1. 業務背景
有些業務請求,屬于耗時操作,需要加鎖,防止后續的并發操作,同時對數據庫的數據進行操作,需要避免對之前的業務造成影響。
2. 分析流程
使用Redis作為分布式鎖,將鎖的狀態放到Redis統一維護,解決集群中單機JVM信息不互通的問題,規定操作順序,保護用戶的數據正確。
梳理設計流程
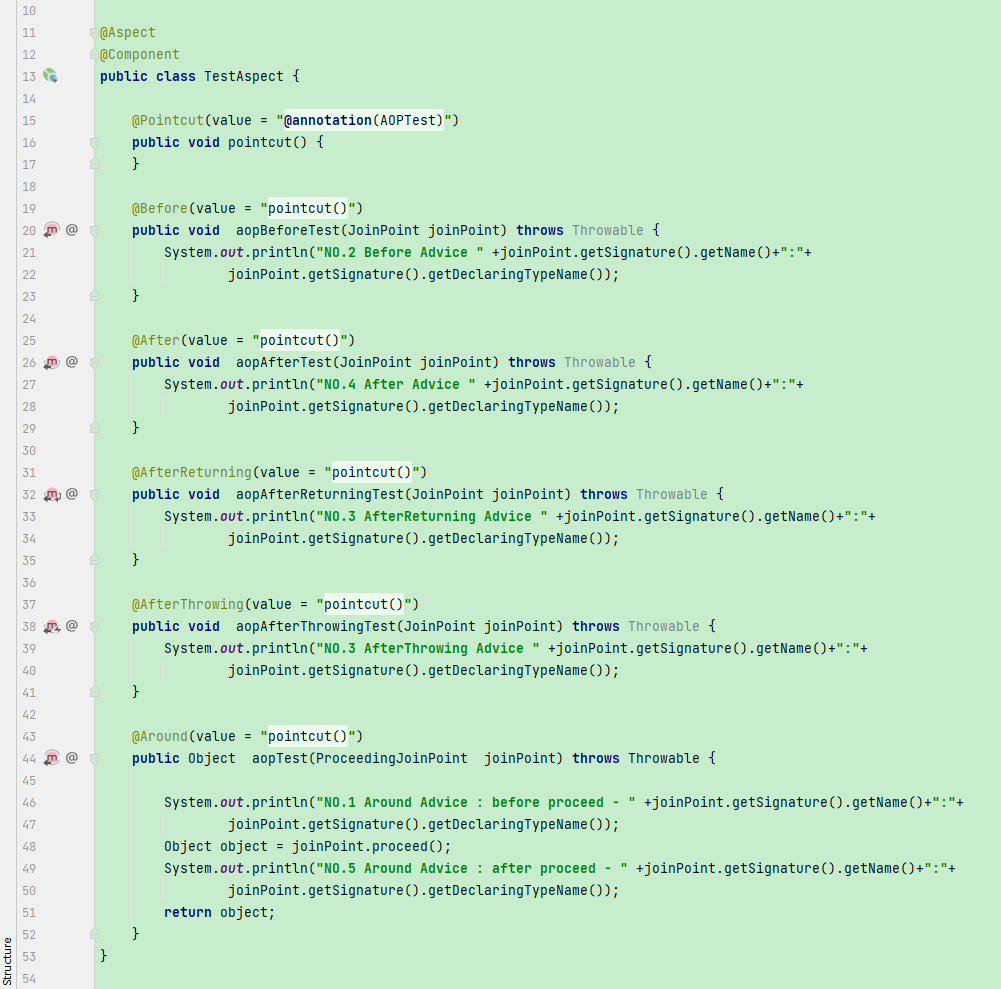
新建注解 @interface,在注解里設定入參標志
增加 AOP 切點,掃描特定注解
建立 @Aspect 切面任務,注冊 bean 和攔截特定方法
特定方法參數 ProceedingJoinPoint,對方法 pjp.proceed() 前后進行攔截
切點前進行加鎖,任務執行后進行刪除 key
核心步驟:加鎖、解鎖和續時
加鎖
使用了 RedisTemplate 的 opsForValue.setIfAbsent 方法,判斷是否有 key,設定一個隨機數 UUID.random().toString,生成一個隨機數作為 value。
從 redis 中獲取鎖之后,對 key 設定 expire 失效時間,到期后自動釋放鎖。
按照這種設計,只有第一個成功設定Key的請求,才能進行后續的數據操作,后續其它請求由于無法獲得資源,將會失敗結束。
超時問題
擔心pjp.proceed()切點執行的方法太耗時,導致Redis中的key由于超時提前釋放了。
例如,線程 A 先獲取鎖,proceed 方法耗時,超過了鎖超時時間,到期釋放了鎖,這時另一個線程 B 成功獲取Redis鎖,兩個線程同時對同一批數據進行操作,導致數據不準確。
解決方案:增加一個「續時」
任務不完成,鎖不釋放:
維護了一個定時線程池ScheduledExecutorService,每隔 2s 去掃描加入隊列中的 Task,判斷是否失效時間是否快到了,公式為:【失效時間】<= 【當前時間】+【失效間隔(三分之一超時)】
/** *線程池,每個JVM使用一個線程去維護keyAliveTime,定時執行runnable */ privatestaticfinalScheduledExecutorServiceSCHEDULER= newScheduledThreadPoolExecutor(1, newBasicThreadFactory.Builder().namingPattern("redisLock-schedule-pool").daemon(true).build()); static{ SCHEDULER.scheduleAtFixedRate(()->{ //dosomethingtoextendtime },0,2,TimeUnit.SECONDS); }
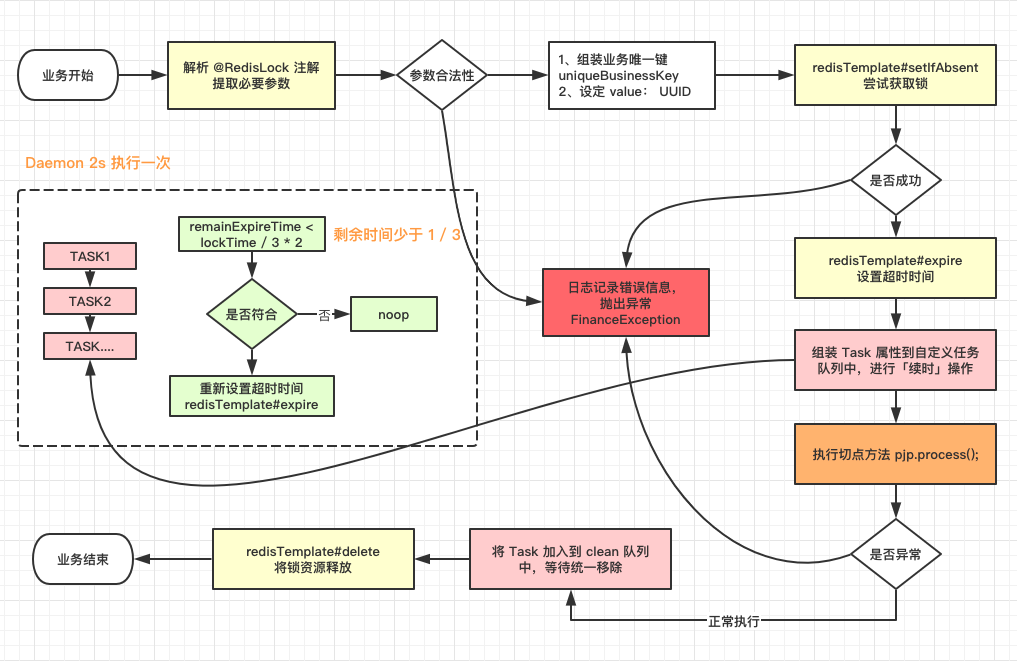
3. 設計方案
經過上面的分析,設計出了這個方案:
 圖片
圖片
前面已經說了整體流程,這里強調一下幾個核心步驟:
攔截注解 @RedisLock,獲取必要的參數
加鎖操作
續時操作
結束業務,釋放鎖
4. 實操
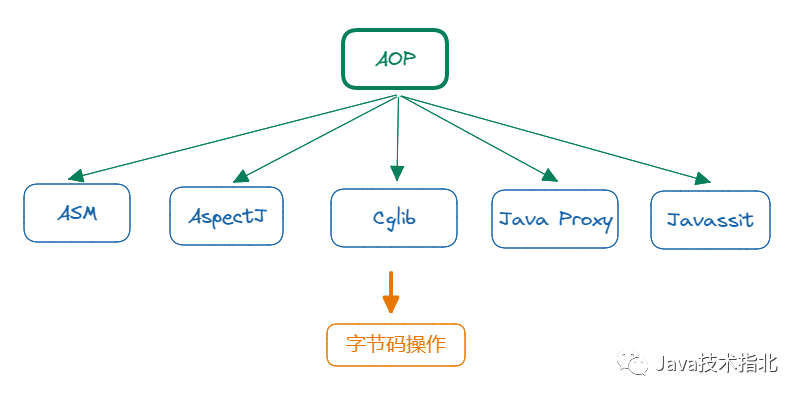
之前也有整理過AOP使用方法,可以參考一下
相關屬性類配置
業務屬性枚舉設定
publicenumRedisLockTypeEnum{
/**
*自定義key前綴
*/
ONE("Business1","Test1"),
TWO("Business2","Test2");
privateStringcode;
privateStringdesc;
RedisLockTypeEnum(Stringcode,Stringdesc){
this.code=code;
this.desc=desc;
}
publicStringgetCode(){
returncode;
}
publicStringgetDesc(){
returndesc;
}
publicStringgetUniqueKey(Stringkey){
returnString.format("%s:%s",this.getCode(),key);
}
}
任務隊列保存參數
publicclassRedisLockDefinitionHolder{
/**
*業務唯一key
*/
privateStringbusinessKey;
/**
*加鎖時間(秒s)
*/
privateLonglockTime;
/**
*上次更新時間(ms)
*/
privateLonglastModifyTime;
/**
*保存當前線程
*/
privateThreadcurrentTread;
/**
*總共嘗試次數
*/
privateinttryCount;
/**
*當前嘗試次數
*/
privateintcurrentCount;
/**
*更新的時間周期(毫秒),公式=加鎖時間(轉成毫秒)/3
*/
privateLongmodifyPeriod;
publicRedisLockDefinitionHolder(StringbusinessKey,LonglockTime,LonglastModifyTime,ThreadcurrentTread,inttryCount){
this.businessKey=businessKey;
this.lockTime=lockTime;
this.lastModifyTime=lastModifyTime;
this.currentTread=currentTread;
this.tryCount=tryCount;
this.modifyPeriod=lockTime*1000/3;
}
}
設定被攔截的注解名字
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Target({ElementType.METHOD,ElementType.TYPE})
public@interfaceRedisLockAnnotation{
/**
*特定參數識別,默認取第0個下標
*/
intlockFiled()default0;
/**
*超時重試次數
*/
inttryCount()default3;
/**
*自定義加鎖類型
*/
RedisLockTypeEnumtypeEnum();
/**
*釋放時間,秒s單位
*/
longlockTime()default30;
}
核心切面攔截的操作
RedisLockAspect.java該類分成三部分來描述具體作用
Pointcut 設定
/**
*@annotation中的路徑表示攔截特定注解
*/
@Pointcut("@annotation(cn.sevenyuan.demo.aop.lock.RedisLockAnnotation)")
publicvoidredisLockPC(){
}
Around 前后進行加鎖和釋放鎖
前面步驟定義了我們想要攔截的切點,下一步就是在切點前后做一些自定義操作:
@Around(value="redisLockPC()")
publicObjectaround(ProceedingJoinPointpjp)throwsThrowable{
//解析參數
Methodmethod=resolveMethod(pjp);
RedisLockAnnotationannotation=method.getAnnotation(RedisLockAnnotation.class);
RedisLockTypeEnumtypeEnum=annotation.typeEnum();
Object[]params=pjp.getArgs();
StringukString=params[annotation.lockFiled()].toString();
//省略很多參數校驗和判空
StringbusinessKey=typeEnum.getUniqueKey(ukString);
StringuniqueValue=UUID.randomUUID().toString();
//加鎖
Objectresult=null;
try{
booleanisSuccess=redisTemplate.opsForValue().setIfAbsent(businessKey,uniqueValue);
if(!isSuccess){
thrownewException("Youcan'tdoit,becauseanotherhasgetthelock=-=");
}
redisTemplate.expire(businessKey,annotation.lockTime(),TimeUnit.SECONDS);
ThreadcurrentThread=Thread.currentThread();
//將本次Task信息加入「延時」隊列中
holderList.add(newRedisLockDefinitionHolder(businessKey,annotation.lockTime(),System.currentTimeMillis(),
currentThread,annotation.tryCount()));
//執行業務操作
result=pjp.proceed();
//線程被中斷,拋出異常,中斷此次請求
if(currentThread.isInterrupted()){
thrownewInterruptedException("Youhadbeeninterrupted=-=");
}
}catch(InterruptedExceptione){
log.error("Interruptexception,rollbacktransaction",e);
thrownewException("Interruptexception,pleasesendrequestagain");
}catch(Exceptione){
log.error("hassomeerror,pleasecheckagain",e);
}finally{
//請求結束后,強制刪掉key,釋放鎖
redisTemplate.delete(businessKey);
log.info("releasethelock,businessKeyis["+businessKey+"]");
}
returnresult;
}
上述流程簡單總結一下:
解析注解參數,獲取注解值和方法上的參數值
redis 加鎖并且設置超時時間
將本次 Task 信息加入「延時」隊列中,進行續時,方式提前釋放鎖
加了一個線程中斷標志
結束請求,finally 中釋放鎖
續時操作
這里用了ScheduledExecutorService,維護了一個線程,不斷對任務隊列中的任務進行判斷和延長超時時間:
//掃描的任務隊列 privatestaticConcurrentLinkedQueueholderList=newConcurrentLinkedQueue(); /** *線程池,維護keyAliveTime */ privatestaticfinalScheduledExecutorServiceSCHEDULER=newScheduledThreadPoolExecutor(1, newBasicThreadFactory.Builder().namingPattern("redisLock-schedule-pool").daemon(true).build()); { //兩秒執行一次「續時」操作 SCHEDULER.scheduleAtFixedRate(()->{ //這里記得加try-catch,否者報錯后定時任務將不會再執行=-= Iterator iterator=holderList.iterator(); while(iterator.hasNext()){ RedisLockDefinitionHolderholder=iterator.next(); //判空 if(holder==null){ iterator.remove(); continue; } //判斷key是否還有效,無效的話進行移除 if(redisTemplate.opsForValue().get(holder.getBusinessKey())==null){ iterator.remove(); continue; } //超時重試次數,超過時給線程設定中斷 if(holder.getCurrentCount()>holder.getTryCount()){ holder.getCurrentTread().interrupt(); iterator.remove(); continue; } //判斷是否進入最后三分之一時間 longcurTime=System.currentTimeMillis(); booleanshouldExtend=(holder.getLastModifyTime()+holder.getModifyPeriod())<=?curTime;?? ????????????if?(shouldExtend)?{?? ????????????????holder.setLastModifyTime(curTime);?? ????????????????redisTemplate.expire(holder.getBusinessKey(),?holder.getLockTime(),?TimeUnit.SECONDS);?? ????????????????log.info("businessKey?:?["?+?holder.getBusinessKey()?+?"],?try?count?:?"?+?holder.getCurrentCount());?? ????????????????holder.setCurrentCount(holder.getCurrentCount()?+?1);?? ????????????}?? ????????}?? ????},?0,?2,?TimeUnit.SECONDS);?? }??
這段代碼,用來實現設計圖中虛線框的思想,避免一個請求十分耗時,導致提前釋放了鎖。
這里加了「線程中斷」**Thread#interrupt,希望超過重試次數后,能讓線程中斷**(未經嚴謹測試,僅供參考哈哈哈哈)
不過建議如果遇到這么耗時的請求,還是能夠從根源上查找,分析耗時路徑,進行業務優化或其它處理,避免這些耗時操作。
所以記得多打點Log,分析問題時可以更快一點。記錄項目日志,一個注解搞定
五、開始測試
在一個入口方法中,使用該注解,然后在業務中模擬耗時請求,使用了Thread#sleep
@GetMapping("/testRedisLock")
@RedisLockAnnotation(typeEnum=RedisLockTypeEnum.ONE,lockTime=3)
publicBooktestRedisLock(@RequestParam("userId")LonguserId){
try{
log.info("睡眠執行前");
Thread.sleep(10000);
log.info("睡眠執行后");
}catch(Exceptione){
//logerror
log.info("hassomeerror",e);
}
returnnull;
}
使用時,在方法上添加該注解,然后設定相應參數即可,根據typeEnum可以區分多種業務,限制該業務被同時操作。
測試結果:
2020-04-041450.864INFO9326---[nio-8081-exec-1]c.s.demo.controller.BookController:睡眠執行前 2020-04-041452.855INFO9326---[k-schedule-pool]c.s.demo.aop.lock.RedisLockAspect:businessKey:[Business1:1024],trycount:0 2020-04-041454.851INFO9326---[k-schedule-pool]c.s.demo.aop.lock.RedisLockAspect:businessKey:[Business1:1024],trycount:1 2020-04-041456.851INFO9326---[k-schedule-pool]c.s.demo.aop.lock.RedisLockAspect:businessKey:[Business1:1024],trycount:2 2020-04-041458.852INFO9326---[k-schedule-pool]c.s.demo.aop.lock.RedisLockAspect:businessKey:[Business1:1024],trycount:3 2020-04-041400.857INFO9326---[nio-8081-exec-1]c.s.demo.controller.BookController:hassomeerror java.lang.InterruptedException:sleepinterrupted atjava.lang.Thread.sleep(NativeMethod)[na:1.8.0_221]
我這里測試的是重試次數過多,失敗的場景,如果減少睡眠時間,就能讓業務正常執行。
如果同時請求,你將會發現以下錯誤信息:
 圖片
圖片
表示我們的鎖的確生效了,避免了重復請求。
六、總結
對于耗時業務和核心數據,不能讓重復的請求同時操作數據,避免數據的不正確,所以要使用分布式鎖來對它們進行保護。
再來梳理一下設計流程:
新建注解 @interface,在注解里設定入參標志
增加 AOP 切點,掃描特定注解
建立 @Aspect 切面任務,注冊 bean 和攔截特定方法
特定方法參數 ProceedingJoinPoint,對方法 pjp.proceed() 前后進行攔截
切點前進行加鎖,任務執行后進行刪除 key
本次學習是通過Review小伙伴的代碼設計,從中了解分布式鎖的具體實現,仿照他的設計,重新寫了一份簡化版的業務處理。對于之前沒考慮到的「續時」操作,這里使用了守護線程來定時判斷和延長超時時間,避免了鎖提前釋放。
于是乎,同時回顧了三個知識點:
1、AOP的實現和常用方法
2、定時線程池ScheduledExecutorService的使用和參數含義
3、線程Thread#interrupt的含義以及用法
-
數據庫
+關注
關注
7文章
3822瀏覽量
64506 -
代碼
+關注
關注
30文章
4801瀏覽量
68733
原文標題:SpringBoot 加一個注解,輕松實現 Redis 分布式鎖
文章出處:【微信號:AndroidPush,微信公眾號:Android編程精選】歡迎添加關注!文章轉載請注明出處。
發布評論請先 登錄
相關推薦
Spring AOP如何破解java應用
具有AoP技術的雷達傳感器
個體與群體思維狀態下的AOP語言
在AOP中使用標注改進日志功能的實現
基于AOP的軟件缺陷檢測框架設計
基于AOP的科研申報系統的設計與實現
AWR6843AOP 單芯片60GHz至64GHz毫米波傳感器封裝天線 (AOP) 數據表

IWR6843AOP單芯片60GHz至64GHz毫米波傳感器封裝天線(AOP)數據表

AWR1843AOP單芯片77GHz和79GHz FMCW毫米波傳感器天線封裝(AOP)數據表

IWR1843AOP單芯片77GHz和79GHz FMCW毫米波傳感器天線封裝(AOP)數據表





 AOP 的實現和常用方法
AOP 的實現和常用方法










評論