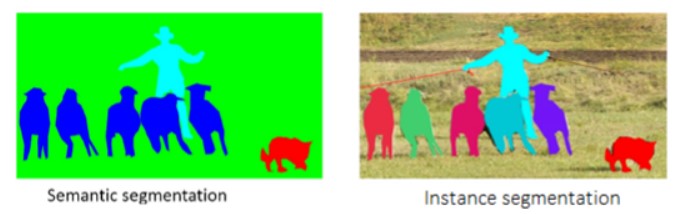
圖像分割就是把圖像分成若干個特定的、具有獨特性質的區域并提出感興趣目標的技術和過程。它是由圖像處理到圖像分析的關鍵步驟。現有的圖像分割方法主要分以下幾類:
基于閾值的分割方法、基于區域的分割方法、基于邊緣的分割方法以及基于特定理論的分割方法等。1998年以來,研究人員不斷改進原有的圖像分割方法并把其它學科的一些新理論和新方法用于圖像分割,提出了不少新的分割方法。圖像分割后提取出的目標可以用于圖像語義識別,圖像搜索等等領域。
圖像分割至今尚無通用的自身理論。隨著各學科許多新理論和新方法的提出,出現了許多與一些特定理論、方法相結合的圖像分割方法。
圖像分割基礎算法及實現實例
近的項目涉及到了圖像處理領域,小小研究了一番,同時收集資料實現了幾個基礎功能。
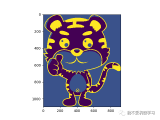
一、圖像反轉
[plain] view plain copyI=imread(‘input_image.jpg’);
J=double(I);
J=-J+(256-1); %圖像反轉線性變換
H=uint8(J);
subplot(3,3,4),imshow(H);
title(‘圖像反轉線性變換’);
axis([50,250,50,200]);
axis on;
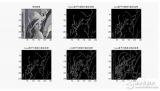
二、灰度線性變換
[plain] view plain copyI=imread(‘input_image.jpg’);
subplot(3,3,1),imshow(I);
title(‘原始圖像’);
axis([50,250,50,200]);
axis on;
I1 = rgb2gray(I);
subplot(3,3,2),imshow(I1)
title(‘灰度圖像’)
axis([50,250,50,200]);
grid on;
axis on;
K=imadjust(I1,[0.3 0.7],[]);
subplot(3,3,3),imshow(K);
title(‘線性變換圖像[0.3 0.7]’);
axis([50,250,20,200]);
grid on;
axis on;
三、非線性變換
[plain] view plain copyI=imread(‘input_image.jpg’);
I1 = rgb2gray(I);
subplot(3,3,5),imshow(I1);
title(‘灰度圖像’);
axis([50,250,50,200]);
grid on; %顯示網格線
axis on; %顯示坐標系
J=double(I1);
J=40*(log(J+1));
H=uint8(J);
subplot(3,3,6),imshow(H);
title(‘對數變換圖像’);
axis([50,250,50,200]);
grid on; %顯示網格線
axis on; %顯示坐標系
上述代碼結果:

四、直方圖均衡化
[plain] view plain copyI=imread(‘input_image.jpg’);
figure;
I=rgb2gray(I);
subplot(2,2,1);
imshow(I);
subplot(2,2,2);
imhist(I);
title(‘直方圖均衡化圖像’);
I1 = histeq(I);
subplot(2,2,3);
imshow(I1);
subplot(2,2,4);
imhist(I1);
上述代碼結果:

五、線性平滑濾波器
[plain] view plain copyI=imread(‘input_image.jpg’);
figure;
subplot(231)
imshow(I)
title(‘原始圖像’)
I=rgb2gray(I);
I1=imnoise(I,‘salt & pepper’,0.02);
subplot(232)
imshow(I1)
title(‘添加椒鹽噪聲的圖像’)
k1=filter2(fspecial(‘average’,3),I1)/255; %進行3*3模板平滑濾波
k2=filter2(fspecial(‘average’,5),I1)/255; %進行5*5模板平滑濾波
k3=filter2(fspecial(‘average’,7),I1)/255; %進行7*7模板平滑濾波
k4=filter2(fspecial(‘average’,9),I1)/255; %進行9*9模板平滑濾波
subplot(233),imshow(k1);title(‘3*3模板平滑濾波’);
subplot(234),imshow(k2);title(‘5*5模板平滑濾波’);
subplot(235),imshow(k3);title(‘7*7模板平滑濾波’);
subplot(236),imshow(k4);title(‘9*9模板平滑濾波’);
上述代碼結果:

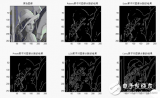
六、中值濾波器
[plain] view plain copyfigure;
I=imread(‘input_image.jpg’);
I=rgb2gray(I);
subplot(231),imshow(I);
title(‘原圖像’);
J=imnoise(I,‘salt & pepper’,0.02);
subplot(232),imshow(J);
title(‘添加椒鹽噪聲圖像’);
k1=medfilt2(J); %進行3*3模板中值濾波
k2=medfilt2(J,[5,5]); %進行5*5模板中值濾波
k3=medfilt2(J,[7,7]); %進行7*7模板中值濾波
k4=medfilt2(J,[9,9]); %進行9*9模板中值濾波
subplot(233),imshow(k1);title(‘3*3模板中值濾波’);
subplot(234),imshow(k2);title(‘5*5模板中值濾波’);
subplot(235),imshow(k3);title(‘7*7模板中值濾波’);
subplot(236),imshow(k4);title(‘9*9模板中值濾波’);
上述代碼結果:

七、用Sobel算子和拉普拉斯對圖像銳化
[plain] view plain copyfigure;
I=imread(‘input_image.jpg’);
subplot(2,2,1),imshow(I);
title(‘原始圖像’);
axis([50,250,50,200]);
grid on; %顯示網格線
axis on; %顯示坐標系
I1=im2bw(I);
subplot(2,2,2),imshow(I1);
title(‘二值圖像’);
axis([50,250,50,200]);
grid on; %顯示網格線
axis on; %顯示坐標系
H=fspecial(‘sobel’); %選擇sobel算子
J=filter2(H,I1); %卷積運算
subplot(2,2,3),imshow(J);
title(‘sobel算子銳化圖像’);
axis([50,250,50,200]);
grid on; %顯示網格線
axis on; %顯示坐標系
I1 = double(I1);
h=[0 1 0,1 -4 1,0 1 0]; %拉普拉斯算子
J1=conv2(I1,h,‘same’); %卷積運算
subplot(2,2,4),imshow(J1);
title(‘拉普拉斯算子銳化圖像’);
axis([50,250,50,200]);
grid on; %顯示網格線
axis on; %顯示坐標系
上述代碼結果:

八、梯度算子檢測邊緣
[plain] view plain copyfigure;
I=imread(‘input_image.jpg’);
subplot(2,3,1);
imshow(I);
title(‘原始圖像’);
axis([50,250,50,200]);
grid on; %顯示網格線
axis on; %顯示坐標系
I1=im2bw(I);
subplot(2,3,2);
imshow(I1);
title(‘二值圖像’);
axis([50,250,50,200]);
grid on; %顯示網格線
axis on; %顯示坐標系
I2=edge(I1,‘roberts’);
subplot(2,3,3);
imshow(I2);
title(‘roberts算子分割結果’);
axis([50,250,50,200]);
grid on; %顯示網格線
axis on; %顯示坐標系
I3=edge(I1,‘sobel’);
subplot(2,3,4);
imshow(I3);
title(‘sobel算子分割結果’);
axis([50,250,50,200]);
grid on; %顯示網格線
axis on; %顯示坐標系
I4=edge(I1,‘Prewitt’);
subplot(2,3,5);
imshow(I4);
title(‘Prewitt算子分割結果’);
axis([50,250,50,200]);
grid on; %顯示網格線
axis on; %顯示坐標系
九、LOG算子檢測邊緣
[plain] view plain copyI1=rgb2gray(I);
I2=edge(I1,‘log’);
subplot(2,3,6);
imshow(I2);
title(‘log算子分割結果’);
上述代碼結果:

十、Canny算子檢測邊緣
[plain] view plain copyfigure;
I=imread(‘input_image.jpg’);
subplot(2,2,1);
imshow(I);
title(‘原始圖像’)
I1=rgb2gray(I);
subplot(2,2,2);
imshow(I1);
title(‘灰度圖像’);
I2=edge(I1,‘canny’);
subplot(2,2,3);
imshow(I2);
title(‘canny算子分割結果’);
上述代碼結果:

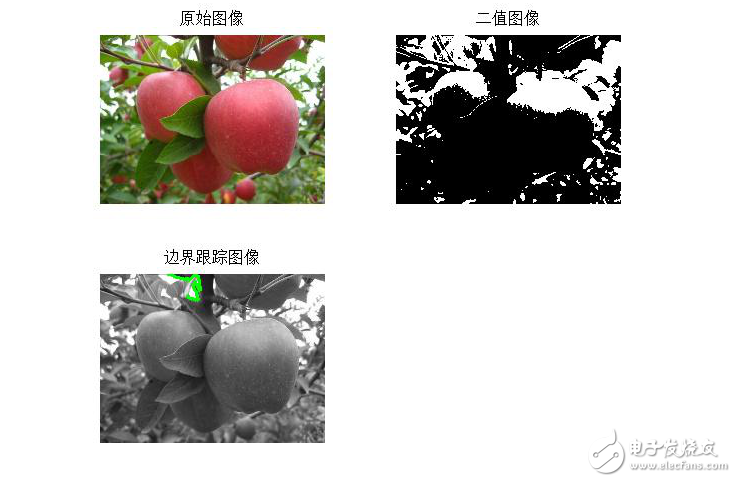
十一、邊界跟蹤(bwtraceboundary函數)
[plain] view plain copyI=imread(‘input_image.jpg’);
figure
subplot(2,2,1);
imshow(I);
title(‘原始圖像’);
I1=rgb2gray(I); %將彩色圖像轉化灰度圖像
threshold=graythresh(I1); %計算將灰度圖像轉化為二值圖像所需的門限
BW=im2bw(I1, threshold); %將灰度圖像轉化為二值圖像
subplot(2,2,2);
imshow(BW);
title(‘二值圖像’);
dim=size(BW);
col=round(dim(2)/2)-90; %計算起始點列坐標
row=find(BW(:,col),1); %計算起始點行坐標
connectivity=8;
num_points=180;
contour=bwtraceboundary(BW,[row,col],‘N’,connectivity,num_points);
%提取邊界
subplot(2,2,3);
imshow(I1);
hold on;
plot(contour(:,2),contour(:,1), ‘g’,‘LineWidth’ ,2);
title(‘邊界跟蹤圖像’);
上述代碼結果:
十二、Hough變換
[plain] view plain copyfigure;
I=imread(‘input_image.jpg’);
rotI=rgb2gray(I);
subplot(2,2,1);
imshow(rotI);
title(‘灰度圖像’);
axis([50,250,50,200]);
grid on;
axis on;
BW=edge(rotI,‘prewitt’);
subplot(2,2,2);
imshow(BW);
title(‘prewitt算子邊緣檢測后圖像’);
axis([50,250,50,200]);
grid on;
axis on;
[H,T,R]=hough(BW);
subplot(2,2,3);
imshow(H,[],‘XData’,T,‘YData’,R,‘InitialMagnification’,‘fit’);
title(‘霍夫變換圖’);
xlabel(‘\theta’),ylabel(‘\rho’);
axis on , axis normal, hold on;
P=houghpeaks(H,5,‘threshold’,ceil(0.3*max(H(:))));
x=T(P(:,2));y=R(P(:,1));
plot(x,y,‘s’,‘color’,‘white’);
lines=houghlines(BW,T,R,P,‘FillGap’,5,‘MinLength’,7);
subplot(2,2,4);imshow(rotI);
title(‘霍夫變換圖像檢測’);
axis([50,250,50,200]);
grid on;
axis on;
hold on;
max_len=0;
for k=1:length(lines)
xy=[lines(k).point1;lines(k).point2];
plot(xy(:,1),xy(:,2),‘LineWidth’,2,‘Color’,‘green’);
plot(xy(1,1),xy(1,2),‘x’,‘LineWidth’,2,‘Color’,‘yellow’);
plot(xy(2,1),xy(2,2),‘x’,‘LineWidth’,2,‘Color’,‘red’);
len=norm(lines(k).point1-lines(k).point2);
if(len》max_len)
max_len=len;
xy_long=xy;
end
end
plot(xy_long(:,1),xy_long(:,2),‘LineWidth’,2,‘Color’,‘cyan’);
上述代碼結果:

十三、直方圖閾值法
[plain] view plain copyfigure;
I=imread(‘input_image.jpg’);
I1=rgb2gray(I);
subplot(2,2,1);
imshow(I1);
title(‘灰度圖像’)
axis([50,250,50,200]);
grid on; %顯示網格線
axis on; %顯示坐標系
[m,n]=size(I1); %測量圖像尺寸參數
GP=zeros(1,256); %預創建存放灰度出現概率的向量
for k=0:255
GP(k+1)=length(find(I1==k))/(m*n); %計算每級灰度出現的概率,將其存入GP中相應位置
end
subplot(2,2,2),bar(0:255,GP,‘g’) %繪制直方圖
title(‘灰度直方圖’)
xlabel(‘灰度值’)
ylabel(‘出現概率’)
I2=im2bw(I,150/255);
subplot(2,2,3),imshow(I2);
title(‘閾值150的分割圖像’)
axis([50,250,50,200]);
grid on; %顯示網格線
axis on; %顯示坐標系
I3=im2bw(I,200/255); %
subplot(2,2,4),imshow(I3);
title(‘閾值200的分割圖像’)
axis([50,250,50,200]);
grid on; %顯示網格線
axis on; %顯示坐標系
上述代碼結果:

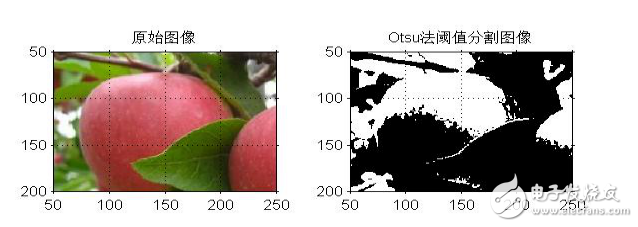
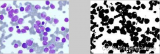
十四、自動閾值法:Otsu法
[plain] view plain copyclc
clear all
figure;
I=imread(‘input_image.jpg’);
subplot(1,2,1),imshow(I);
title(‘原始圖像’)
axis([50,250,50,200]);
grid on; %顯示網格線
axis on; %顯示坐標系
level=graythresh(I); %確定灰度閾值
BW=im2bw(I,level);
subplot(1,2,2),imshow(BW);
title(‘Otsu法閾值分割圖像’)
axis([50,250,50,200]);
grid on; %顯示網格線
axis on; %顯示坐標系
上述代碼結果:
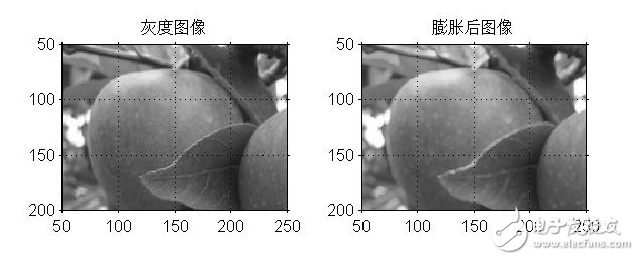
十五、膨脹操作
[plain] view plain copyfigure;
I=imread(‘input_image.jpg’);
I1=rgb2gray(I);
subplot(1,2,1);
imshow(I1);
title(‘灰度圖像’)
axis([50,250,50,200]);
grid on; %顯示網格線
axis on; %顯示坐標系
se=strel(‘disk’,1); %生成圓形結構元素
I2=imdilate(I1,se); %用生成的結構元素對圖像進行膨脹
subplot(1,2,2);
imshow(I2);
title(‘膨脹后圖像’);
axis([50,250,50,200]);
grid on; %顯示網格線
axis on; %顯示坐標系
上述代碼結果:
十六、腐蝕操作
[plain] view plain copyfigure;
I=imread(‘input_image.jpg’);
I1=rgb2gray(I);
subplot(1,2,1);
imshow(I1);
title(‘灰度圖像’)
axis([50,250,50,200]);
grid on; %顯示網格線
axis on; %顯示坐標系
se=strel(‘disk’,1); %生成圓形結構元素
I2=imerode(I1,se); %用生成的結構元素對圖像進行腐蝕
subplot(1,2,2);
imshow(I2);
title(‘腐蝕后圖像’);
axis([50,250,50,200]);
grid on; %顯示網格線
axis on; %顯示坐標系
上述代碼結果:

十七、開啟和閉合操作
[plain] view plain copyfigure;
I=imread(‘input_image.jpg’);
subplot(2,2,1),imshow(I);
title(‘原始圖像’);
axis([50,250,50,200]);
axis on; %顯示坐標系
I1=rgb2gray(I);
subplot(2,2,2),imshow(I1);
title(‘灰度圖像’);
axis([50,250,50,200]);
axis on; %顯示坐標系
se=strel(‘disk’,1); %采用半徑為1的圓作為結構元素
I2=imopen(I1,se); %開啟操作
I3=imclose(I1,se); %閉合操作
subplot(2,2,3),imshow(I2);
title(‘開啟運算后圖像’);
axis([50,250,50,200]);
axis on; %顯示坐標系
subplot(2,2,4),imshow(I3);
title(‘閉合運算后圖像’);
axis([50,250,50,200]);
axis on; %顯示坐標系
上述代碼結果:

十八、開啟和閉合組合操作
[plain] view plain copyfigure;
I=imread(‘input_image.jpg’);
subplot(3,2,1),imshow(I);
title(‘原始圖像’);
axis([50,250,50,200]);
axis on; %顯示坐標系
I1=rgb2gray(I);
subplot(3,2,2),imshow(I1);
title(‘灰度圖像’);
axis([50,250,50,200]);
axis on; %顯示坐標系
se=strel(‘disk’,1);
I2=imopen(I1,se); %開啟操作
I3=imclose(I1,se); %閉合操作
subplot(3,2,3),imshow(I2);
title(‘開啟運算后圖像’);
axis([50,250,50,200]);
axis on; %顯示坐標系
subplot(3,2,4),imshow(I3);
title(‘閉合運算后圖像’);
axis([50,250,50,200]);
axis on; %顯示坐標系
se=strel(‘disk’,1);
I4=imopen(I1,se);
I5=imclose(I4,se);
subplot(3,2,5),imshow(I5); %開—閉運算圖像
title(‘開—閉運算圖像’);
axis([50,250,50,200]);
axis on; %顯示坐標系
I6=imclose(I1,se);
I7=imopen(I6,se);
subplot(3,2,6),imshow(I7); %閉—開運算圖像
title(‘閉—開運算圖像’);
axis([50,250,50,200]);
axis on; %顯示坐標系
上述代碼結果:

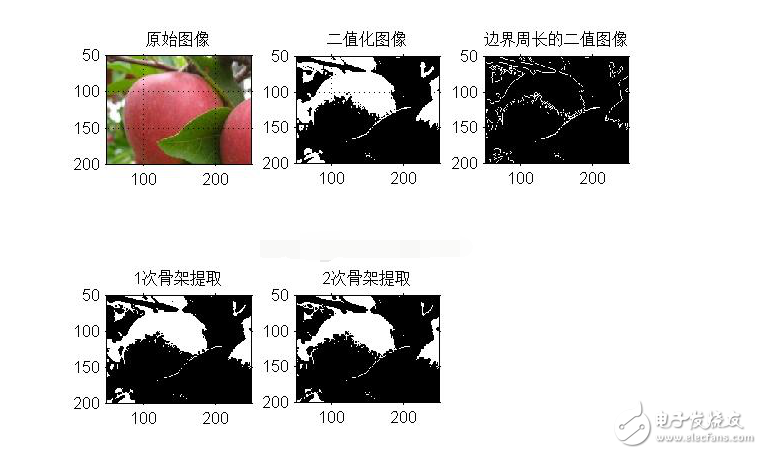
十九、形態學邊界提取
[plain] view plain copyfigure;
I=imread(‘input_image.jpg’);
subplot(2,3,1),imshow(I);
title(‘原始圖像’);
axis([50,250,50,200]);
grid on; %顯示網格線
axis on; %顯示坐標系
I1=im2bw(I);
subplot(2,3,2),imshow(I1);
title(‘二值化圖像’);
axis([50,250,50,200]);
grid on; %顯示網格線
axis on; %顯示坐標系
I2=bwperim(I1); %獲取區域的周長
subplot(2,3,3),imshow(I2);
title(‘邊界周長的二值圖像’);
axis([50,250,50,200]);
grid on;
axis on;
I3=bwmorph(I1,‘skel’,1);
subplot(2,3,4),imshow(I3);
title(‘1次骨架提取’);
axis([50,250,50,200]);
axis on;
I4=bwmorph(I1,‘skel’,2);
subplot(2,3,5),imshow(I4);
title(‘2次骨架提取’);
axis([50,250,50,200]);
axis on;
上述代碼結果:

 電子發燒友App
電子發燒友App










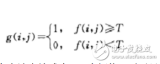

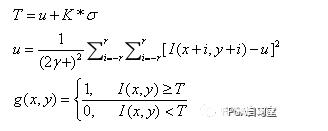















評論