RBF神經(jīng)網(wǎng)絡(luò)和BP神經(jīng)網(wǎng)絡(luò)的區(qū)別就在于訓(xùn)練方法上面:RBF的隱含層與輸入層之間的連接權(quán)值不是隨機確定的,是有一種固定算式的。下面以精確型RBF為例。
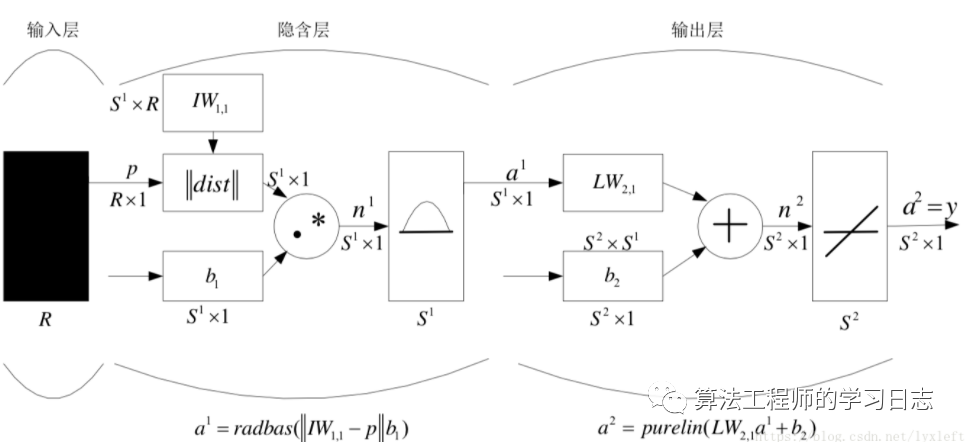
假設(shè)每個樣本有R維的特征。有S1個訓(xùn)練集樣本。IW1表示訓(xùn)練集,即S1XR的一個矩陣。
此時,輸入一個R維的測試集樣本p,首先將p和IW1計算歐氏距離。
RBF徑向基函數(shù)的效果是:
所謂徑向基函數(shù) (Radial Basis Function 簡稱 RBF), 就是某種沿徑向?qū)ΨQ的標(biāo)量函數(shù)。通常定義為空間中任一點x到某一中心xc之間歐氏距離的單調(diào)函數(shù) , 可記作 k(||x-xc||), 其作用往往是局部的 , 即當(dāng)x遠(yuǎn)離xc時函數(shù)取值很小。最常用的徑向基函數(shù)是高斯核函數(shù) ,形式為 k(||x-xc||)=exp{- ||x-xc||^2/(2*σ^2) } 其中xc為核函數(shù)中心,σ為函數(shù)的寬度參數(shù) , 控制了函數(shù)的徑向作用范圍。
簡單地說,就是某個測試集樣本p和某個訓(xùn)練集樣本越接近,即歐氏距離越小,那么在RBF作用后輸出的值就越大。
假設(shè)這個樣本p和訓(xùn)練集中某個樣本(即IW1中某一列)很相似(即歐氏距離dist很小),那么輸出結(jié)果a1中(a1維度是S1X1)就有一個值會很大。經(jīng)過權(quán)重和偏置的作用后,再進(jìn)入線性分類器中,就很容易可以分出來。這是我的直觀的理解。
生成RBF的matlab函數(shù):net = newrbe(P,T,spread)。只有一個參數(shù)spread需要調(diào)整。
P
RxQ matrix of Q R-element input vectors
T
SxQ matrix of Q S-element target class vectors
spread
Spread of radial basis functions (default = 1.0)
The larger the spread is, the smoother the function approximation will be. Too large a spread can cause numerical problems.
也就是說,spread這個參數(shù)越大,RBF圖像越平滑,RBF的輸出差距不大,則所有輸入的作用都會被減弱。
關(guān)于此算法,MATLAB文檔中給出了很精煉的解釋:
newrbe creates a two-layer network. The first layer has radbas neurons, and calculates its weighted inputs with dist and its net input with netprod. The second layer has purelin neurons, and calculates its weighted input withdotprod and its net inputs with netsum. Both layers have biases.
newrbe sets the first-layer weights to P', and the first-layer biases are all set to 0.8326/spread, resulting in radial basis functions that cross 0.5 at weighted inputs of +/– spread.
(就是說這樣設(shè)計出默認(rèn)的RBF的效果是,關(guān)于X=0對稱,橫軸為+/-0.8333時函數(shù)的縱軸坐標(biāo)值大約是0.5,表現(xiàn)在圖中就是cross于這個點。如果加權(quán)后輸入是+/- spread的話,正好產(chǎn)生此效果。)
The second-layer weights IW{2,1} and biases b{2} are found by simulating the first-layer outputs A{1} and then solving the following linear expression:
[W{2,1} b{2}] * [A{1}; ones] = T
也就是說,RBF實際上是一個兩層的神經(jīng)網(wǎng)絡(luò)。很簡單,隱層是使用RBF作為激活函數(shù)的神經(jīng)元,輸出層采用線性函數(shù)的神經(jīng)元,做一個線性分類。在前面的dist計算歐氏距離過程中,RBF采用高斯函數(shù),實際上是將數(shù)據(jù)轉(zhuǎn)化到高維空間,認(rèn)為存在某個高維空間能夠使得數(shù)據(jù)在這個空間是線性可分的。因此輸出層是線性的。
上面也解釋了本文開頭中講的,神經(jīng)元之間非隨機的權(quán)值是如何計算的:實際上,第一層的權(quán)值設(shè)為輸入矩陣P的轉(zhuǎn)置。而第二層的權(quán)值和偏置是要通過輸入?yún)?shù)T、第一層的output結(jié)果來反推的。
下面是MATLAB文檔中給的簡單代碼:

下面是一個例子
%% I. 清空環(huán)境變量
clear all
clc
%% II. 訓(xùn)練集/測試集產(chǎn)生
%%
% 1. 產(chǎn)生隨機數(shù)據(jù)
NIR = rand(60,5);
%%
% 2. 隨機產(chǎn)生訓(xùn)練集和測試集
temp = randperm(size(NIR,1));
% 訓(xùn)練集――50個樣本
P_train = NIR(temp(1:50),:)';
T_train = NIR(temp(1:50),:)';
% 測試集――10個樣本
P_test = NIR(temp(51:end),:)';
T_test = NIR(temp(51:end),:)';
N = size(P_test,2);
%% III. RBF神經(jīng)網(wǎng)絡(luò)創(chuàng)建及仿真測試
%%
% 1. 創(chuàng)建網(wǎng)絡(luò)
net = newrbe(P_train,T_train,30);
%%
% 2. 仿真測試
T_sim = sim(net,P_test);
%% IV. 性能評價
%%
% 1. 相對誤差error
error = abs(T_sim - T_test)./T_test;
%%
% 2. 結(jié)果對比
result = [T_test' T_sim' error']
%% V. 繪圖
figure
plot(1:N,T_test,'b:*',1:N,T_sim,'r-o')
legend('真實值','預(yù)測值')
xlabel('預(yù)測樣本')
-
神經(jīng)網(wǎng)絡(luò)
+關(guān)注
關(guān)注
42文章
4771瀏覽量
100772 -
仿真器
+關(guān)注
關(guān)注
14文章
1018瀏覽量
83746 -
MATLAB仿真
+關(guān)注
關(guān)注
4文章
176瀏覽量
19929 -
RBF
+關(guān)注
關(guān)注
0文章
40瀏覽量
15717
發(fā)布評論請先 登錄
相關(guān)推薦
基于RBF 的模糊神經(jīng)網(wǎng)絡(luò)控制器設(shè)計與仿真分析
matlab神經(jīng)網(wǎng)絡(luò)在圖書資源管理中的應(yīng)用
基于RBF神經(jīng)網(wǎng)絡(luò)的軟儀表的開發(fā)
matlab神經(jīng)網(wǎng)絡(luò)應(yīng)用設(shè)計
人工神經(jīng)網(wǎng)絡(luò)原理及仿真實例
基于RBF神經(jīng)網(wǎng)絡(luò)的通信用戶規(guī)模預(yù)測模型
基于RBF神經(jīng)網(wǎng)絡(luò)的辨識
BP神經(jīng)網(wǎng)絡(luò)的簡單MATLAB實例免費下載
基于FPGA的RBF神經(jīng)網(wǎng)絡(luò)硬件實現(xiàn)
自構(gòu)造RBF神經(jīng)網(wǎng)絡(luò)及其參數(shù)優(yōu)化
基于FPGA的RBF神經(jīng)網(wǎng)絡(luò)的硬件實現(xiàn)





 Matlab RBF神經(jīng)網(wǎng)絡(luò)及其實例
Matlab RBF神經(jīng)網(wǎng)絡(luò)及其實例










評論