資料介紹
描述
概述
2022 年 1 月 28 日,匹茲堡(賓夕法尼亞州)一座有 50 年歷史的橋梁倒塌。混凝土橋等堅固結構突然倒塌的原因只有一個:磨損。
混凝土結構通常在大約 40 到 50 年后開始惡化。因此,忽視磨損跡象可能會導致嚴重事故,這就是為什么混凝土結構的檢查和維修對于保護我們的生活方式至關重要。裂縫是用于診斷混凝土結構劣化的重要標準之一。通常,專家會通過目視檢查裂縫、勾畫檢查結果,然后根據他們的發現準備檢查數據來檢查此類結構。像這樣的檢查方法不僅非常耗時和昂貴,而且不能準確地檢測到裂縫。在這個項目中,我使用機器學習構建了一個表面裂紋檢測應用程序。
為什么要本地化?
為什么我們要使用圖像分類模型來定位檢測?我們不能使用對象檢測模型嗎?是的,我們可以使用對象檢測模型,但我們需要手動將邊界框添加到數千個樣本中。現有的對象檢測模型可能不是自動注釋這些裂縫的好選擇,因為它們是在確定形狀的對象上訓練的。重新利用分類模型來定位檢測可以節省大量精力,并且仍然能夠識別感興趣的區域。
它是如何工作的?
具有已針對分類任務訓練的 GAP(全局平均池化)層的 CNN(卷積神經網絡)也可用于對象定位。也就是說,GAP-CNN 不僅可以告訴我們圖像中包含什么對象 - 它還可以告訴我們對象在圖像中的位置,并且無需我們進行額外的工作!定位表示為熱圖(類激活圖),其中顏色編碼方案識別對 GAP-CNN 執行對象識別任務相對重要的區域。
硬件設置
由于我想要一個緊湊且便攜的硬件設置,我們將使用 Seeed reTerminal,它帶有一個緊湊形式的 LCD 和按鈕。它由具有 4 GB RAM 的 Raspberry Pi 4 Compute 模塊提供支持,這對于這個概念驗證項目來說已經足夠了。我們需要 Raspberry Pi Camera V2 和一個亞克力支架。

我們需要打開 reTerminal 的后蓋才能訪問 15 針 FPC 攝像頭連接器。請按照此處的分步說明進行操作:https://wiki.seeedstudio.com/reTerminal。
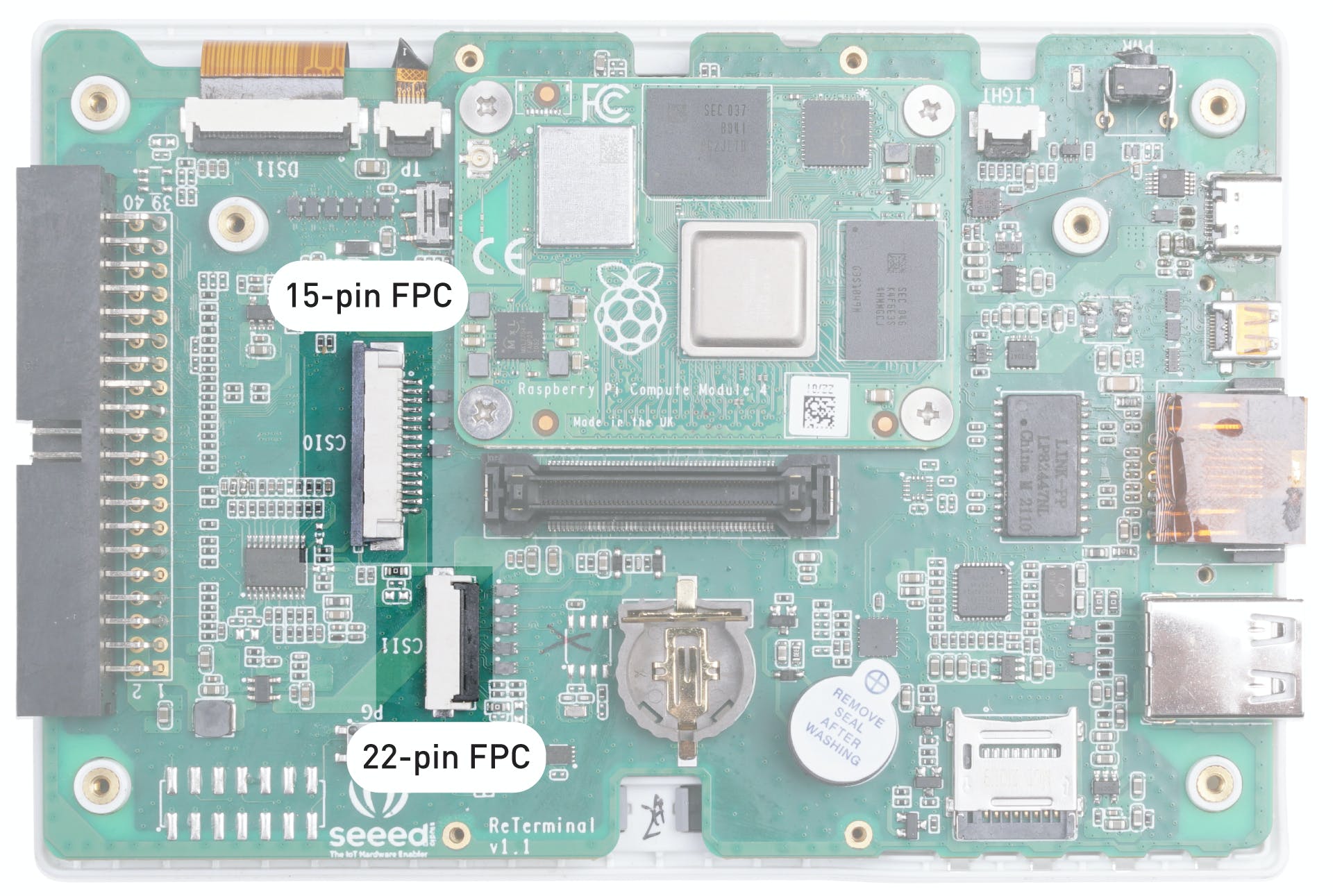
相機使用 FPC 帶狀電纜連接,并使用底座連接到重新終端。

設置開發環境
reTerminal 配備 32 位 Raspberry Pi 操作系統,但我們將使用 64 位 Raspberry Pi 操作系統以獲得更好的性能。
要安裝我們將在推理代碼中使用的 python 包,請執行以下命令。
$ sudo pip3 install seeed-python-reterminal
$ sudo apt install -y libhdf5-dev python3-pyqt5 libatlas-base-dev
$ pip3 install opencv-contrib-python==4.5.3.56
$ pip3 install matplotlib
數據采集
數據集是從 Mendeley Data (Concrete Crack Images for Classification) 下載的。數據集包含有裂縫和沒有裂縫的各種混凝土表面。數據是從多個 METU 校園建筑中收集的。將數據集分為正反兩幅裂紋圖像進行圖像分類。每個類有 20,000 張圖像,總共 40,000 張圖像,227 x 227 像素,RGB 通道。
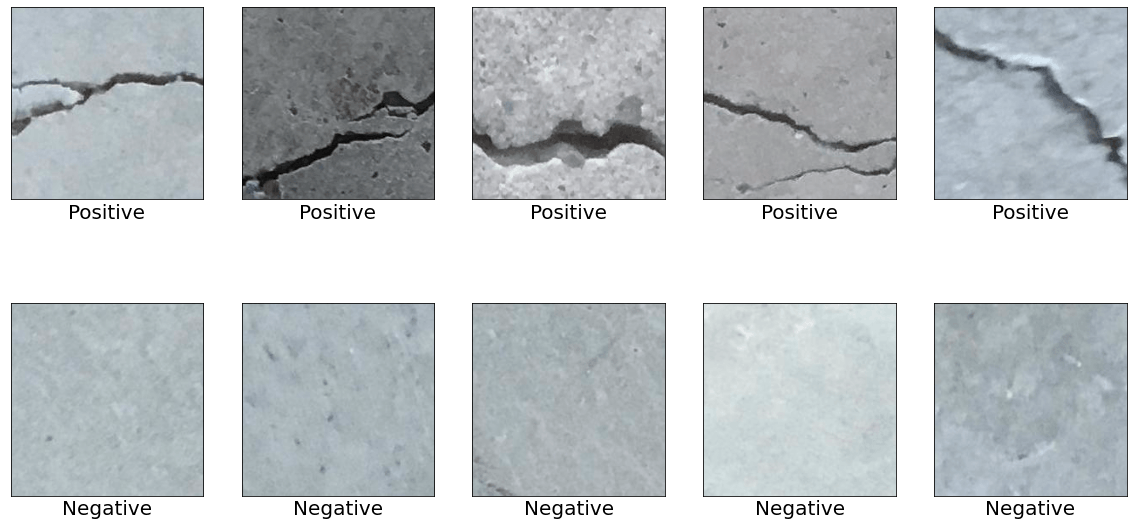
為了將裂紋和非裂紋表面圖像與其他自然世界場景區分開來,下載了來自 COCO-Minitrain(COCO train2017 數據集的子集)的 80 個對象類別的 25,000 張隨機采樣圖像。可以從下面的鏈接訪問數據。
- 表面裂紋數據集:
- COCO-Minitrain 數據集:
將數據上傳到 Edge Impulse Studio
我們需要創建一個新項目來將數據上傳到 Edge Impulse Studio。
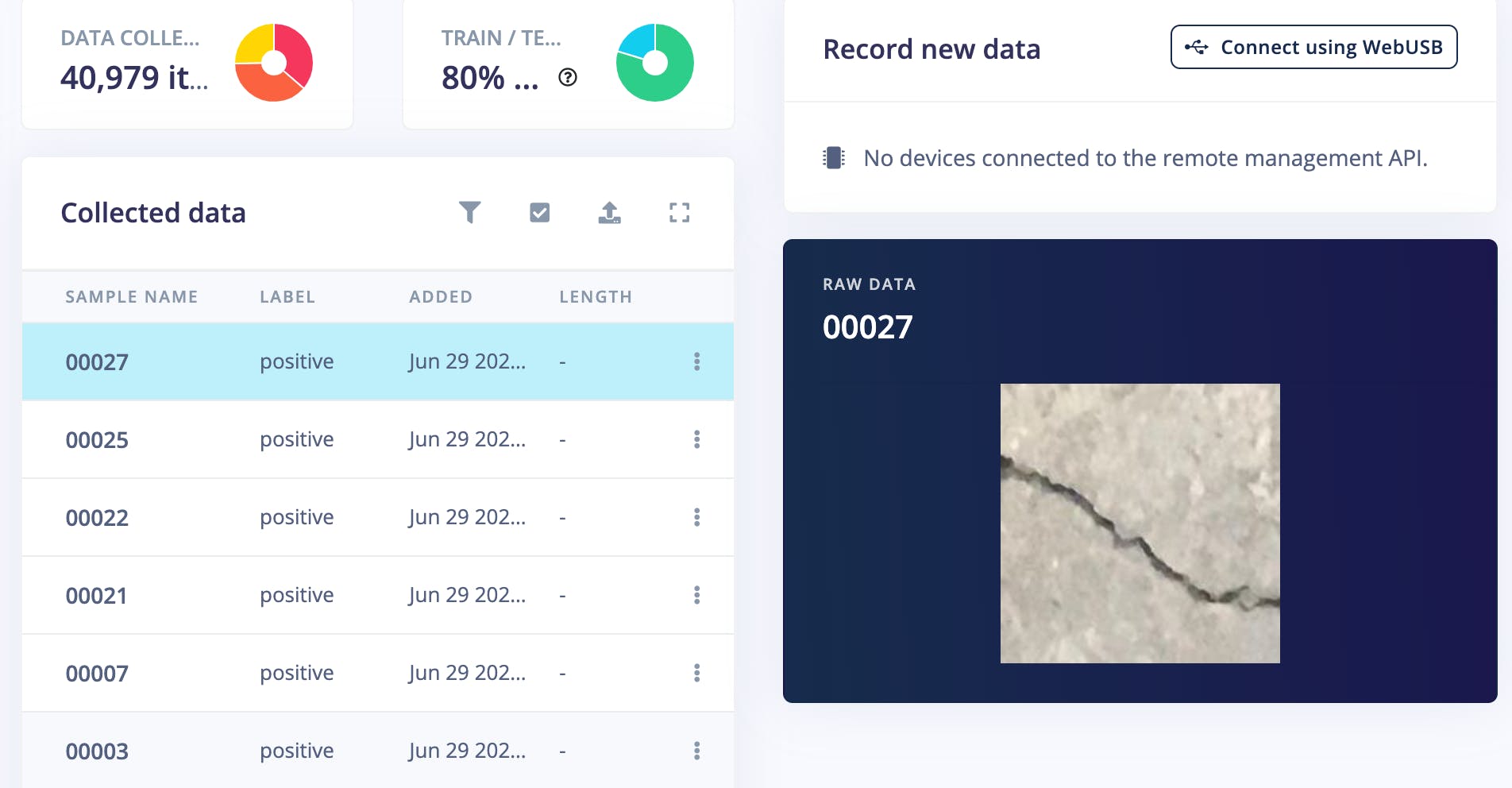
使用 Edge Impulse CLI 上傳數據。請按照說明在此處安裝 CLI:
下載的圖像被標記為 3 類,并保存到帶有標簽名稱的目錄中。
- 正面- 有裂紋的表面
- 負片——表面無裂紋
- 未知- 來自 80 個對象的圖像
執行以下命令將圖像上傳到 Edge Impulse Studio。數據集會自動拆分為訓練和測試數據集。
$ edge-impulse-uploader --category split --label positive positive/*.jpg
$ edge-impulse-uploader --category split --label negative negative/*.jpg
$ edge-impulse-uploader --category split --label unknown unknown/*.jpg
我們可以在 Edge Impulse Studio 的數據采集頁面上看到上傳的數據集。
訓練
進入Impulse Design > Create Impulse頁面,單擊Add a processing block ,然后選擇Image ,它對圖像數據進行預處理和標準化,并可選擇降低顏色深度。此外,在同一頁面上,單擊Add a learning block ,然后選擇Transfer Learning (Images ),這會在數據上微調預訓練的圖像分類模型。我們使用的是 160x160 的圖像尺寸。現在單擊保存脈沖按鈕。
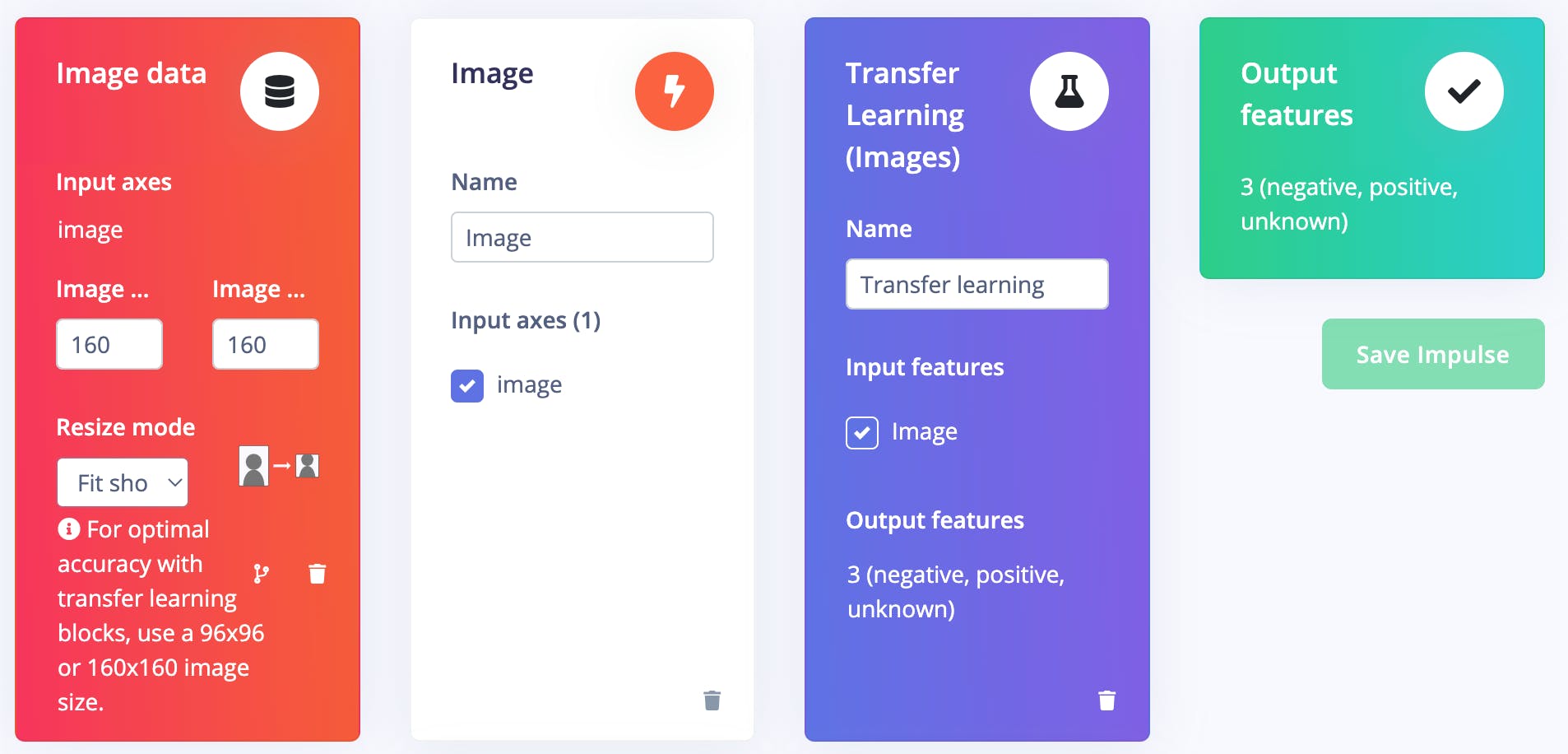
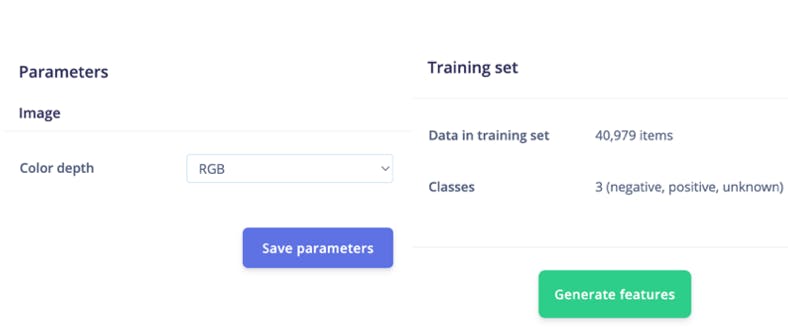
接下來,轉到Impulse Design > Image頁面并將顏色深度參數設置為 RGB,然后單擊Save parameters按鈕,該按鈕將重定向到另一個頁面,我們應該單擊Generate Feature按鈕。完成特征生成通常需要幾分鐘。
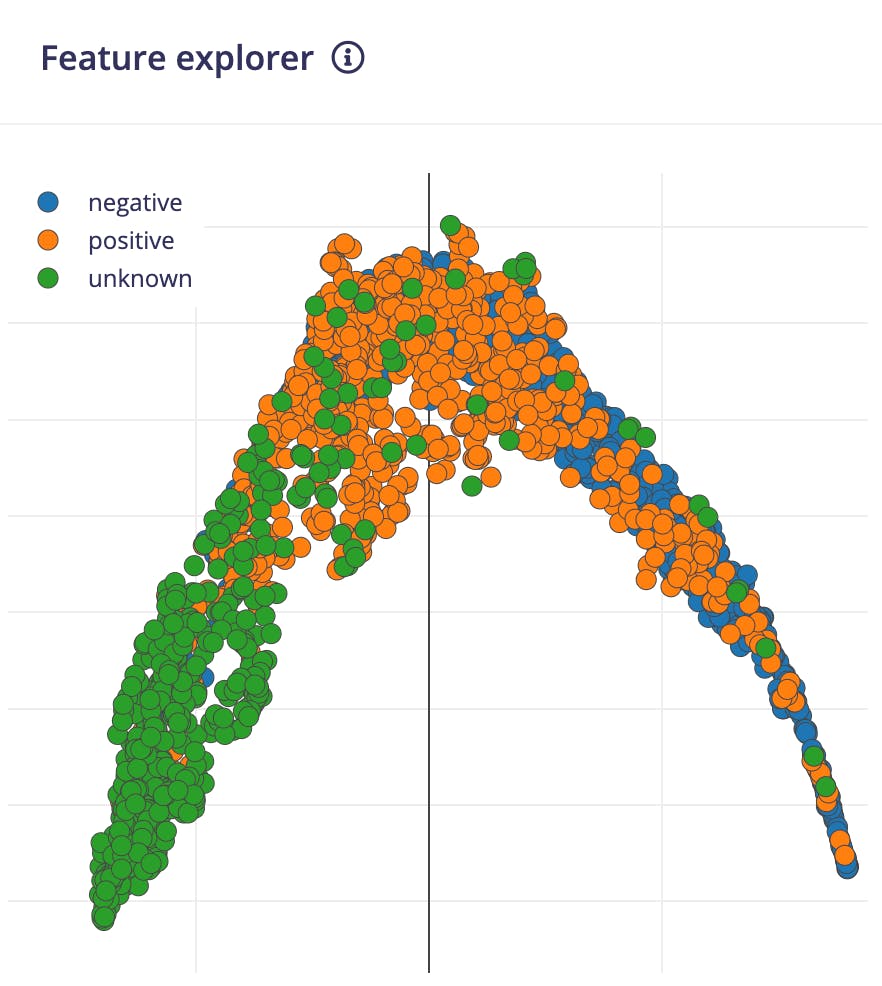
我們可以在 Feature Explorer 中看到生成的特征的 2D 可視化。
?
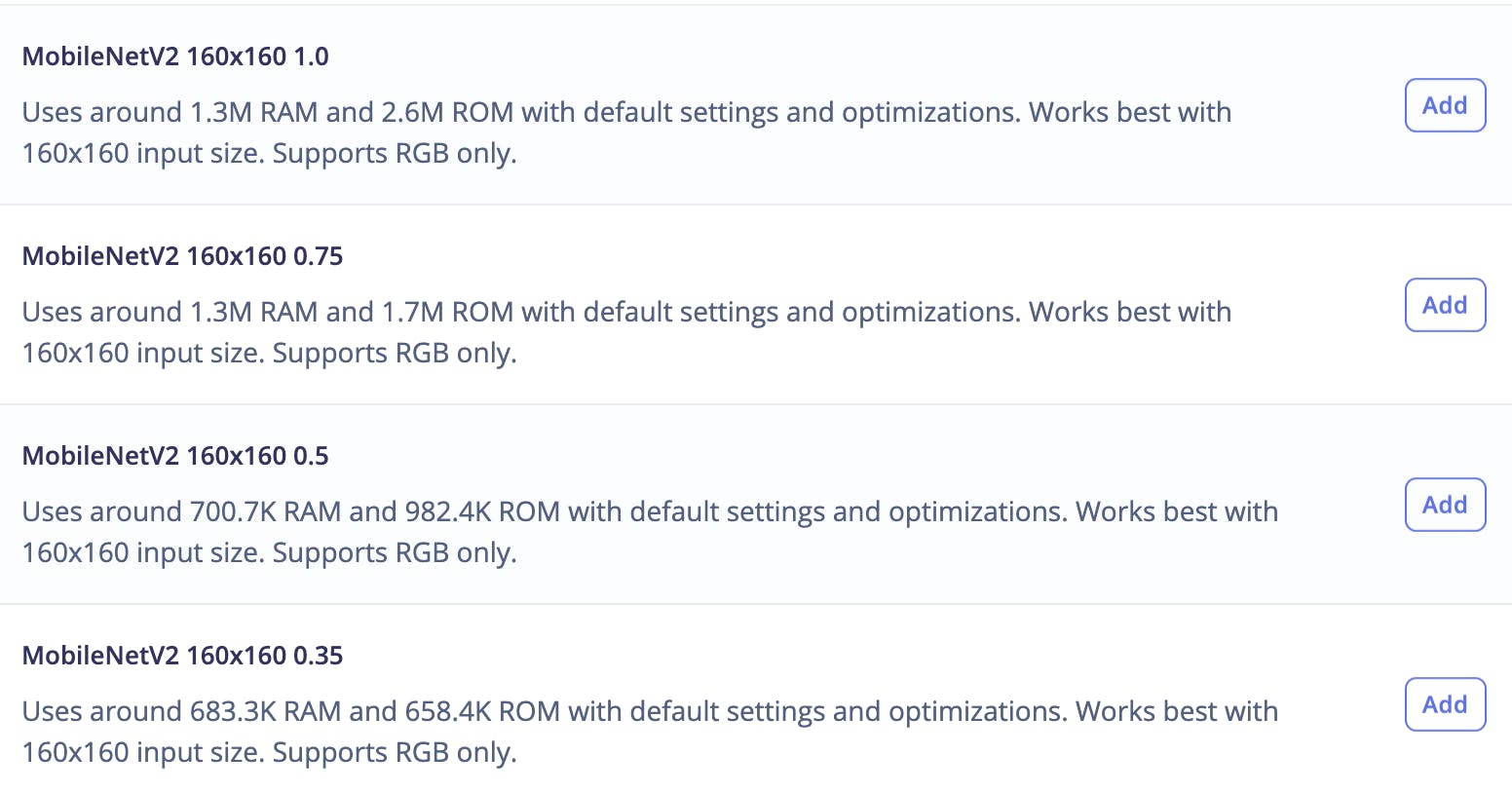
現在轉到Impulse Design > Transfer Learning頁面并選擇神經網絡架構。我們使用MobileNetV2 160x160 1.0遷移學習模型和 Edge Impulse Studio 提供的預訓練權重。
預訓練模型輸出類預測概率。要獲得類激活圖,我們需要修改模型并使其成為多輸出模型。要自定義模型,我們需要切換到Keras(專家)模式。
我們可以在文本編輯器中修改生成的代碼,如下所示。

我們將使用 3 個神經元(在我們的例子中為 3 個類)將作為 GAP 層的最后第二層連接到 Dense 層。稍后我們將使用這個 Dense 層權重來生成類激活圖。
base_model = tf.keras.applications.MobileNetV2(
input_shape = INPUT_SHAPE, alpha=1,
weights = WEIGHTS_PATH
)
last_layer = base_model.layers[-2].output
dense_layer = Dense(classes)
output_pred = Softmax(name="prediction")(dense_layer(last_layer))
對于類激活圖,我們需要計算最后一個卷積塊輸出和最終密集層權重的點積。Keras Dot 層不廣播具有動態批量大小的乘數向量,因此我們不能使用它。但是我們可以利用Dense 層,它在內部將內核權重與輸入進行點積。這種方法有一個副作用,密集層將偏置權重添加到每個點積。但是這個偏差權重非常小,不會改變類激活圖的最終歸一化值,所以我們可以毫無問題地使用它。
conv_layer = base_model.layers[-4].output
reshape_layer = Reshape((conv_layer.shape[1] * conv_layer.shape[2] , -1))(conv_layer)
dot_output = dense_layer(reshape_layer)
我們需要將點積輸出重新采樣到與輸入圖像(160x160)相同的大小,以便我們可以覆蓋熱圖。為此,我們使用UpSampling2D 層。
transpose = Permute((2, 1))(dot_output)
reshape_2_layer = Reshape((-1, conv_layer.shape[1] , conv_layer.shape[2]))(transpose)
SIZE = (int(INPUT_SHAPE[1] / conv_layer.shape[2]),
int(INPUT_SHAPE[0] / conv_layer.shape[1]))
output_act_map = UpSampling2D(size=SIZE, interpolation="bilinear", data_format="channels_first", name="activation_map")(reshape_2_layer)
model = Model(inputs=base_model.inputs, outputs=[output_pred, output_act_map])
此外,我們將從最后兩個卷積塊訓練模型,并在此之前凍結所有層。
TRAINABLE_START_IDX = -12
for layer in model.layers[:TRAINABLE_START_IDX]:
layer.trainable = False
下面給出了最后一個卷積塊之后的修改網絡架構。這是一個多輸出模型,其中第一個輸出提供預測類概率,第二個輸出提供類激活圖。
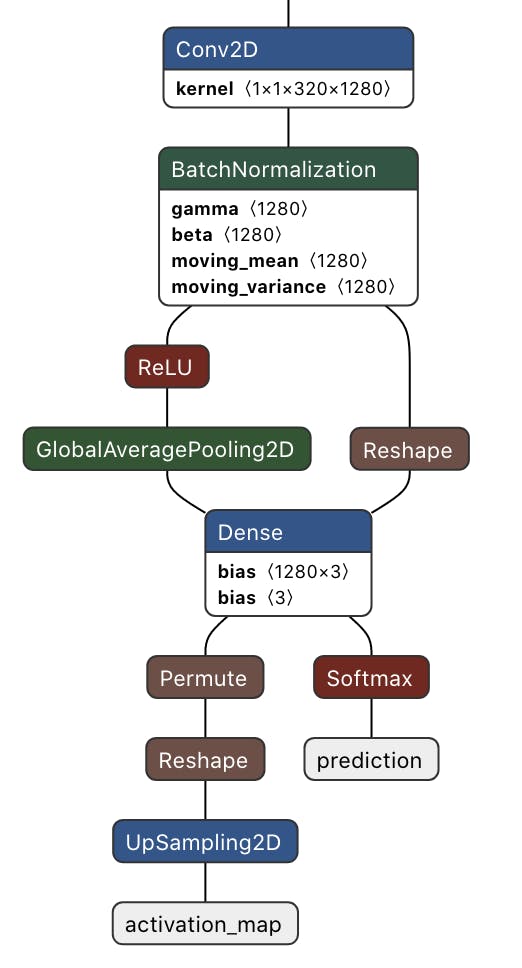
完整修改后的訓練代碼如下。
import math
from pathlib import Path
import tensorflow as tf
from tensorflow.keras import Model
from tensorflow.keras.layers import Dense, UpSampling2D, Permute, Reshape, Softmax
from tensorflow.keras.optimizers import Adam
from tensorflow.keras.losses import categorical_crossentropy
sys.path.append('./resources/libraries')
import ei_tensorflow.training
WEIGHTS_PATH = './transfer-learning-weights/keras/mobilenet_v2_weights_tf_dim_ordering_tf_kernels_1.0_160.h5'
INPUT_SHAPE = (160, 160, 3)
base_model = tf.keras.applications.MobileNetV2(
input_shape = INPUT_SHAPE, alpha=1,
weights = WEIGHTS_PATH
)
last_layer = base_model.layers[-2].output
dense_layer = Dense(classes)
output_pred = Softmax(name="prediction")(dense_layer(last_layer))
conv_layer = base_model.layers[-4].output
reshape_layer = Reshape((conv_layer.shape[1] * conv_layer.shape[2] , -1))(conv_layer)
dot_output = dense_layer(reshape_layer)
transpose = Permute((2, 1))(dot_output)
reshape_2_layer = Reshape((-1, conv_layer.shape[1] , conv_layer.shape[2]))(transpose)
SIZE = (int(INPUT_SHAPE[1] / conv_layer.shape[2]),
int(INPUT_SHAPE[0] / conv_layer.shape[1]))
output_act_map = UpSampling2D(size=SIZE, interpolation="bilinear", data_format="channels_first", name="activation_map")(reshape_2_layer)
model = Model(inputs=base_model.inputs, outputs=[output_pred, output_act_map])
TRAINABLE_START_IDX = -12
for layer in model.layers[:TRAINABLE_START_IDX]:
layer.trainable = False
model.compile(optimizer=tf.keras.optimizers.Adam(learning_rate=0.0005),
loss={'prediction': 'categorical_crossentropy', 'activation_map': None},
metrics={'prediction': ['accuracy'], 'activation_map': [None]})
BATCH_SIZE = 32
EPOCHS=5
train_dataset = train_dataset.batch(BATCH_SIZE, drop_remainder=False)
validation_dataset = validation_dataset.batch(BATCH_SIZE, drop_remainder=False)
callbacks.append(BatchLoggerCallback(BATCH_SIZE, train_sample_count, epochs=EPOCHS))
model.fit(train_dataset, validation_data=validation_dataset, epochs=EPOCHS, verbose=2, callbacks=callbacks)
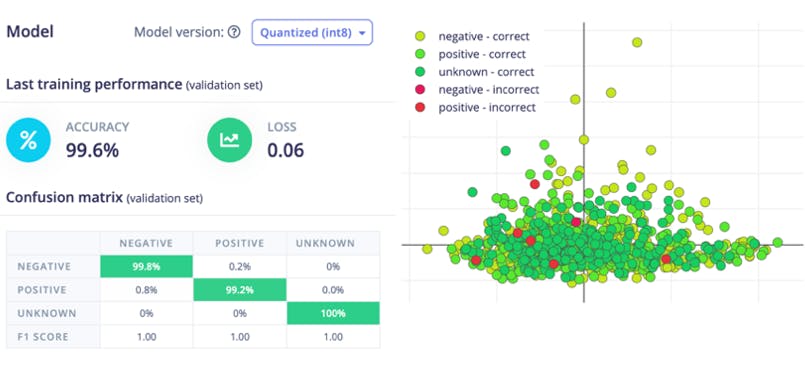
現在單擊“開始訓練”按鈕并等待大約 30 分鐘,直到訓練完成。我們可以在下面看到訓練輸出。量化的(int8)模型有 99.6% 的準確率,相當不錯。
模型部署
目前,Edge Impulse for Linux SDK 不支持多輸出模型,因此我們將使用編譯后的 TensorFlow Lite 運行時進行推理。這個僅解釋器的包是完整 TensorFlow 包大小的一小部分,并且包含使用 TensorFlow Lite 運行推理所需的最少代碼。為了加速推理,TFLite 解釋器可以與 XNNPACK 一起使用,XNNPACK是針對 ARM 和其他平臺的高度優化的神經網絡推理算子庫。要為 64 位 Raspberry Pi OS啟用XNNPACK ,我們需要從源代碼構建 TFLite Runtime Python 包。我們需要在速度更快的 Debian/Ubuntu Linux 機器上使用 Docker 執行以下命令來交叉編譯和構建包。
$ git clone -b v2.9.0 https://github.com/tensorflow/tensorflow.git
cd tensorflow/
$ curl -L -o tensorflow/tools/ci_build/Dockerfile.pi-python37 https://github.com/tensorflow/tensorflow/raw/v2.8.0/tensorflow/tools/ci_build/Dockerfile.pi-python37
$ sed -i -e 's/FROM ubuntu:16.04/FROM ubuntu:18.04/g' tensorflow/tools/ci_build/Dockerfile.pi-python37
$ sed -i '30a apt-get update && apt-get install -y dirmngr' tensorflow/tools/ci_build/install/install_deb_packages.sh
$ sed -i -e 's/xenial/bionic/g' tensorflow/tools/ci_build/install/install_pi_python3x_toolchain.sh
要為浮點 (F32) 和量化 (INT8) 模型啟用XNNPACK ,請將以下行(以粗體顯示)添加到 tensorflow/lite/tools/pip_package/build_pip_package_with_bazel.sh 文件中。
aarch64)
BAZEL_FLAGS="--config=elinux_aarch64
--define tensorflow_mkldnn_contraction_kernel=0
--define=tflite_with_xnnpack=true
--define=tflite_with_xnnpack_qs8=true
--copt=-O3"
;;
執行以下命令構建 pip 包。
$ sudo CI_DOCKER_EXTRA_PARAMS="-e CI_BUILD_PYTHON=python3.7 -e CROSSTOOL_PYTHON_INCLUDE_PATH=/usr/include/python3.7" tensorflow/tools/ci_build/ci_build.sh PI-PYTHON37 tensorflow/lite/tools/pip_package/build_pip_package_with_bazel.sh aarch64
將 pip 包復制到 reTerminal。
$ scp tensorflow/lite/tools/pip_package/gen/tflite_pip/python3.7/dist/tflite_runtime-2.9.0-cp37-cp37m-linux_aarch64.whl pi@raspberrypi.local:/home/pi
要安裝軟件包,請執行以下命令。
$ pip3 install -U tflite_runtime-2.9.0-cp37-cp37m-linux_aarch64.whl
現在我們可以從 Edge Impulse Studio Dashboard 下載量化模型。
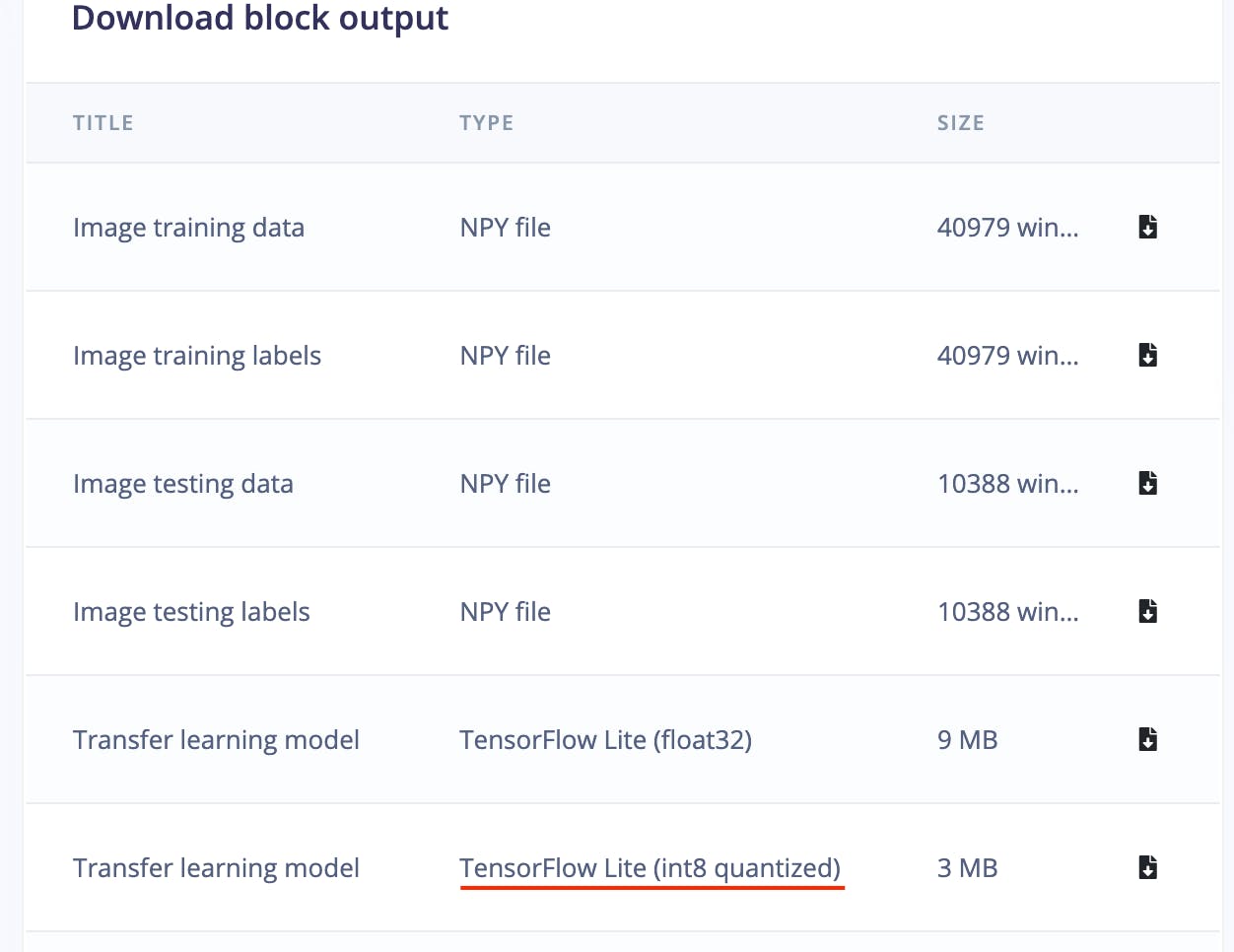
下面是用于推理的完整 Python 腳本。
#!/usr/bin/python3
import sys
import signal
import time
import cv2
import numpy as np
import traceback
import threading
import logging
import queue
import collections
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from matplotlib import cm
from tflite_runtime.interpreter import Interpreter
def avg_fps_counter(window_size):
window = collections.deque(maxlen=window_size)
prev = time.monotonic()
yield 0.0 # First fps value.
while True:
curr = time.monotonic()
window.append(curr - prev)
prev = curr
yield len(window) / sum(window)
def sigint_handler(sig, frame):
logging.info('Interrupted')
sys.exit(0)
signal.signal(signal.SIGINT, sigint_handler)
def capture(queueIn):
global terminate
global zoom
videoCapture = cv2.VideoCapture(0)
if not videoCapture.isOpened():
logging.error("Cannot open camera")
sys.exit(-1)
while True:
if terminate:
logging.info("Capture terminate")
break
prev = time.time()
try:
success, frame = videoCapture.read()
if success:
frame = cv2.rotate(frame, cv2.ROTATE_90_CLOCKWISE)
img = cv2.cvtColor(frame, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB)
if zoom:
w, h = 320, 320
x = (img.shape[1] - w) / 2
y = (img.shape[0] - h)/ 2
img = img[int(y):int(y+h), int(x):int(x+w)]
img = cv2.resize(img, (width, height))
img = img / 255.0
img = img.astype(np.float32)
img_scaled = (img / input_scale) + input_zero_point
input_data = np.expand_dims(img_scaled, axis=0).astype(input_details[0]["dtype"])
if not queueIn.full():
queueIn.put((img, input_data))
logging.info('Image Captured')
else:
raise RuntimeError('Failed to get frame!')
except Exception as inst:
logging.error("Exception", inst)
logging.error(traceback.format_exc())
videoCapture.release()
break
def inferencing(interpreter, queueIn, queueOut):
global terminate
global show_heatmap
while True:
if terminate:
logging.info("Inferencing terminate")
break
start_time = time.time()
try:
if queueIn.empty():
time.sleep(0.01)
continue
img, input_data = queueIn.get()
interpreter.set_tensor(input_details[0]['index'], input_data)
interpreter.invoke()
output_0_tensor = interpreter.tensor(output_details[0]['index'])
output_1_tensor = interpreter.tensor(output_details[1]['index'])
output_1 = output_1_scale * ((output_1_tensor()).astype(np.float32) - output_1_zero_point)
pred_class = np.argmax(np.squeeze(output_1))
pred_score = np.squeeze(output_1)[pred_class]
dp_out = None
if pred_class == 1 and show_heatmap is True :
dp_out = output_0_scale * (np.squeeze(output_0_tensor())[pred_class].astype(np.float32) - output_0_zero_point)
if not queueOut.full():
queueOut.put((img, pred_class, pred_score, dp_out))
except Exception as inst:
logging.error("Exception", inst)
logging.error(traceback.format_exc())
break
logging.info('Inferencing time: {:.3f}ms'.format((time.time() - start_time) * 1000))
def display(queueOut):
global show_heatmap
global zoom
global terminate
dimension = (960, 720)
ei_logo = cv2.imread('/home/pi/surface_crack_detection/ei_logo.jpg')
ei_logo = cv2.cvtColor(ei_logo, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB)
ei_logo = ei_logo / 255.0
ei_logo = ei_logo.astype(np.float32)
ei_logo = cv2.copyMakeBorder(ei_logo, 0, dimension[1] - ei_logo.shape[0], 70, 70, cv2.BORDER_CONSTANT, None, (255, 255, 255))
ei_logo = cv2.copyMakeBorder(ei_logo, 0, dimension[1] - ei_logo.shape[0], 70, 70, cv2.BORDER_CONSTANT, None, (255, 255, 255))
fps_counter = avg_fps_counter(30)
while True:
if queueOut.empty():
time.sleep(0.2)
continue
start_time = time.time()
img, pred_class, pred_score, dp_out = queueOut.get()
if pred_class == 1:
label = 'Crack'
color = (0, 0, 255)
if show_heatmap and dp_out is not None:
heatmap = None
heatmap = cv2.normalize(dp_out, heatmap, alpha=0, beta=255, norm_type=cv2.NORM_MINMAX, dtype=cv2.CV_8U)
colormap = plt.get_cmap('jet')
img = cv2.addWeighted(img, 1.0, colormap(heatmap).astype(np.float32)[:,:,:3], 0.4, 0)
else:
if pred_class == 0:
label = 'No Crack'
color = (0, 0, 0)
else:
label = 'Unknown'
color = (255, 0, 0)
final_img = cv2.resize(img, dimension, interpolation=cv2.INTER_CUBIC)
font = cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX
final_img = np.hstack((final_img, ei_logo))
final_img = cv2.cvtColor(final_img, cv2.COLOR_RGB2BGR)
final_img = cv2.putText(final_img, label, (980, 200), font, 2, color, 3, cv2.LINE_AA)
final_img = cv2.putText(final_img, f'({pred_score*100:0.1f}%)', (980, 280), font, 2, (0, 0, 0), 3, cv2.LINE_AA)
fps = round(next(fps_counter))
final_img = cv2.putText(final_img, f'Fps:{fps}', (980, 360), font, 2, (0, 0, 0), 3, cv2.LINE_AA)
final_img = cv2.putText(final_img, f'Heat:{"On" if show_heatmap else "Off"}', (980, 440), font, 2, (0, 0, 0), 3, cv2.LINE_AA)
final_img = cv2.putText(final_img, f'Crop:{"On" if zoom else "Off"}', (980, 520), font, 2, (0, 0, 0), 3, cv2.LINE_AA)
window_name = "Edge Impulse Inferencing"
cv2.imshow(window_name, final_img)
key = cv2.waitKey(1)
if key == ord('a'):
show_heatmap = not show_heatmap
logging.info(f"Heatmap: {show_heatmap}")
if key == ord('s'):
zoom = not zoom
logging.info(f"Zoom: {zoom}")
if key == ord('f'):
terminate = True
logging.info("Display Terminate")
break
logging.info('Display time: {:.3f}ms'.format((time.time() - start_time) * 1000))
if __name__ == '__main__':
log_fmt = "%(asctime)s: %(message)s"
logging.basicConfig(format=log_fmt, level=logging.ERROR,)
model_file = '/home/pi/surface_crack_detection/model/quantized-model.lite'
interpreter = Interpreter(model_path=model_file, num_threads=2)
interpreter.allocate_tensors()
input_details = interpreter.get_input_details()
#logging.debug(input_details)
output_details = interpreter.get_output_details()
height = input_details[0]['shape'][1]
width = input_details[0]['shape'][2]
input_scale, input_zero_point = input_details[0]['quantization']
output_0_scale, output_0_zero_point = output_details[0]['quantization']
output_1_scale, output_1_zero_point = output_details[1]['quantization']
queueIn = queue.Queue(maxsize=1)
queueOut = queue.Queue(maxsize=1)
show_heatmap = False
zoom = False
terminate = False
t1 = threading.Thread(target=capture, args=(queueIn,), daemon=True)
t2 = threading.Thread(target=inferencing, args=(interpreter, queueIn, queueOut), daemon=True)
t3 = threading.Thread(target=display, args=(queueOut,), daemon=True)
t1.start()
logging.info("Thread start: 1")
t2.start()
logging.info("Thread start: 2")
t3.start()
logging.info("Thread start: 3")
t1.join()
t2.join()
t3.join()
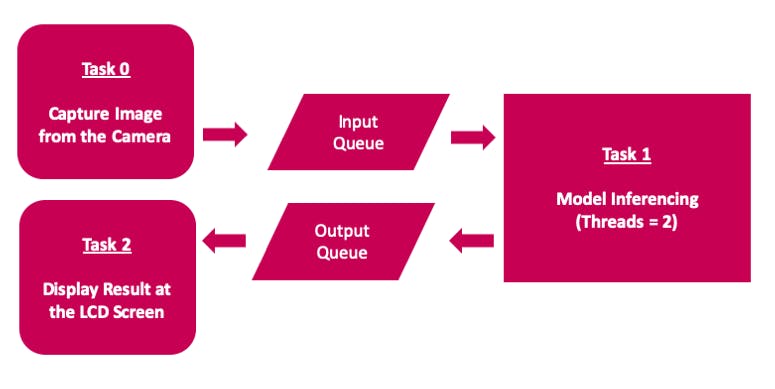
申請工作流程圖
該應用程序使用多線程來使用 Raspberry Pi 4 計算模塊上的所有可用 4 核,以實現低延遲和更好的 FPS。
桌面應用程序
通過單擊桌面應用程序圖標來執行推理腳本,該圖標是通過在 /home/pi/Desktop 目錄中添加 ei.desktop 文件而創建的。
[Desktop Entry]
Version=1.0
Comment=Run Inferencing Quantized Model
Terminal=false
Name=Surface Crack Detection
Exec=/home/pi/surface_crack_detection/surface_crack_detection_quant.py
Type=Application
Icon=/home/pi/surface_crack_detection/images/ei_logo.jpg

此外,reTerminal 前面板按鈕(在上圖中)用于以下功能。
- F1按鈕:切換熱圖
- F2按鈕:切換中心裁剪(放大)預覽圖像
- O按鈕:關閉應用程序
推理演示
結論
該項目展示了可用于預測性維護的表面裂紋檢測工業用例。該項目具有以下主要特點。
- 在 Edge Impulse Studio 專家模式下自定義預訓練的遷移學習模型
- 演示如何使用使用 Edge Impulse 訓練的多輸出模型
- 運行時熱圖可視化以定位檢測到的裂縫。
- 多線程應用程序以提高 FPS
- 可擴展的便攜式解決方案
盡管該項目是使用 Raspberry Pi 4 計算模塊創建的,但它可以輕松移植到更高規格的邊緣設備,以提高 FPS 和實時檢測。
- Seeed Grove傳感器閃電檢測
- 教你如何快速修復壓縮機裂紋 6次下載
- 基于深度學習的道路表面裂縫檢測技術 73次下載
- 基于Harris-SUSAN的發動機葉片裂紋檢測系統 16次下載
- 如何使用機器視覺實現發動機表面缺陷檢測的技術 12次下載
- 表面處理對A7N01鋁合金MIG焊接頭疲勞裂紋擴展速率的影響 0次下載
- 基于鋼軌裂紋檢測對比 0次下載
- 機械裂紋無損檢測方法 5次下載
- 基于超聲波的和田玉裂紋檢測儀 6次下載
- 基于機器視覺的密封件表面缺陷檢測研究 27次下載
- 超聲衍射回波渡越時間方法焊縫裂紋原位定量無損估計
- 電力機車主極裂紋渦流檢測系統的研制
- 基于數字圖像處理的表面裂紋檢測算法
- 牽引電機主極裂紋渦流檢測原理與設計
- 基于LabVIEW的鋼桿裂紋定量識別技術的研究
- 工業產品表面缺陷檢測方法研究 863次閱讀
- 機器視覺檢測與機器視覺定位的區別與應用 914次閱讀
- 基于改進FCOS的鋼帶表面缺陷檢測算法 1394次閱讀
- 基于S3C2440A控制芯片實現鋼鐵材料裂紋質量檢測系統的設計 2874次閱讀
- 一文解析什么是表面缺陷檢測系統 2972次閱讀
- 淬火裂紋和非淬火裂紋的區別_如何區分 6051次閱讀
- 淬火裂紋的分類_淬火裂紋的特征 9874次閱讀
- 延遲裂紋產生的原因_延遲裂紋的解決辦法 2.1w次閱讀
- 焊接熱裂紋的種類及特征 8445次閱讀
- 焊接縱向裂紋產生的原因及解決辦法 2.3w次閱讀
- 焊接冷裂紋和熱裂紋的區別 3w次閱讀
- 焊接結晶裂紋的形成機理_防止焊接結晶裂紋的措施 1.2w次閱讀
- smt回流焊點裂紋產生原因_smt回流焊點裂紋防止措施 3355次閱讀
- 氬弧焊有裂紋怎么辦 1.7w次閱讀
- 采用機器視覺的方法來檢測表面質量 4397次閱讀
下載排行
本周
- 1美的電磁爐維修手冊大全
- 1.56 MB | 5次下載 | 5 積分
- 2SMD LED選型手冊 貼片燈珠
- 5.47 MB | 3次下載 | 免費
- 3基于PLC的拉絲機張力控制系統研究
- 0.14 MB | 2次下載 | 5 積分
- 4加密芯片的一種破解方法和對應加密方案改進設計
- 0.29 MB | 1次下載 | 免費
- 5萬用表UT58A原理圖
- 0.09 MB | 1次下載 | 5 積分
- 6多功能MPU芯片GC9005數據手冊
- 2.67 MB | 1次下載 | 免費
- 7面向NXP i.MX8處理器的電源解決方案
- 47.47KB | 次下載 | 免費
- 8LP8733-Q1和LP8732-Q1為DRA78x和TDA3x供電的用戶指南
- 61.31KB | 次下載 | 免費
本月
- 1使用單片機實現七人表決器的程序和仿真資料免費下載
- 2.96 MB | 44次下載 | 免費
- 2UC3842/3/4/5電源管理芯片中文手冊
- 1.75 MB | 20次下載 | 免費
- 3華瑞昇CR216芯片數字萬用表規格書附原理圖及校正流程方法
- 0.74 MB | 14次下載 | 3 積分
- 4DMT0660數字萬用表產品說明書
- 0.70 MB | 13次下載 | 免費
- 53314A函數發生器維修手冊
- 16.30 MB | 13次下載 | 免費
- 6TPS54202H降壓轉換器評估模塊用戶指南
- 1.02MB | 9次下載 | 免費
- 7STM32F101x8/STM32F101xB手冊
- 1.69 MB | 8次下載 | 1 積分
- 8感應筆電路圖
- 0.06 MB | 7次下載 | 免費
總榜
- 1matlab軟件下載入口
- 未知 | 935119次下載 | 10 積分
- 2開源硬件-PMP21529.1-4 開關降壓/升壓雙向直流/直流轉換器 PCB layout 設計
- 1.48MB | 420062次下載 | 10 積分
- 3Altium DXP2002下載入口
- 未知 | 233084次下載 | 10 積分
- 4電路仿真軟件multisim 10.0免費下載
- 340992 | 191367次下載 | 10 積分
- 5十天學會AVR單片機與C語言視頻教程 下載
- 158M | 183335次下載 | 10 積分
- 6labview8.5下載
- 未知 | 81581次下載 | 10 積分
- 7Keil工具MDK-Arm免費下載
- 0.02 MB | 73807次下載 | 10 積分
- 8LabVIEW 8.6下載
- 未知 | 65987次下載 | 10 積分
 電子發燒友App
電子發燒友App

















 創作
創作 發文章
發文章 發帖
發帖  提問
提問  發資料
發資料 發視頻
發視頻 上傳資料賺積分
上傳資料賺積分









評論