以下是在編程面試中排名前 9 的算法相關的概念,我會通過一些簡單的例子來闡述這些概念。由于完全掌握這些概念需要更多的努力,因此這份列表只是作為一個介紹。本文將從Java的角度看問題,包含下面的這些概念:
1. 字符串
2. 鏈表
3. 樹
4. 圖
5. 排序
6. 遞歸 vs. 迭代
7. 動態規劃
8. 位操作
9. 概率問題
1. 字符串
如果IDE沒有代碼自動補全功能,所以你應該記住下面的這些方法。
toCharArray()// 獲得字符串對應的char數組
Arrays.sort()// 數組排序
Arrays.toString(char[]a)// 數組轉成字符串
charAt(intx)// 獲得某個索引處的字符
length()// 字符串長度
length// 數組大小
2. 鏈表
在Java中,鏈表的實現非常簡單,每個節點Node都有一個值val和指向下個節點的鏈接next。
classNode{
intval;
Nodenext;
Node(intx){
val=x;
next=null;
}
}
鏈表兩個著名的應用是棧Stack和隊列Queue。
棧:
classStack{
Nodetop;
publicNode peek(){
if(top!=null){
returntop;
}
returnnull;
}
publicNode pop(){
if(top==null){
returnnull;
}else{
Nodetemp=newNode(top.val);
top=top.next;
returntemp;
}
}
publicvoidpush(Noden){
if(n!=null){
n.next=top;
top=n;
}
}
}
隊列:
classQueue{
Nodefirst,last;
publicvoidenqueue(Noden){
if(first==null){
first=n;
last=first;
}else{
last.next=n;
last=n;
}
}
publicNode dequeue(){
if(first==null){
returnnull;
}else{
Nodetemp=newNode(first.val);
first=first.next;
if(last==temp)last=first;
returntemp;
}
}
}
3. 樹
這里的樹通常是指二叉樹,每個節點都包含一個左孩子節點和右孩子節點,像下面這樣:
classTreeNode{
intvalue;
TreeNodeleft;
TreeNoderight;
}
下面是與樹相關的一些概念:
平衡 vs. 非平衡:平衡二叉樹中,每個節點的左右子樹的深度相差至多為1(1或0)。
滿二叉樹(Full Binary Tree):除葉子節點以為的每個節點都有兩個孩子。
完美二叉樹(Perfect Binary Tree):是具有下列性質的滿二叉樹:所有的葉子節點都有相同的深度或處在同一層次,且每個父節點都必須有兩個孩子。
完全二叉樹(Complete Binary Tree):二叉樹中,可能除了最后一個,每一層都被完全填滿,且所有節點都必須盡可能想左靠。
譯者注:完美二叉樹也隱約稱為完全二叉樹。完美二叉樹的一個例子是一個人在給定深度的祖先圖,因為每個人都一定有兩個生父母。完全二叉樹可以看成是可以有若干額外向左靠的葉子節點的完美二叉樹。疑問:完美二叉樹和滿二叉樹的區別?
4. 圖
圖相關的問題主要集中在深度優先搜索(depth first search)和廣度優先搜索(breath first search)。
下面是一個簡單的圖廣度優先搜索的實現。
1) 定義GraphNode
classGraphNode{
intval;
GraphNodenext;
GraphNode[]neighbors;
booleanvisited;
GraphNode(intx){
val=x;
}
GraphNode(intx,GraphNode[]n){
val=x;
neighbors=n;
}
publicStringtoString(){
return"value: "+this.val;
}
}
2) 定義一個隊列Queue
classQueue{
GraphNodefirst,last;
publicvoidenqueue(GraphNoden){
if(first==null){
first=n;
last=first;
}else{
last.next=n;
last=n;
}
}
publicGraphNode dequeue(){
if(first==null){
returnnull;
}else{
GraphNodetemp=newGraphNode(first.val,first.neighbors);
first=first.next;
returntemp;
}
}
}
3) 用隊列Queue實現廣度優先搜索
publicclassGraphTest{
publicstaticvoidmain(String[]args){
GraphNoden1=newGraphNode(1);
GraphNoden2=newGraphNode(2);
GraphNoden3=newGraphNode(3);
GraphNoden4=newGraphNode(4);
GraphNoden5=newGraphNode(5);
n1.neighbors=newGraphNode[]{n2,n3,n5};
n2.neighbors=newGraphNode[]{n1,n4};
n3.neighbors=newGraphNode[]{n1,n4,n5};
n4.neighbors=newGraphNode[]{n2,n3,n5};
n5.neighbors=newGraphNode[]{n1,n3,n4};
breathFirstSearch(n1,5);
}
publicstaticvoidbreathFirstSearch(GraphNoderoot,intx){
if(root.val==x)
System.out.println("find in root");
Queuequeue=newQueue();
root.visited=true;
queue.enqueue(root);
while(queue.first!=null){
GraphNodec=(GraphNode)queue.dequeue();
for(GraphNoden:c.neighbors){
if(!n.visited){
System.out.print(n+" ");
n.visited=true;
if(n.val==x)
System.out.println("Find "+n);
queue.enqueue(n);
}
}
}
}
}
5. 排序
下面是不同排序算法的時間復雜度,你可以去wiki看一下這些算法的基本思想。
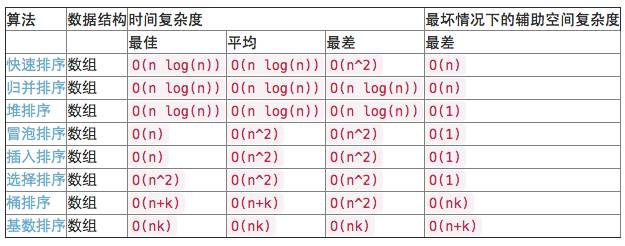
6. 遞歸 vs. 迭代
對程序員來說,遞歸應該是一個與生俱來的思想(a built-in thought),可以通過一個簡單的例子來說明。
問題: 有n步臺階,一次只能上1步或2步,共有多少種走法。
步驟1:找到走完前n步臺階和前n-1步臺階之間的關系。
為了走完n步臺階,只有兩種方法:從n-1步臺階爬1步走到或從n-2步臺階處爬2步走到。如果f(n)是爬到第n步臺階的方法數,那么f(n) = f(n-1) + f(n-2)。
f(0) = 0;f(1) = 1;
步驟2: 確保開始條件是正確的。
publicstaticintf(intn){
if(n<=?2)returnn;
intx=f(n-1)+f(n-2);
returnx;
}
遞歸方法的時間復雜度是n的指數級,因為有很多冗余的計算,如下:
f(5)
f(4) + f(3)
f(3) + f(2) + f(2) + f(1)
f(2) + f(1) + f(1) + f(0) + f(1) + f(0) + f(1)
f(1) + f(0) + f(1) + f(1) + f(0) + f(1) + f(0) + f(1)
直接的想法是將遞歸轉換為迭代:
publicstaticintf(intn){
if(n<=?2){
returnn;
}
intfirst=1,second=2;
intthird=0;
for(inti=3;i<=?n;i++){
third=first+second;
first=second;
second=third;
}
returnthird;
}
7. 動態規劃
動態規劃是解決下面這些性質類問題的技術:
一個問題可以通過更小子問題的解決方法來解決(譯者注:即問題的最優解包含了其子問題的最優解,也就是最優子結構性質)。
有些子問題的解可能需要計算多次(譯者注:也就是子問題重疊性質)。
子問題的解存儲在一張表格里,這樣每個子問題只用計算一次。
需要額外的空間以節省時間。
爬臺階問題完全符合上面的四條性質,因此可以用動態規劃法來解決。
publicstaticint[]A=newint[100];
publicstaticintf3(intn){
if(n<=?2)
A[n]=n;
if(A[n]>0)
returnA[n];
else
A[n]=f3(n-1)+f3(n-2);//store results so only calculate once!
returnA[n];
}
8. 位操作
位操作符:
| 或 | 與 | 亦或 | 左移 | 右移 | 非 |
| 1|0=1 | 1&0=0 | 1^0=1 | 0010<<2=1000 | 1100>>2=0011 | ~1=0 |
獲得給定數字n的第i位:( i 從 0 計數,并從右邊開始)
publicstaticbooleangetBit(intnum,inti){
intresult=num&(1<
if(result==0){
returnfalse;
}else{
returntrue;
}
例如,獲得數字10的第2位:
i=1, n=101<<1= 101010&10=1010 is not 0, so return true;
9. 概率問題
解決概率相關的問題通常需要很好的規劃了解問題(formatting the problem),這里剛好有一個這類問題的簡單例子:
一個房間里有50個人,那么至少有兩個人生日相同的概率是多少?(忽略閏年的事實,也就是一年365天)
計算某些事情的概率很多時候都可以轉換成先計算其相對面。在這個例子里,我們可以計算所有人生日都互不相同的概率,也就是:365/365 * 364/365 * 363/365 * ... * (365-49)/365,這樣至少兩個人生日相同的概率就是1 – 這個值。
publicstaticdoublecaculateProbability(intn){
doublex=1;
for(inti=0;i
x*=(365.0-i)/365.0;
}
doublepro=Math.round((1-x)*100);
returnpro/100;
}
calculateProbability(50) = 0.97
-
算法
+關注
關注
23文章
4612瀏覽量
92927 -
編程
+關注
關注
88文章
3616瀏覽量
93752
原文標題:經典:編程面試的 10 大算法概念匯總
文章出處:【微信號:LinuxHub,微信公眾號:Linux愛好者】歡迎添加關注!文章轉載請注明出處。
發布評論請先 登錄
相關推薦
程序員面試寶典pdf 電子書
關在釘釘和企業微信上使用AI視頻面試——AI得賢招聘官操作說明
史上最全面Java面試匯總(面試題+答案)精選資料分享
編程之美--微軟技術面試心得





 編程面試的 9 大算法概念
編程面試的 9 大算法概念










評論