuekey1 = lifecyclekey2 = viewModel) {lifecycle.repeatOnLifecycle(state = STARTED) {viewModel.uiState.collect { value = it }}}AuthorScreen(...)}
推薦大家以生命周期感知方式在 Android 上收集數(shù)據(jù)流,這樣做可以使應(yīng)用的其他部分在需要時釋放資源。 如果您正在使用 Jetpack Compose 構(gòu)建 Android 應(yīng)用,請使用 collectAsStateWithLifecycle 可組合函數(shù)來執(zhí)行此操作。 另外: 感謝 Jose Alcérreca、Marton Braun、Alejandra Stamato 和 Jake Roseman 對文章內(nèi)容進行審核。
-
Jose Alcérreca
https://medium.com/u/e0a4c9469bb5 -
Marton Braun
https://medium.com/u/ec2087b3c81f -
Alejandra Stamato
https://medium.com/u/92c44d274e60
審核編輯 :李倩
-
Android
+關(guān)注
關(guān)注
12文章
3938瀏覽量
127569 -
API
+關(guān)注
關(guān)注
2文章
1505瀏覽量
62168 -
數(shù)據(jù)流
+關(guān)注
關(guān)注
0文章
120瀏覽量
14372
原文標(biāo)題:在 Jetpack Compose 中安全地使用數(shù)據(jù)流
文章出處:【微信號:Google_Developers,微信公眾號:谷歌開發(fā)者】歡迎添加關(guān)注!文章轉(zhuǎn)載請注明出處。
發(fā)布評論請先 登錄
相關(guān)推薦
什么是PLM產(chǎn)品生命周期管理系統(tǒng)?
如何確保車規(guī)級芯片全生命周期的安全
半導(dǎo)體全生命周期測試:哪些設(shè)備在默默守護你的電子產(chǎn)品?

鴻蒙開發(fā)組件:DataAbility的生命周期
鴻蒙開發(fā):【PageAbility的生命周期】
設(shè)備全生命周期管理流程有哪些?

鴻蒙Ability Kit(程序框架服務(wù))【UIAbility組件生命周期】實例
如何保護電子元器件以延長生命周期

Traveo II B-H中的SECURE和SECURE_WITH_DEBUG生命周期階段有何不同?
HarmonyOS開發(fā)案例:【UIAbility和自定義組件生命周期】

IBM推出全新IT生命周期管理模式
IBM推出IBM Storage Assurance這一全新的IT生命周期管理模式
企業(yè)數(shù)據(jù)備份體系化方法論的七大原則:數(shù)據(jù)生命周期規(guī)劃:資產(chǎn)管理的新篇章
什么是設(shè)備全生命周期管理系統(tǒng)?





 了解此API、以生命周期感知方式收集數(shù)據(jù)流的理由
了解此API、以生命周期感知方式收集數(shù)據(jù)流的理由










評論