作者:Prabowo Yoga Wicaksana來源:DeepHub IMBA
神經(jīng)網(wǎng)絡(luò)在訓(xùn)練時的優(yōu)化首先是對模型的當(dāng)前狀態(tài)進行誤差估計,然后為了減機器學(xué)習(xí)或深度學(xué)習(xí)模型的訓(xùn)練的目標(biāo)是成為“通用”模型。這就需要模型沒有過度擬合訓(xùn)練數(shù)據(jù)集,或者換句話說,我們的模型對看不見的數(shù)據(jù)有很好的了解。數(shù)據(jù)增強也是避免過度擬合的眾多方法之一。擴展用于訓(xùn)練模型的數(shù)據(jù)量的過程稱為數(shù)據(jù)增強。通過訓(xùn)練具有多種數(shù)據(jù)類型的模型,我們可以獲得更“泛化”的模型。“多種數(shù)據(jù)類型”是什么意思呢?本篇文章只討論“圖像”數(shù)據(jù)增強技術(shù),只詳細地介紹各種圖片數(shù)據(jù)增強策略。我們還將使用 PyTorch 動手實踐并實現(xiàn)圖像數(shù)據(jù)或計算機視覺中主要使用的數(shù)據(jù)增強技術(shù)。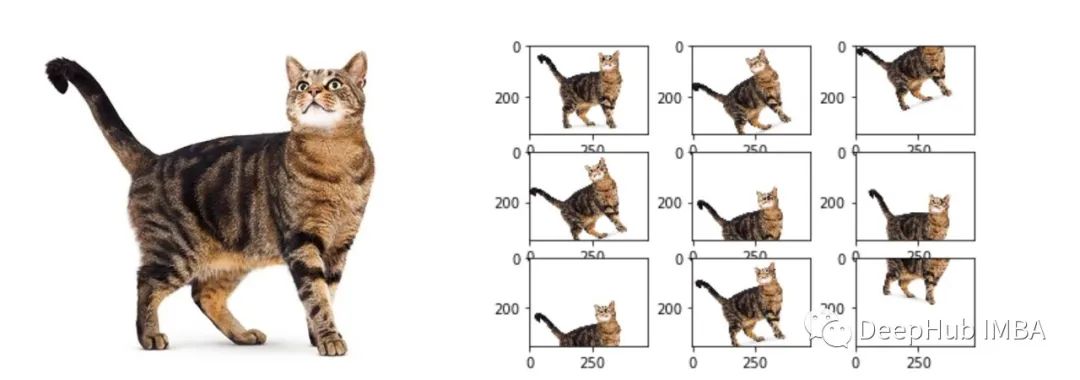 因為介紹的是數(shù)據(jù)增強技術(shù)。所以只使用一張圖片就可以了,我們先看看可視話的代碼?import PIL.Image as Image
因為介紹的是數(shù)據(jù)增強技術(shù)。所以只使用一張圖片就可以了,我們先看看可視話的代碼?import PIL.Image as Image
import torch
from torchvision import transforms
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
import warnings
def imshow(img_path, transform):
"""
Function to show data augmentation
Param img_path: path of the image
Param transform: data augmentation technique to apply
"""
img = Image.open(img_path)
fig, ax = plt.subplots(1, 2, figsize=(15, 4))
ax[0].set_title(f'Original image {img.size}')
ax[0].imshow(img)
img = transform(img)
ax[1].set_title(f'Transformed image {img.size}')
ax[1].imshow(img)Resize/Rescale
此函數(shù)用于將圖像的高度和寬度調(diào)整為我們想要的特定大小。下面的代碼演示了我們想要將圖像從其原始大小調(diào)整為 224 x 224。
path = './kitten.jpeg'
transform = transforms.Resize((224, 224))
imshow(path, transform)
Cropping
該技術(shù)將要選擇的圖像的一部分應(yīng)用于新圖像。例如,使用 CenterCrop 來返回一個中心裁剪的圖像。transform = transforms.CenterCrop((224, 224))
imshow(path, transform)
RandomResizedCrop
這種方法同時結(jié)合了裁剪和調(diào)整大小。transform = transforms.RandomResizedCrop((100, 300))
imshow(path, transform)
Flipping
水平或垂直翻轉(zhuǎn)圖像,下面代碼將嘗試應(yīng)用水平翻轉(zhuǎn)到我們的圖像。transform = transforms.RandomHorizontalFlip()
imshow(path, transform)
Padding
填充包括在圖像的所有邊緣上按指定的數(shù)量填充。我們將每條邊填充50像素。transform = transforms.Pad((50,50,50,50))
imshow(path, transform)
Rotation
對圖像隨機施加旋轉(zhuǎn)角度。我們將這個角設(shè)為15度。transform = transforms.RandomRotation(15)
imshow(path, transform)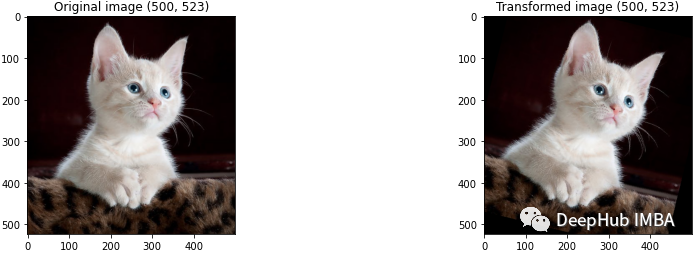
Random Affine
這種技術(shù)是一種保持中心不變的變換。這種技術(shù)有一些參數(shù):
degrees:旋轉(zhuǎn)角度
translate:水平和垂直轉(zhuǎn)換
scale:縮放參數(shù)
share:圖片裁剪參數(shù)
fillcolor:圖像外部填充的顏色
transform = transforms.RandomAffine(1, translate=(0.5, 0.5), scale=(1, 1), shear=(1,1), fillcolor=(256,256,256))
imshow(path, transform)
Gaussian Blur
圖像將使用高斯模糊進行模糊處理。transform = transforms.GaussianBlur(7, 3)
imshow(path, transform)
Grayscale
將彩色圖像轉(zhuǎn)換為灰度。transform = transforms.Grayscale(num_output_channels=3)
imshow(path, transform) 顏色增強,也稱為顏色抖動,是通過改變圖像的像素值來修改圖像的顏色屬性的過程。下面的方法都是顏色相關(guān)的操作。
顏色增強,也稱為顏色抖動,是通過改變圖像的像素值來修改圖像的顏色屬性的過程。下面的方法都是顏色相關(guān)的操作。
Brightness
改變圖像的亮度當(dāng)與原始圖像對比時,生成的圖像變暗或變亮。transform = transforms.ColorJitter(brightness=2)
imshow(path, transform)
Contrast
圖像最暗和最亮部分之間的區(qū)別程度被稱為對比度。圖像的對比度也可以作為增強進行調(diào)整。transform = transforms.ColorJitter(contrast=2)
imshow(path, transform)
Saturation
圖片中顏色的分離被定義為飽和度。transform = transforms.ColorJitter(saturation=20)
imshow(path, transform)
Hue
色調(diào)被定義為圖片中顏色的深淺。transform = transforms.ColorJitter(hue=2)
imshow(path, transform)
總結(jié)
圖像本身的變化將有助于模型對未見數(shù)據(jù)的泛化,從而不會對數(shù)據(jù)進行過擬合。
-
神經(jīng)網(wǎng)絡(luò)
+關(guān)注
關(guān)注
42文章
4776瀏覽量
100940 -
圖像數(shù)據(jù)
+關(guān)注
關(guān)注
0文章
52瀏覽量
11293
發(fā)布評論請先 登錄
相關(guān)推薦
【每天學(xué)點AI】實戰(zhàn)圖像增強技術(shù)在人工智能圖像處理中的應(yīng)用

基于差分卷積神經(jīng)網(wǎng)絡(luò)的低照度車牌圖像增強網(wǎng)絡(luò)

如何使用base64處理圖像數(shù)據(jù)
深圳單片機開發(fā)公司常用的12個硬件電路,你用過幾個?
圖像采集卡:增強視覺數(shù)據(jù)采集

說明增強現(xiàn)實技術(shù)的產(chǎn)生原因
Cricket XL全新亮相:革新圖像增強技術(shù)的解決方案




 12個常用的圖像數(shù)據(jù)增強技術(shù)總結(jié)
12個常用的圖像數(shù)據(jù)增強技術(shù)總結(jié)











評論