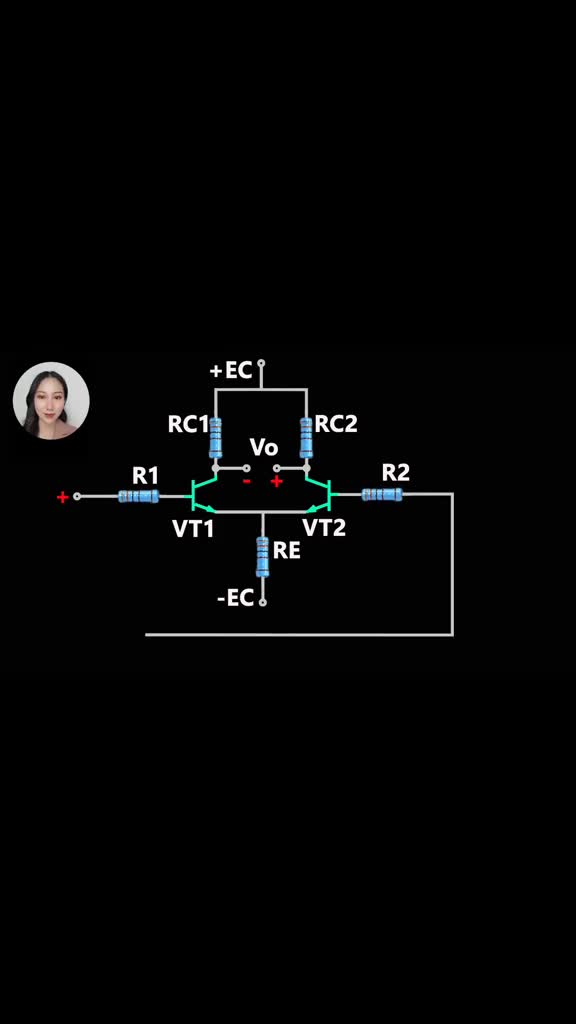
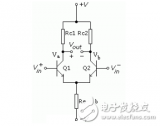
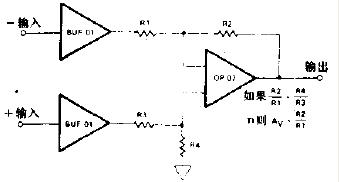
差分放大器:The Difference Amplifier
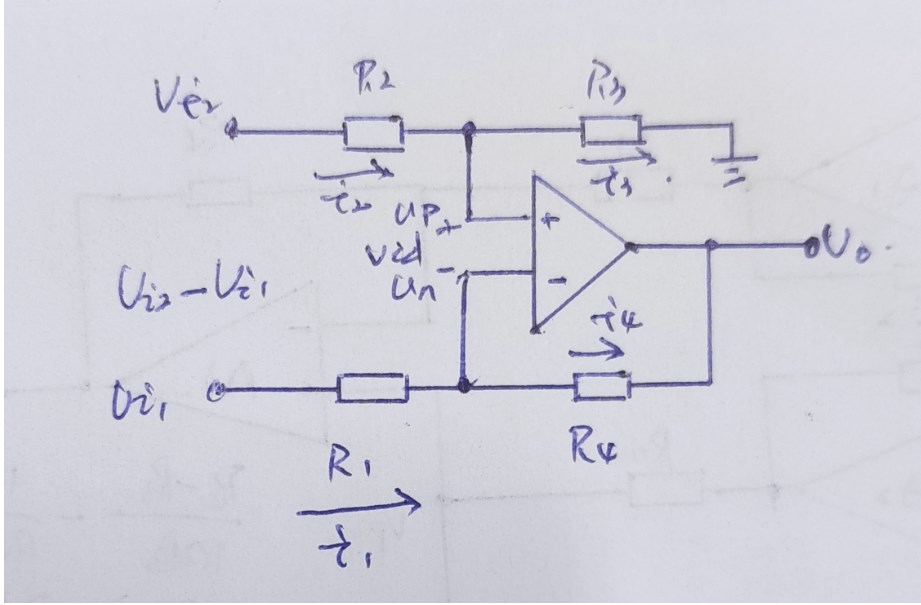
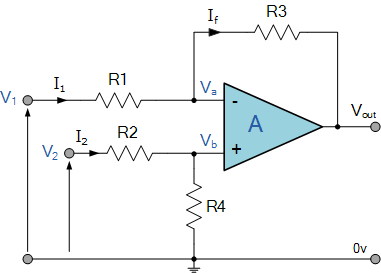
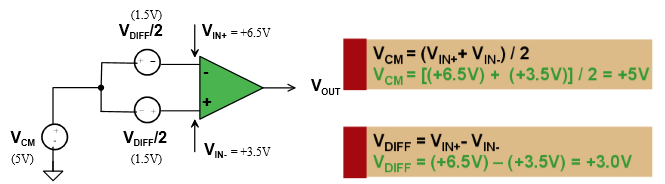
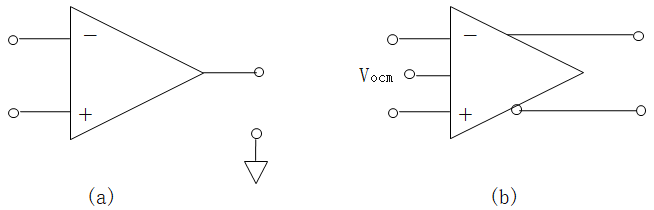
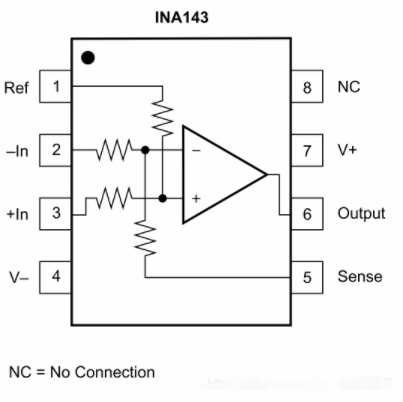
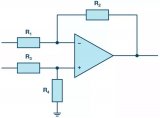
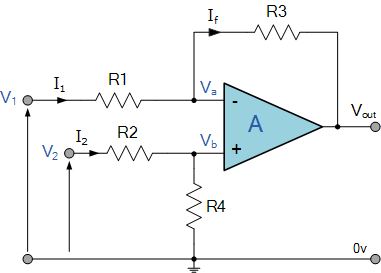
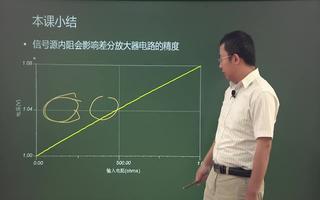
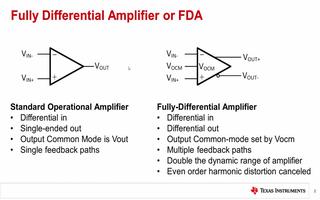
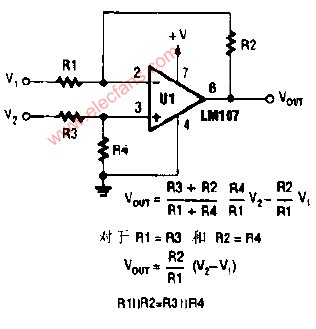
The difference amplifier is the complement of the summing amplifier and allows the subtraction of two voltages or, as a special case, the cancellation of a signal common to the two inputs. This circuit is shown in Figure 5 and is useful as a computational amplifier, in making a differential to single-ended conversion or in rejecting a common mode signal.
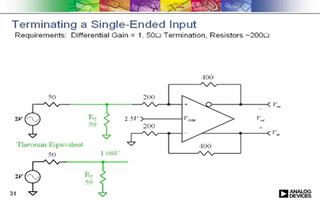
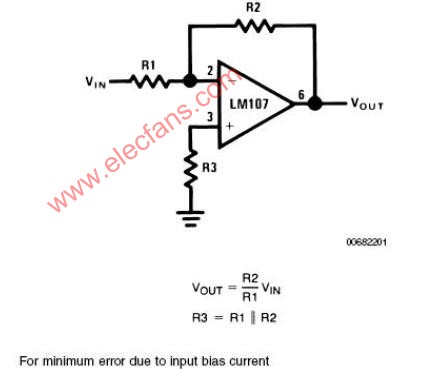
Circuit bandwidth may be calculated in the same manner as for the inverting amplifier, but input impedance is somewhat more complicated. Input impedance for the two inputs is not necessarily equal; inverting input impedance is the same as for the inverting amplifier of Figure 1 and the non-inverting input impedance is the sum of R3 and R4. Gain for either input is the ratio of R1 to R2 for the special case of a differential input single-ended output where R1 = R3 and R2 = R4. The general expression for gain is given in the figure. Compensation should be chosen on the basis of amplifier bandwidth. Care must be exercised in applying this circuit since input impedances are not equal for minimum bias current error.

差分放大器是對求和電路的發(fā)展,這種電路可以減小甚至去處兩個輸入信號中的共模成分。電路見圖5,這種電路在運算電路中相當(dāng)有用,比如差分對單端的轉(zhuǎn)換,抑制共模信號。
電路帶寬的計算方式和反相電路相同。輸入阻抗的計算方式相對復(fù)雜。兩個輸入端的輸入阻抗沒有必要相等;反相放大部分的輸入阻抗和反相放大器的計算方法相同。同相放大部分的輸入阻抗為R3、R4之和。在R1=R3,R2=R4,差分輸入,單端輸出的特殊情況下,兩個輸入的增益都是R2/R1。一般情況下增益的計算方法見圖中說明。補償可以按照放大器的具體帶寬進行。在應(yīng)用中應(yīng)該注意一點:兩端的輸入阻抗是不相等的,要注意輸入偏置電流的引起的誤差。
 電子發(fā)燒友App
電子發(fā)燒友App














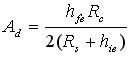
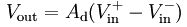
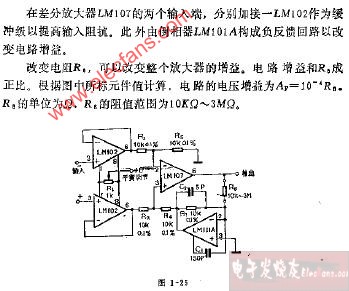
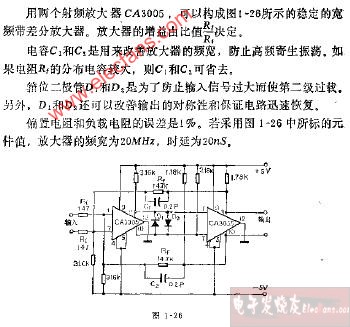
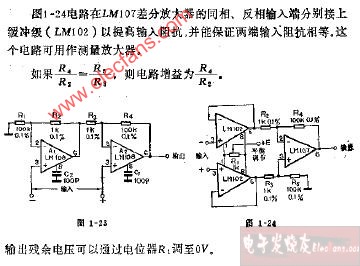



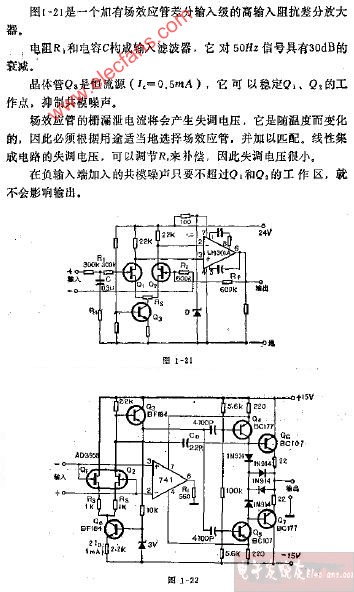










評論