第1回:用Raspberry Pi和傳感器制作“可自動營造舒適空間的裝置” 第一部分
第2回:用Raspberry Pi和傳感器制作“可自動營造舒適空間的裝置” 第二部分
第3回:用Raspberry Pi和傳感器制作“可自動營造舒適空間的裝置” 第三部分
大家好,我是吉田!
創作一款讓家中更舒適、讓在家辦公更高效的設備,這個項目終于迎來了劇終篇。這次我們將會再增加一些功能,以完成這個項目。我們會添加一個根據天氣預報信息和天氣情況提示主人行動的功能,最終創作完成這個可以營造舒適環境的設備,讓您即使在家辦公也可以舒適地工作!
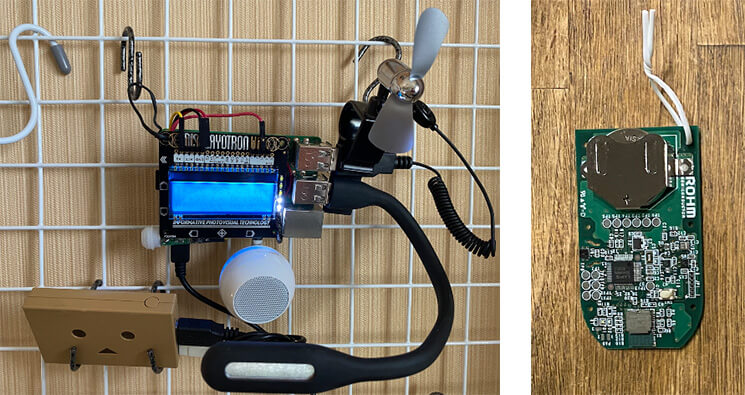
本部分所需部件
Raspberry Pi 3 B+ 或 Raspberry Pi 4 Model B
Raspberry Pi 3 B+
Raspberry Pi 4 Model B
Raspberry Pi用液晶顯示器 或 觸控顯示器

Raspberry Pi用液晶顯示器

觸控顯示器
羅姆SensorMedal(SensorMedal-EVK-002)
熱釋電紅外線傳感器 (SB412A)

小型揚聲器

手機電池

USB設備

本部分的流程
根據傳感器的值控制硬件
關聯天氣信息和互聯網信息
完成這款可以營造舒適環境的裝置
總結
1. 根據傳感器的值控制硬件
在第二部分中,我們使用SensorMedal測量了溫度和濕度;在第三部分中,我們添加了人體傳感器。最初,我們也是打算利用傳感器的值來實現下面這些功能的,所以讓我們來把它們變為現實吧。
| 編號 | 檢測功能 | 檢測后希望具備的功能 |
| 1 | 檢測房間的溫度 | 根據室溫控制風扇等 |
| 2 | 檢測房間的舒適度(例如濕度) | 如果濕度高,將空調設置為除濕模式 |
| 5 | 檢測坐在椅子上的時間 | 檢測到坐的時間太久(久坐不動),督促主人站起來活動活動 |
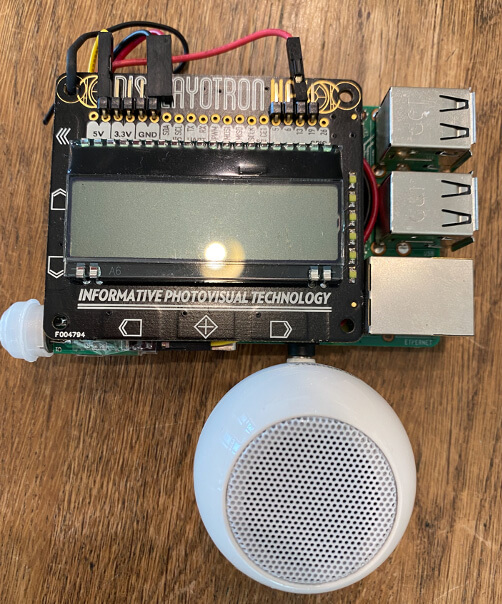
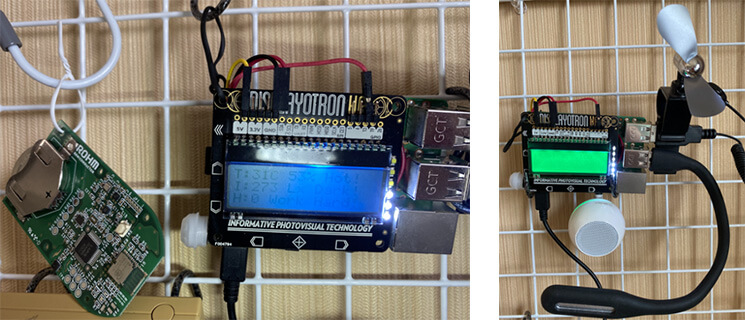
首先是檢測完溫度后,如果室溫高于一定水平,需要自動打開風扇保持涼爽。在Raspberry Pi上插入USB迷你風扇。

要想讓風扇根據室溫情況打開或關閉,需要使用第二部分中用過的hub-ctrl命令來控制Raspberry Pi的USB功能。例如,當室溫超過26℃時,給USB通電讓風扇轉起來。
另外,當使用人體傳感器測得您在工作臺周圍停留超過某一時長(久坐)時,讓Raspberry Pi發出聲音來提醒您可能會很有趣。下面,我們將迷你揚聲器插入Raspberry Pi。

獲取名為“AquesTalkPi”的可以朗讀的語音合成軟件,在Programs下解壓。
$ cd ~/Programs $ wget http://www.a-quest.com/download/package/aquestalkpi-20130827.tgz $ sudo tar zxvf aquestalkpi-20130827.tgz $ cd aquestalkpi
然后,我們嘗試讓它播放“該休息了”之類的聲音。
$ ./AquesTalkPi "休憩しましょう!" | aplay
要實現這些功能,需要在第三部分中使用過的ble_lcd.py程序中,添加下面的第2行、第29?36行(溫濕度控制)和第4?6行、第12?17行、第38?43行(人體傳感器控制)的內容。
[ble_lcd.py]
… import os human_count = 0 human_check = 30 aquest_path = "/home/pi/Programs/aquestalkpi/" scanner = btle.Scanner() while True: … human = GPIO.input(human_pin) if human == 1: human_count+=1 else: human_count=0 print('HCount:'+str(human_count)) ... # 針對接收到的數據,對每一個BLE設備進行處理 for dev in devices: ... ''' for key, value in sorted(sensors.items(), key=lambda x:x[0]): print(' ',key,'=',value) ''' temp = sensors['Temperature'] humid = sensors['Humidity'] if temp > 26 or humid > 60: temp_msg = "Hot!" os.system("sudo hub-ctrl -b 1 -d 2 -P 2 -p 1") else: temp_msg = "Not bad" os.system("sudo hub-ctrl -b 1 -d 2 -P 2 -p 0") human_msg = str(human_count) if human_count > human_check: human_msg += ' Take Rest!' os.system(aquest_path+'AquesTalkPi "休憩しましょう!" | aplay') else: human_msg += ' Work Hard!'
2. 關聯天氣信息和互聯網信息
最后,我們可以從網上獲取天氣預報等信息,這樣會很方便。如果要下雨,最好讓它大聲朗讀并提醒主人采取必要的行動。
| 編號 | 檢測功能 | 檢測后希望具備的功能 |
| 6 | 確認天氣 | 如果天氣預報有雨,提醒主人將曬在外面的衣物收回來 |
首先,我們需要使用名為“OpenWeatherMap”的服務來獲取天氣預報。如下圖所示,該網站是英文的,但是從上面可以輕松獲取日本國內天氣,所以我們將使用這里提供的API。
https://openweathermap.org/api
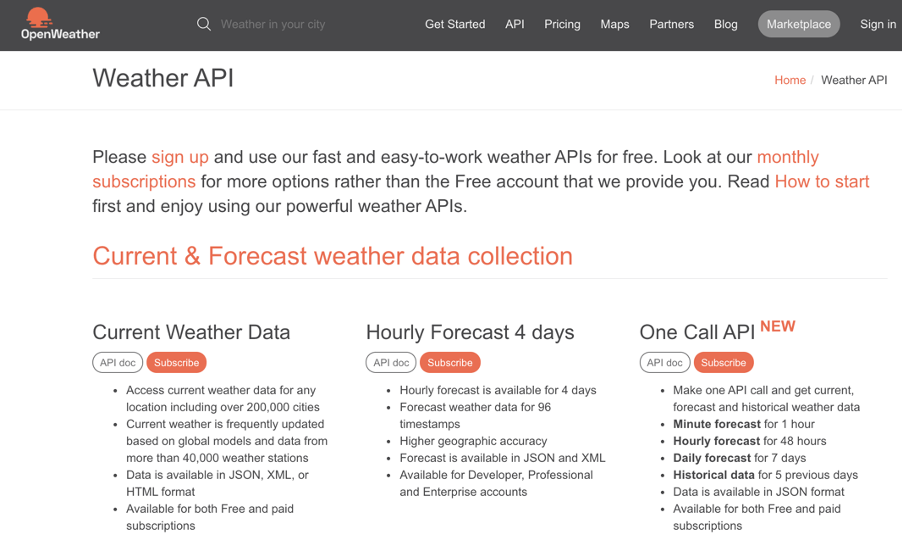
從該頁面的右上方創建一個帳戶并登錄。
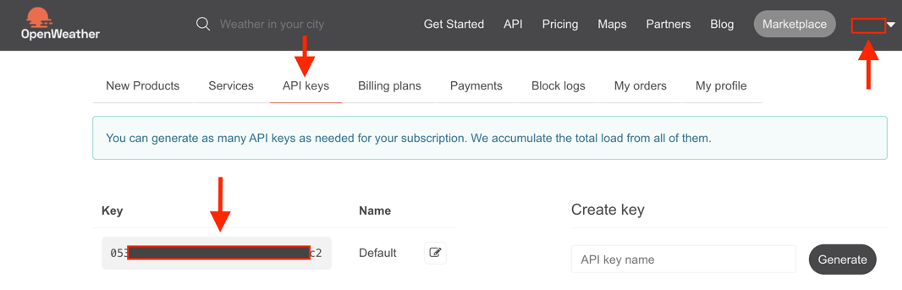
然后進入稱為“API Keys”的頁面,確認Key(秘鑰)并復制此密鑰。
接下來,我們需要創建一個可以獲取天氣預報的程序。首先,要安裝以下庫文件。
$ sudo pip3 install pytz requests
創建一個名為“forecast.py”的示例程序。將剛剛復制的密鑰輸入API_KEY部分。另外,需要在ZIP部分輸入您的郵政編碼,并添加國家代碼“JP”。下面,我們讓剛剛的Aquestalk軟件也能夠播報天氣吧。
[forecast.py]
#! /usr/bin/python3 # -*- coding: utf-8 -*- import json import datetime import os import requests import sys from pytz import timezone API_KEY = "XXX" ZIP = "123-4567,JP" API_URL = "http://api.openweathermap.org/data/2.5/forecast?zip={0}&units=metric&lang=ja&APPID={1}" def getWeatherForecast(): url = API_URL.format(ZIP, API_KEY) response = requests.get(url) forecastData = json.loads(response.text) if not ('list' in forecastData): print('error') return for item in forecastData['list']: forecastDatetime = timezone( 'Asia/Tokyo').localize(datetime.datetime.fromtimestamp(item['dt'])) weatherDescription = item['weather'][0]['description'] temperature = item['main']['temp'] rainfall = 0 if 'rain' in item and '3h' in item['rain']: rainfall = item['rain']['3h'] break print('Date:{0} Weather:{1} Temp:{2} C Rain:{3}mm'.format( forecastDatetime, weatherDescription, temperature, rainfall)) return forecastDatetime, weatherDescription, temperature, rainfall forecastDatetime, weatherDescription, temperature, rainfall = getWeatherForecast() os.system(“/home/pi/aquestalkpi/AquesTalkPi “ + weatherDescription + “ | aplay”)
如下所示,運行該程序時,將會返回指定地區的天氣預報。于是,Raspberry Pi就會向您播報今天的天氣預報了,比如“多云”。
$ python3 forecast.py Date:2020-06-05 00:00:00+09:00 Weather:多云 Temp:23.29 C Rain:0mm
3. 完成這款可以營造舒適環境的裝置
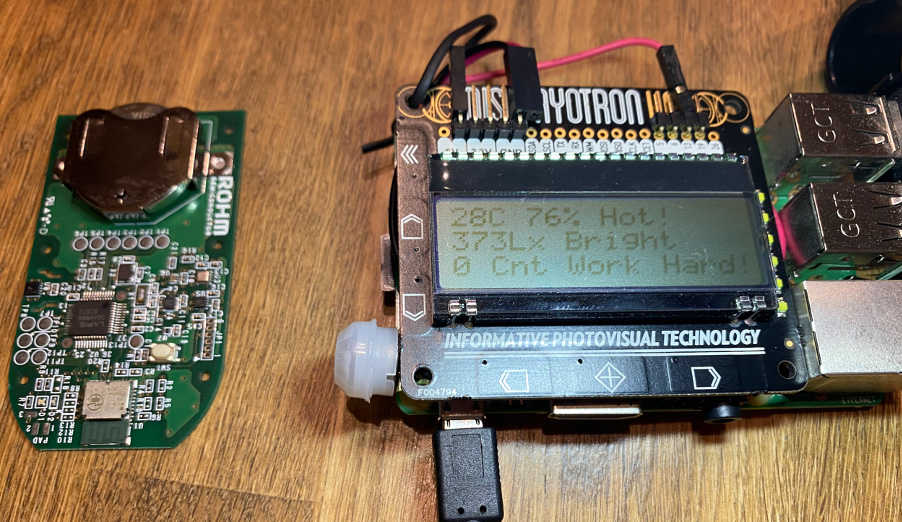
下面,我們將液晶顯示器、揚聲器、人體傳感器和USB設備都連接到Raspberry Pi,以完成該設備。
SensorMedal可以放置在BLE范圍內的任何位置,因此可以將其放置在您桌子周圍或窗戶附近。當然,您也可以將它放在電腦附近或掛在墻上。
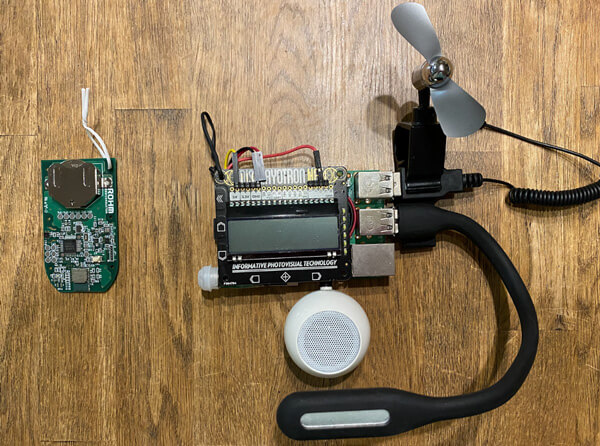
下面是該設備的最終程序,可以讓設備根據SensorMedal、人體傳感器和天氣預報等信息執行任務。程序僅供參考。
[ble_lcd.py]
#!/usr/bin/env python3 # coding: utf-8 import dothat import dothat.backlight as backlight import dothat.lcd as lcd interval = 10 # 動作間隔 from datetime import datetime from bluepy import btle from sys import argv import getpass from time import sleep import os import RPi.GPIO as GPIO human_pin = 13 GPIO.setmode(GPIO.BCM) GPIO.setup(human_pin, GPIO.IN) human_count = 0 human_check = 3 import json import requests import sys from pytz import timezone API_KEY = "xxx" #WeatherMap API Key ZIP = "123-4567,JP" #Your address API_URL = "http://api.openweathermap.org/data/2.5/forecast?zip={0}&units=metric&lang=ja&APPID={1}" aquest_path = "/home/pi/Programs/aquestalkpi/" #AquesTalkPi path def getWeatherForecast(): url = API_URL.format(ZIP, API_KEY) response = requests.get(url) forecastData = json.loads(response.text) if not ('list' in forecastData): print('error') return #print(forecastData) for item in forecastData['list']: forecastDatetime = timezone('Asia/Tokyo').localize(datetime.fromtimestamp(item['dt'])) weatherDescription = item['weather'][0]['description'] temperature = item['main']['temp'] rainfall = 0 if 'rain' in item and '3h' in item['rain']: rainfall = item['rain']['3h'] break print('Date:{0} Weather:{1} Temp:{2} C Rain:{3}mm'.format(forecastDatetime, weatherDescription, temperature, rainfall)) return forecastDatetime, weatherDescription, temperature, rainfall def payval(num, bytes=1, sign=False): global val a = 0 for i in range(0, bytes): a += (256 ** i) * int(val[(num - 2 + i) * 2 : (num - 1 + i) * 2],16) if sign: if a >= 2 ** (bytes * 8 - 1): a -= 2 ** (bytes * 8) return a scanner = btle.Scanner() while True: now = datetime.now() d = '{0:0>4d}/{1:0>2d}/{2:0>2d}({3})'.format(now.year, now.month, now.day, now.strftime('%a')) t = '{0:0>2d}:{1:0>2d}:{2:0>2d}'.format(now.hour, now.minute, now.second) forecastDatetime, weatherDescription, temperature, rainfall = getWeatherForecast() lcd.clear() lcd.set_cursor_position(0, 0) lcd.write('{}'.format(d)) lcd.set_cursor_position(2, 1) lcd.write('{}'.format(t)) lcd.set_cursor_position(0, 2) lcd.write('W:{0}C {1}mm'.format(round(temperature,0), rainfall)) if rainfall > 0: print(weatherDescription, rainfall) os.system(aquest_path+'AquesTalkPi '+weatherDescription+' | aplay') human = GPIO.input(human_pin) if human == 1: human_count+=1 else: human_count=0 print('HCount:'+str(human_count)) try: devices = scanner.scan(interval) except Exception as e: print("ERROR",e) if getpass.getuser() != 'root': print('使用方法: sudo', argv[0]) exit() sleep(interval) continue # 受信データについてBLEデバイス毎の処理 for dev in devices: print("nDevice %s (%s), RSSI=%d dB" % (dev.addr, dev.addrType, dev.rssi)) isRohmMedal = False sensors = dict() for (adtype, desc, val) in dev.getScanData(): print(" %s = %s" % (desc, val)) if desc == 'Short Local Name' and val[0:10] == 'ROHMMedal2': isRohmMedal = True if isRohmMedal and desc == 'Manufacturer': # センサ値を辭書型変數sensorsへ代入 sensors['ID'] = hex(payval(2,2)) sensors['Temperature'] = -45 + 175 * payval(4,2) / 65536 sensors['Humidity'] = 100 * payval(6,2) / 65536 sensors['Pressure'] = payval(22,3) / 2048 sensors['Illuminance'] = payval(25,2) / 1.2 sensors['Battery Level'] = payval(30) sensors['RSSI'] = dev.rssi # 畫面へ表示 print(' ID =',sensors['ID']) print(' Temperature =',round(sensors['Temperature'],2),'℃') print(' Humidity =',round(sensors['Humidity'],2),'%') print(' Pressure =',round(sensors['Pressure'],3),'hPa') print(' Illuminance =',round(sensors['Illuminance'],1),'lx') print(' Battery Level =',sensors['Battery Level'],'%') print(' RSSI =',sensors['RSSI'],'dB') ''' for key, value in sorted(sensors.items(), key=lambda x:x[0]): print(' ',key,'=',value) ''' temp = sensors['Temperature'] humid = sensors['Humidity'] lcd.clear() dothat.backlight.set_graph(0.5) # 50% backlight.rgb(0, 0, 0) if temp > 28 or humid > 80: temp_msg = "Hot!" backlight.rgb(255, 0, 0) #Red else: temp_msg = "Not bad" illum = sensors['Illuminance'] if illum < 200: illum_msg = "Dark!" os.system("sudo hub-ctrl -b 1 -d 2 -P 2 -p 1") backlight.rgb(255, 255, 255) else: illum_msg = "Bright" os.system("sudo hub-ctrl -b 1 -d 2 -P 2 -p 0") backlight.rgb(0, 0, 255) #Blue human_msg = str(human_count) dothat.backlight.off() for led in range(human_count): backlight.graph_set_led_state(led, 0.2) if human_count > human_check: human_msg += ' Take Rest!' backlight.rgb(0, 255, 0) #Green os.system(aquest_path+'AquesTalkPi "休憩しましょう!" | aplay') else: human_msg += ' Work Hard!' backlight.rgb(0, 255, 255) #Lightblue lcd.clear() lcd.set_cursor_position(0, 0) lcd.write('T:{0:1.0f}C {1:1.0f}% {2}'.format(temp,humid,temp_msg)) lcd.set_cursor_position(0, 1) lcd.write('I:{0:1.0f} Lx {1}'.format(illum,illum_msg)) lcd.set_cursor_position(0, 2) lcd.write('H:{}'.format(human_msg)) sleep(interval)
最后,我們讓這個程序能夠自動啟動吧。首先,創建一個shell程序來運行Python程序。需要進行服務設置,以使啟動該shell程序時能夠執行Python程序。
[blelcd.sh]
#!/bin/sh sudo /usr/bin/python3 /home/pi/Programs/ble_lcd.py
[blelcd.service]
Description=ROHM MEDAL BLE to LCD [Service] ExecStart=/bin/bash /home/pi/Programs/blelcd.sh WorkingDirectory=/home/pi/Programs User=pi [Install] WantedBy=multi-user.target
現在,當您重新啟動它時,Raspberry Pi將會顯示傳感器的值,指示燈開始閃爍。
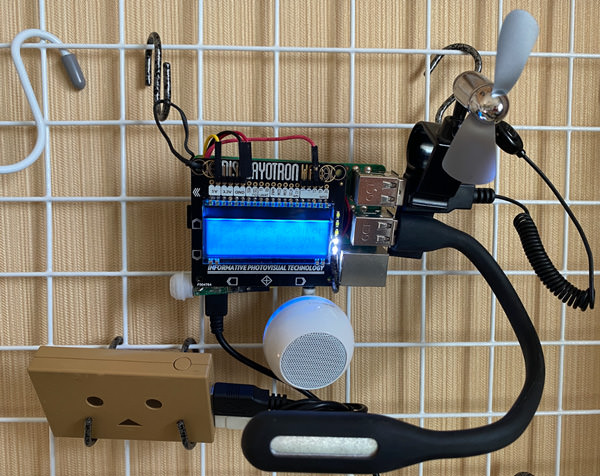

4. 總結
在這個連載系列中,我們針對在家辦公時間增加的情況,創作了一個可以檢測辦公環境并改善環境的設備。
在第一部分中,我們思考并列舉了希望實現的目標,也了解了用羅姆的SensorMedal可以測得多種值。
在第二部分中,我們創建了實際通過Raspberry Pi和BLE連接SensorMedal用的程序。
在第三部分中,我們使用人體傳感器,實現了檢測是否有人(是否久坐不動)的功能。此外,還用液晶顯示器成功顯示了溫濕度和亮度等信息。
在第四部分,也就是本文中,我們增加了天氣預報等功能,完成了這個用起來非常方便的設備。當您打開Raspberry Pi的電源時,它會自動啟動并執行自動檢測和提醒等任務。
事實上,它現在每天都在我家工作,它會告訴我周圍的亮度,并提醒我別忘了收回曬在外面的衣服!
鼓勵大家也嘗試制作方便您居家生活和在家辦公的設備!
相關連載一覽
第1部分:用Raspberry Pi和傳感器制作“可自動營造舒適空間的裝置” 第一部分
第2部分:用Raspberry Pi和傳感器制作“可自動營造舒適空間的裝置” 第二部分
第3部分:用Raspberry Pi和傳感器制作“可自動營造舒適空間的裝置” 第三部分
第4部分:用Raspberry Pi和傳感器制作“可自動營造舒適空間的裝置” 第四部分?劇終篇(本章)
審核編輯黃宇
-
傳感器
+關注
關注
2551文章
51125瀏覽量
753760 -
python
+關注
關注
56文章
4797瀏覽量
84711 -
Raspberry Pi
+關注
關注
2文章
559瀏覽量
22260
發布評論請先 登錄
相關推薦
獨特的51單片機教程第四部分—牛人經驗,論壇獨家奉獻
【藍牙4.1】+ 分享一本好書《Psoc 體系結構與編程》四部分完全版
Raspberry Pi機器人制作實例 用PYTHON、LINUX和傳感器搭建智能小車
火力發電廠水汽分析方法 第四部分:氯化物的測定 (電極法)D
國內衛星通信地球站發射接收和地面通信設備技術要求 第四部分中
用Raspberry Pi和SensorMedal制作IoT跳繩設備 第四部分:在設備上安裝顯示器以增加動力

用Raspberry Pi和傳感器制作“可自動營造舒適空間的裝置” 第三部分
用Raspberry Pi和傳感器制作“可自動營造舒適空間的裝置” 第二部分

使用Crystal Signal Pi第3部分:使用Raspberry Pi創建警示燈解決方案—創建工具

使用Raspberry Pi 3自制智能相框和日歷—第二部分
【北京迅為】iTOP-i.MX6開發板使用手冊第四部分固件編譯第十四章非設備樹Android4.4系統編譯





 用Raspberry Pi和傳感器制作“可自動營造舒適空間的裝置” 第四部分?劇終篇
用Raspberry Pi和傳感器制作“可自動營造舒適空間的裝置” 第四部分?劇終篇












評論