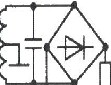
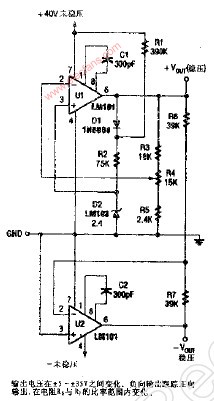
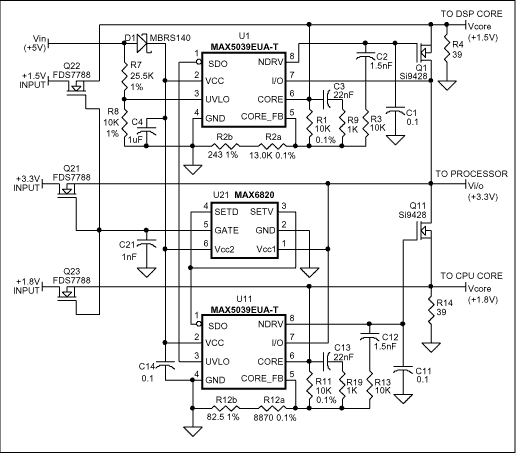
自動跟蹤對稱電源:Tracking Regulated Power Supply
A tracking regulated power supply is shown in Figure 29. This supply is very suitable for powering an operational amplifier system since positive and negative voltages track, eliminating common mode signals originating in the supply voltage. In addition, only one voltage reference and a minimum number of passive components are required.
Power supply operation may be understood by considering first the positive regulator. The positive regulator compares the voltage at the wiper of R4 to the voltage reference, D2. The difference between these two voltages is the input voltage for the amplifier and since R3, R4, and R5 form a negative feedback loop, the amplifier output voltage changes in such a way as to minimize this difference. The voltage reference current is supplied from the amplifier output to increase power supply line regulation. This allows the regulator to operate from supplies with large ripple voltages. Regulating the reference current in this way requires a separate source of current for supply start-up. Resistor R1 and diode D1 provide this start-up current. D1 decouples the reference string from the amplifier output during start-up and R1 supplies the start-up current from the unregulated positive supply. After start-up, the low amplifier output impedance reduces reference current variations due to the current through R1.
The negative regulator is simply a unity-gain inverter withinput resistor, R6, and feedback resistor, R7.
The amplifiers must be compensated for unity-gain operation. The power supply may be modulated by injecting current into the wiper of R4. In this case, the output voltage variations will be equal and opposite at the positive and negative outputs.
The power supply voltage may be controlled by replacing D1, D2, R1 and R2 with a variable voltage reference.
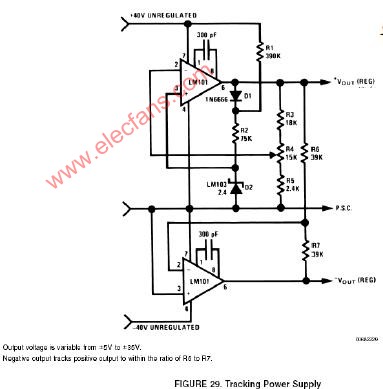
圖29的電路是一個輸出對稱的穩(wěn)壓電源,它非常適合給OP供電,這是因?yàn)槠湔?fù)電源電壓是對稱的,所以電源的共模干擾可以被抑制掉。此外,這個電路比較簡潔,僅使用了一個基準(zhǔn)電壓源和很少的無源器件。
下面從正電源整流部分入手來介紹本電路的原理。正電源整流部分的OP對從電位器R4取出的電壓和穩(wěn)壓管D2給出的參考電壓進(jìn)行比較,這兩個電壓的差值構(gòu)成OP的輸入電壓;R3、R4、R5構(gòu)成了OP的負(fù)反饋路徑,因此OP的輸出變化趨勢會使得輸入的差值盡量減小;基準(zhǔn)電壓源的電流由放大器的輸出端提供,這樣可以提高對電源的線性范圍,使本電路可以適應(yīng)紋波較大的供電電源。這樣一種調(diào)節(jié)基準(zhǔn)電壓源的電流的方法需要一個單獨(dú)的電流源來提供初始啟動電流,電阻R1和二極管D1就起到這個作用:D1用于在啟動時將啟動電路和OP的輸出端隔離開,而輸入電源會經(jīng)R1為D1提供啟動電流。完成啟動后,放大器很低的輸出阻抗將會降低因流經(jīng)R1的電流不足以影響穩(wěn)壓管上的電壓穩(wěn)定性。
負(fù)電源整流部分就是一個簡單的單位增益反相器,輸入電阻是R6,反饋電阻是R7。
圖中所用OP必須進(jìn)行單位增益穩(wěn)定的補(bǔ)償。如果在電位器R4的抽頭處注入外接信號,就可以實(shí)現(xiàn)供電電源調(diào)制。這時,輸出正負(fù)電壓始終對稱,變化量相等。
將D1、D2、R1和R2換成一個可變參考電壓源,本電路就變成了一個可控電源。
 電子發(fā)燒友App
電子發(fā)燒友App























評論