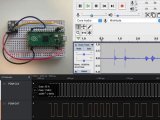
在樹莓派 Pico 小小的板子上總是能讓我們發(fā)現(xiàn)一些驚喜。其所使用的RP2040芯片還具備8個可編程I/O(PIO)狀態(tài)機(jī),用于自定義外圍設(shè)備,與 FPGA 類似,開發(fā)者可以靈活的使用 PIO 自定義功能。
可編程I/O(PIO)是為 RP2040 開發(fā)的一種新型硬件,可以通過 PIO 創(chuàng)建新類型的(或附加)硬件接口。通過使用 PIO ,可以模擬更多,更豐富,更快的硬件接口,有助于提升性能和擴(kuò)展性。
與 PIO 相比,F(xiàn)PGA 往往更加昂貴,而且需要使用其他的編程模式編寫程序。但 PIO 僅僅只需要通過匯編語言就可以實(shí)現(xiàn),開發(fā)者不需要去適應(yīng) FPGA 那種編程模式即可很快的實(shí)現(xiàn)自定義硬件接口。
PIO 一個簡單的 demo:
主要需要用到一個匯編實(shí)現(xiàn)的pio文件,一些C文件,和Cmake文件,實(shí)現(xiàn)串口打印 hello
pio文件:
.program hello
; Repeatedly get one word of data from the TX FIFO, stalling when the FIFO is
; empty. Write the least significant bit to the OUT pin group.
loop:
pull
out pins, 1
jmp loop
% c-sdk {
static inline void hello_program_init(PIO pio, uint sm, uint offset, uint pin) {
pio_sm_config c = hello_program_get_default_config(offset);
// Map the state machine's OUT pin group to one pin, namely the pin
// parameter to this function.
sm_config_set_out_pins(&c, pin, 1);
// Set this pin's GPIO function (connect PIO to the pad)
pio_gpio_init(pio, pin);
// Set the pin direction to output at the PIO
pio_sm_set_consecutive_pindirs(pio, sm, pin, 1, true);
// Load our configuration, and jump to the start of the program
pio_sm_init(pio, sm, offset, &c);
// Set the state machine running
pio_sm_set_enabled(pio, sm, true);
}
%}
其流程主要如下:
將程序加載到PIO的指令存儲器中;
設(shè)置PIO狀態(tài)機(jī)以運(yùn)行程序;
在狀態(tài)機(jī)運(yùn)行時與狀態(tài)機(jī)交互。
C文件:
#include "pico/stdlib.h"
#include "hardware/pio.h"
// Our assembled program:
#include "hello.pio.h"
int main() {
#ifndef PICO_DEFAULT_LED_PIN
#warning pio/hello_pio example requires a board with a regular LED
#else
// Choose which PIO instance to use (there are two instances)
PIO pio = pio0;
// Our assembled program needs to be loaded into this PIO's instruction
// memory. This SDK function will find a location (offset) in the
// instruction memory where there is enough space for our program. We need
// to remember this location!
uint offset = pio_add_program(pio, &hello_program);
// Find a free state machine on our chosen PIO (erroring if there are
// none). Configure it to run our program, and start it, using the
// helper function we included in our .pio file.
uint sm = pio_claim_unused_sm(pio, true);
hello_program_init(pio, sm, offset, PICO_DEFAULT_LED_PIN);
// The state machine is now running. Any value we push to its TX FIFO will
// appear on the LED pin.
while (true) {
// Blink
pio_sm_put_blocking(pio, sm, 1);
sleep_ms(500);
// Blonk
pio_sm_put_blocking(pio, sm, 0);
sleep_ms(500);
}
#endif
}
我們會發(fā)現(xiàn)其中調(diào)用了 “hello.pio.h” 頭文件,其與之前的 pio 文件相關(guān),但 pio 文件并不能在 c 文件中直接調(diào)用,于是就需要 Cmake 文件將 pio 文件和 c 文件聯(lián)系到一起,并構(gòu)建一個可執(zhí)行文件。
Cmake文件
add_executable(hello_pio)
pico_generate_pio_header(hello_pio ${CMAKE_CURRENT_LIST_DIR}/hello.pio)
target_sources(hello_pio PRIVATE hello.c)
target_link_libraries(hello_pio PRIVATE
pico_stdlib
hardware_pio
)
pico_add_extra_outputs(hello_pio)
add url via pico_set_program_url
example_auto_set_url(hello_pio)
其中的 pico_generate_pio_header 非常重要,其將之前用匯編語言寫的 pio 文件生成為一個 .h 頭文件,以供 c 文件調(diào)用。
通過這寫文件和 pico 官方提供的 sdk 就可以構(gòu)建一個串口打印 hello 的程序了。
其他
我是在移植 pico-w 板載的 Wi-Fi 功能時注意到這一功能的,因?yàn)樾枰褂玫?cyw43_bus_pio_spi.pio 。但是由于 RT-Thread 這邊使用的是 Scons,于是我就先利用 pico-examples 的 cmake 生成該 pio文件對應(yīng)的 .h 文件 cyw43_bus_pio_spi.pio.h 然后復(fù)制過來是以供項(xiàng)目調(diào)用。
-
FPGA
+關(guān)注
關(guān)注
1629文章
21753瀏覽量
604195 -
存儲器
+關(guān)注
關(guān)注
38文章
7512瀏覽量
163980 -
狀態(tài)機(jī)
+關(guān)注
關(guān)注
2文章
492瀏覽量
27571 -
RT-Thread
+關(guān)注
關(guān)注
31文章
1293瀏覽量
40225 -
樹莓派
+關(guān)注
關(guān)注
117文章
1709瀏覽量
105714
發(fā)布評論請先 登錄
相關(guān)推薦
樹莓派pico入門學(xué)習(xí)筆記(一)相關(guān)資料推薦
樹莓派Pico的相關(guān)資料分享
樹莓派Pico的相關(guān)資料推薦
樹莓派也出MCU了?樹莓派Pico來了!

樹莓派不講武德,自研雙核MCU Pico,STM32哭暈在廁所!

樹莓派Pico:僅4美元的MCU

樹莓派pico入門學(xué)習(xí)筆記(一)

距離檢測報(bào)警使用樹莓派Pico

基于樹莓派pico的可編程游戲手柄設(shè)計(jì)
使用樹莓派Pico制作USB麥克風(fēng)




 樹莓派PICO pio使用
樹莓派PICO pio使用










評論