Annotation
注解(Annotation),也叫元數(shù)據(jù)。一種代碼級(jí)別的說(shuō)明。它是JDK1.5及以后版本引入的一個(gè)特性,與類(lèi)、接口、枚舉是在同一個(gè)層次。它可以聲明在包、類(lèi)、字段、方法、局部變量、方法參數(shù)等的前面,用來(lái)對(duì)這些元素進(jìn)行說(shuō)明,注釋。作用分類(lèi):
- 編寫(xiě)文檔:通過(guò)代碼里標(biāo)識(shí)的元數(shù)據(jù)生成文檔【生成文檔doc文檔】
- 代碼分析:通過(guò)代碼里標(biāo)識(shí)的元數(shù)據(jù)對(duì)代碼進(jìn)行分析【使用反射】
- 編譯檢查:通過(guò)代碼里標(biāo)識(shí)的元數(shù)據(jù)讓編譯器能夠?qū)崿F(xiàn)基本的編譯檢查【Override】
注解不會(huì)改變程序的語(yǔ)義,只是作為注解(標(biāo)識(shí))存在,我們可以通過(guò)反射機(jī)制編程實(shí)現(xiàn)對(duì)這些元數(shù)據(jù)(用來(lái)描述數(shù)據(jù)的數(shù)據(jù))的訪問(wèn)
分類(lèi)
- 運(yùn)行期注解 程序運(yùn)行時(shí)才會(huì)被解析到的注解,一般通過(guò)反射機(jī)制來(lái)實(shí)現(xiàn),很多框架中都會(huì)用到,經(jīng)常會(huì)看到一個(gè)注解和一些簡(jiǎn)單的配置來(lái)實(shí)現(xiàn)非常復(fù)雜的功能
- 編譯期注解 一般用來(lái)解析類(lèi)型元數(shù)據(jù),根據(jù)特定注解解析并生成代碼,或者生成一些描述性文件,比如properties、json等,比如為Pojo生成getter和setter方法
關(guān)鍵注解
@java.lang.annotation.Retention定義注解的有效時(shí)期
相關(guān)參數(shù):RetentionPolicy.SOURCE: 編譯期生效,編譯器會(huì)丟棄,編譯后的class文件并不包含該注解 RetentionPolicy.CLASS: 注解會(huì)被保留在class文件中,但是運(yùn)行期不會(huì)生效,被JVM忽略 RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME: 注解會(huì)被保留在class文件中,并且會(huì)在運(yùn)行期生效,JVM會(huì)讀取
@Target定義注解作用對(duì)象,也就是注解是可以用在類(lèi)、方法、參數(shù)還是其他等待
相關(guān)參數(shù):ElementType.TYPE: 該注解只能運(yùn)用到Class, Interface, enum上 ElementType.FIELD: 該注解只能運(yùn)用到Field上 ElementType.METHOD: 該注解只能運(yùn)用到方法上 ElementType.PARAMETER: 該注解只能作用在參數(shù)上 ElementType.CONSTRUCTOR: 該注解只能作用在構(gòu)造方法上 ElementType.LOCAL_VARIABLE: 該注解作用在地變量或catch語(yǔ)句 ElementType.ANNOTATION_TYPE: 該注解只能作用在注解上 ElementType.PACKAGE: 該注解只能用在包上
Java中常見(jiàn)的內(nèi)置注解:
- @Override
- @Deprecated
- @SuppressWarnings
繼承關(guān)系
- @Inherited
如果某個(gè)注解上有@Inherited注解,當(dāng)查找該類(lèi)型的注解時(shí),會(huì)先查找目標(biāo)類(lèi)型是否存在注解,如果有,直接返回;否則,繼續(xù)在父類(lèi)上尋找注解, 停止的條件為在父類(lèi)上找到該類(lèi)型的注解或者父類(lèi)為Object類(lèi)型。
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
@Inherited
public @interface ClassMapper {
}
下面的示例中,如果ClassMapper沒(méi)有@Inherited修飾,則返回null
Child.class.getAnnotation(ClassMapper.class);
@Slf4j
public class ExtendAnnotationTests {
@ClassMapper
public class Demo { }
public class Child extends Demo{ }
}
- 元注解 (注解上的注解)
我們知道,在Spring中,注解@Service與@Component都是用來(lái)標(biāo)記類(lèi),交由Spring容器管理其對(duì)應(yīng)的Bean,是結(jié)果是等效的。主要是Spring將注解和元注解進(jìn)行了合并
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Target(ElementType.ANNOTATION_TYPE)
public @interface Mapper {
}
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
@Mapper
public @interface ClassMapper {
}
通過(guò)下面的方法可以拿到元注解,從而進(jìn)行其他擴(kuò)展。
public class Tests {
@Test
public void test(){
ClassMapper classMapper = Demo.class.getAnnotation(ClassMapper.class);
log.info("classMapper: {}", classMapper);
Mapper mapper = classMapper.annotationType().getAnnotation(Mapper.class);
log.info("mapper: {}", mapper);
}
}
示例
示例主要針對(duì)@java.lang.annotation.Retention參數(shù)的三種情況,了解注解是生效時(shí)期:
RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME
該示例實(shí)現(xiàn)通過(guò)自定義注解@SystemProperty,實(shí)現(xiàn)為對(duì)象字段設(shè)置系統(tǒng)屬性
- 定義注解@SystemProperty
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Target(ElementType.FIELD)
@Documented
public @interface SystemProperty {
String value();
}
- 定義對(duì)象工廠
主要作用是在運(yùn)行時(shí)解析注解@SystemProperty,并實(shí)現(xiàn)系統(tǒng)屬性注入的邏輯。前面說(shuō)到,注解的作用主要是標(biāo)記,針對(duì)RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME類(lèi)型的注解,一般是在運(yùn)行時(shí) 通過(guò)反射實(shí)現(xiàn)注解標(biāo)識(shí)的類(lèi)、字段或方法等等元數(shù)的處理過(guò)程。
ObjectFactory是一個(gè)對(duì)象生產(chǎn)工廠,這樣我們可以在運(yùn)行期解析目標(biāo)對(duì)象中的是否有@SystemProperty標(biāo)識(shí)的字段,并對(duì)該字段進(jìn)行值的設(shè)定,這樣式該注解設(shè)計(jì)的初衷,但是 實(shí)現(xiàn)需要我們根據(jù)需求實(shí)現(xiàn)
@Slf4j
public class ObjectFactory {
// 省略 ...
public static < T > T getObject(Class< T > type, Object... args){
Constructor< T > constructor = findTypeConstructor(type, args);
T object = constructor.newInstance(args);
// 通過(guò)反射找到對(duì)象中@SystemProperty的字段,并根據(jù)其設(shè)置參數(shù)將系統(tǒng)屬性設(shè)定到該對(duì)象字段中
processFieldAnnotations(object, type, SystemProperty.class);
return object;
}
// 省略 ...
}
- 驗(yàn)證
可以查看對(duì)象中被注解標(biāo)識(shí)的屬性被設(shè)置上去了
@Slf4j
public class RuntimeAnnotationTests {
@Test
public void run(){
Demo demo = ObjectFactory.getObject(Demo.class);
log.info(" >> result: {}", demo.user);
}
@Data
public static class Demo{
@SystemProperty("user.name")
private String user;
}
}
RetentionPolicy.CLASS
該示例主要實(shí)現(xiàn),編譯器判斷通過(guò)@FinalClass注解標(biāo)記的類(lèi)是否為final類(lèi)型
- 定義注解
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.CLASS)
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
@Documented
public @interface FinalClass {
}
- 編寫(xiě)AbstractProcessor的實(shí)現(xiàn)
@SupportedAnnotationTypes({FinalClassProcessor.FINAL_CLASS})
@SupportedSourceVersion(SourceVersion.RELEASE_8)
@AutoService(Processor.class)
public class FinalClassProcessor extends AbstractProcessor {
public static final String FINAL_CLASS = "com.sucl.blog.jdk.annotation.compile.FinalClass";
@Override
public boolean process(Set< ? extends TypeElement > annotations, RoundEnvironment roundEnv) {
TypeElement annotationType = this.processingEnv.getElementUtils().getTypeElement(FINAL_CLASS);
if( annotationType != null ){
for (Element element : roundEnv.getElementsAnnotatedWith(annotationType)) {
if( element instanceof TypeElement ){
TypeElement typeElement = (TypeElement) element;
if( !typeElement.getModifiers().contains(Modifier.FINAL) ){
String message = String.format("類(lèi)【%s】必須為final類(lèi)型", typeElement);
this.processingEnv.getMessager().printMessage(Diagnostic.Kind.ERROR, message);
}
}
}
}
return true;
}
}
- 使FinalClassProcessor生效
- 基于google auto-service
3.1 添加依賴(lài)
< dependency >
< groupId >com.google.auto.service< /groupId >
< artifactId >auto-service< /artifactId >
< version >1.1.0< /version >
< /dependency >
3.2 在Processor通過(guò)注解@AutoService標(biāo)識(shí)
@AutoService(Processor.class)
public class FinalClassProcessor extends AbstractProcessor{}
- 基于maven插件
< plugin >
< groupId >org.apache.maven.plugins< /groupId >
< artifactId >maven-compiler-plugin< /artifactId >
< configuration >
< annotationProcessors >
< annotationProcessor >
com.sucl.blog.jdk.annotation.compile.FinalClassProcessor
< /annotationProcessor >
< /annotationProcessors >
< /configuration >
< /plugin >
- 驗(yàn)證
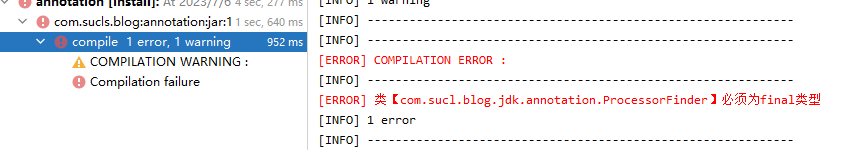
打包,在項(xiàng)目中引入該jar,定義一個(gè)類(lèi),類(lèi)似下面這樣,當(dāng)該類(lèi)沒(méi)有final修飾時(shí),通過(guò)maven install命令,可以看到控制臺(tái)打印自定義的錯(cuò)誤信息
@FinalClass
public final class ProcessorFinder {}
注意
RetentionPolicy.CLASS的使用需要達(dá)打成jar包才行,不然無(wú)法再編譯時(shí)處理注解
RetentionPolicy.SOURCE
定義一個(gè)注解,通過(guò)打包后的結(jié)果觀察該注解的狀態(tài)
- 定義注解
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.SOURCE)
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
@Documented
public @interface System {
}
- 定義測(cè)試類(lèi),并通過(guò)@System修飾
@System
public class SystemProvider {
}
- 打包,借助maven-source-plugin同時(shí)將源碼打包
< plugins >
< plugin >
< groupId >org.apache.maven.plugins< /groupId >
< artifactId >maven-source-plugin< /artifactId >
< version >3.2.1< /version >
< executions >
< execution >
< id >attach-sources< /id >
< goals >
< goal >jar< /goal >
< /goals >
< /execution >
< /executions >
< /plugin >
< /plugins >
- 在源碼包中,可以看到該注解仍然存在,但是class文件中卻沒(méi)有
在基于Spring Boot開(kāi)發(fā)項(xiàng)目時(shí),我們一般通過(guò) @ConfigurationProperties 配合 spring-boot-configuration-processor ,可以實(shí)現(xiàn)在項(xiàng)目打包時(shí) 生成一個(gè)spring-configuration-metadata.json的配置描述文件,這樣在編寫(xiě)application.yml配置時(shí),就會(huì)得到配置提示,其實(shí)現(xiàn)方式就是基于 ConfigurationMetadataAnnotationProcessor,
結(jié)束語(yǔ)
注解本身沒(méi)有含義,主要作用是標(biāo)記目標(biāo)元素,后續(xù)拿到改標(biāo)識(shí)的元數(shù)據(jù),進(jìn)行一系列的處理。注解的使用是非常廣泛的,各種框架中都使用頻繁,基于注解可以將很多抽象功能提取出來(lái),通過(guò)簡(jiǎn)單 的標(biāo)識(shí)來(lái)實(shí)現(xiàn)各種復(fù)雜的功能
-
JAVA
+關(guān)注
關(guān)注
19文章
2967瀏覽量
104748 -
代碼
+關(guān)注
關(guān)注
30文章
4788瀏覽量
68603 -
編譯器
+關(guān)注
關(guān)注
1文章
1634瀏覽量
49129 -
元數(shù)據(jù)
+關(guān)注
關(guān)注
0文章
32瀏覽量
9134 -
注解
+關(guān)注
關(guān)注
0文章
18瀏覽量
2674
發(fā)布評(píng)論請(qǐng)先 登錄
相關(guān)推薦
Java中常見(jiàn)的注解

如何通過(guò)注解來(lái)優(yōu)化我們的Java代碼
詳細(xì)介紹了Java泛型、注解、并發(fā)編程
HarmonyOS注解的使用方法分享
關(guān)于Java變量的作用域分析
分析java注解基本概念
Spring Boot中常見(jiàn)的各類(lèi)型注解的使用方式
Spring Boot常用注解與使用方式
注解定義Bean及開(kāi)發(fā)
容器配置及Spring Boot注解

JAVA中注解是怎么做到的(上)
JAVA中注解是怎么做到的(下)
3分鐘純Java注解搭個(gè)管理系統(tǒng)




 Java中注解的作用
Java中注解的作用










評(píng)論