摘要:本應用筆記介紹Maxim的TDM-over-Packet (TDMoP)設備與其它廠家TDMoP設備共同工作時的一些要求。這篇應用筆記涵蓋的Maxim TDMoP芯片包括:DS34T101,DS34T102,DS34T104,DS34T108,DS34S101,DS34S102,DS34S104和DS34S108。
本應用筆記介紹Maxim的TDM-over-Packet (TDMoP)設備與其它廠家TDMoP設備共同工作時的一些要求。這篇應用筆記涵蓋的Maxim TDMoP芯片包括:DS34T101,DS34T102,DS34T104,DS34T108,DS34S101,DS34S102,DS34S104和DS34S108。
Maxim的TDMoP設備產生的報文數據也許和其它廠家的TDMoP設備產生的報文數據采用不同的報文頭信息。為了實現Maxim設備的互操作性,用戶需要知道設置類型。設置類型可以是下列選項中的一種:
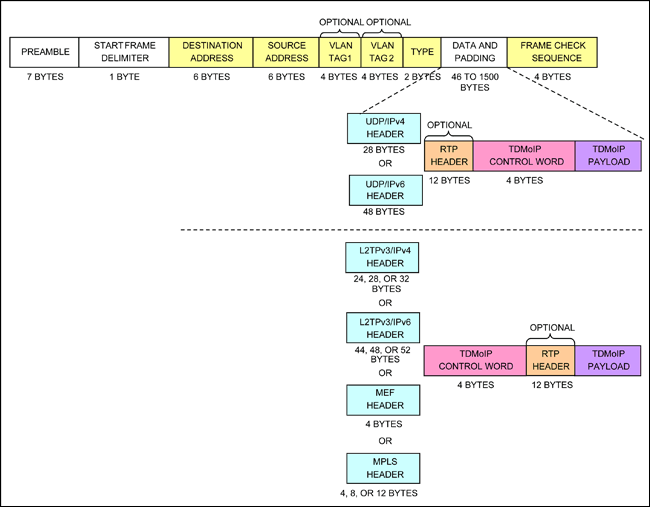
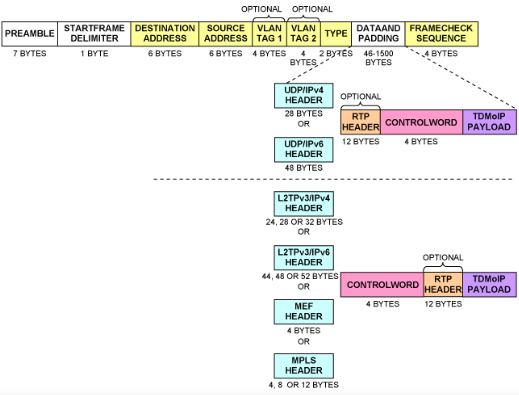
圖1. TDM-over-Packet封裝進入以太報文
表1. 以太報文結構
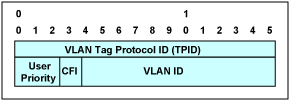
圖2. 單一的VLAN標記
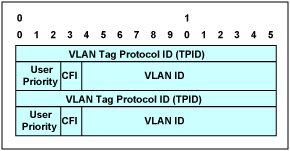
圖3. 嵌套的VLAN標記
VLAN標記的協議ID (TPID)用來識別VLAN標記,它可以是0x8100或者是vlan_2nd_tag_identifier配置寄存器中的數值。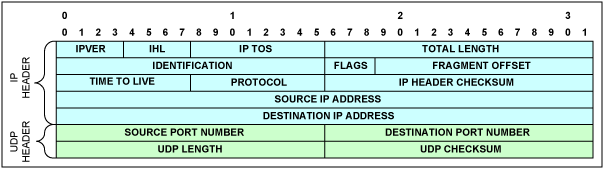
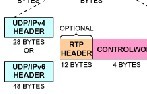
圖4. UDP/IPv4報頭
表2. IPv4報頭結構
表3. UDP報頭結構
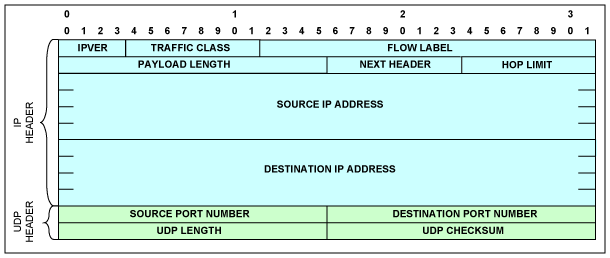
圖5. UDP/IPv6報頭
表4. UDP報頭結構
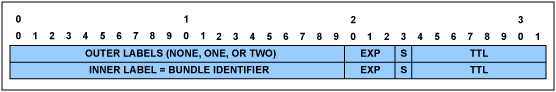
圖6. MPLS報頭
表5. MPLS報頭結構
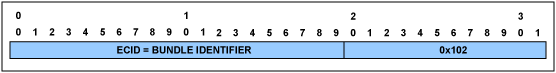
圖7. MEF報頭
表6. MEF報頭結構
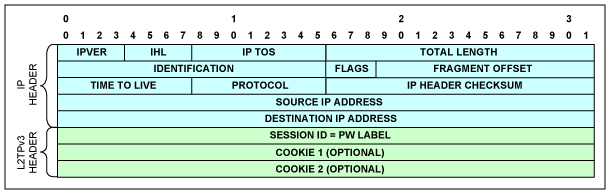
圖8. L2TPv3/IPv4報頭
表7. L2TPv3/IPv4報頭結構
表8. L2TPv3報頭結構
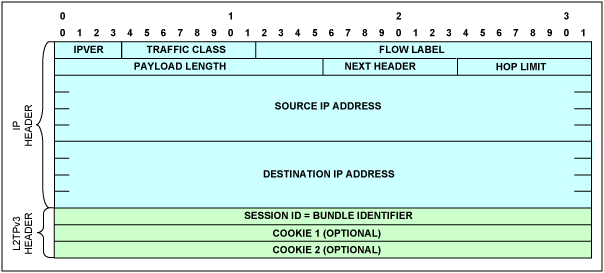
圖9. L2TPv3/IPv6報頭
表9. L2TPv3/IPv6報頭結構
L2TPv3報頭結構見表8。
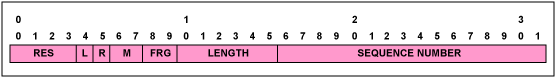
圖10. 控制字
表10. 控制字結構
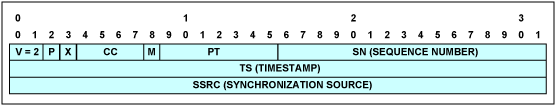
圖11. RTP報頭
表11. RTP報頭結構
為了確認用戶正確的發送了帶有正確協議的報文,用戶需要保證兩塊來自其它廠家的TDMoP系統板間相互同步。完成此步后,用戶需要利用Wireshark程序來捕捉報文。圖12所示為這個程序的截屏圖。
更詳細的圖片(PDF)
圖12. 用來分析以太報文頭的Wireshark程序截屏圖
為了使系統間能夠互通,必須考慮下面的要求:
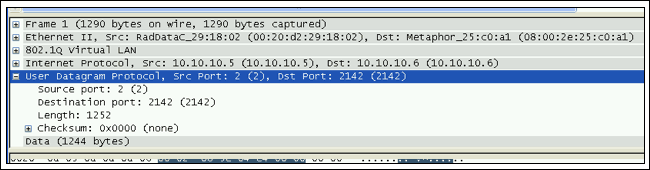
圖13. UDP源和目的端口號
有些廠家插入0x85E作為UDP的源端口號和UDP的目的端口號。在這種情況下,用戶必須通過preconfiguration菜單來配置系統,Maxim軟件的默認值如下所示:
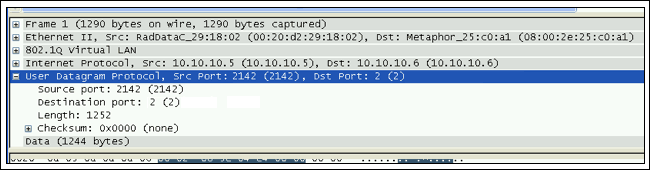
圖14. UDP源和目的端口號與圖13中相反
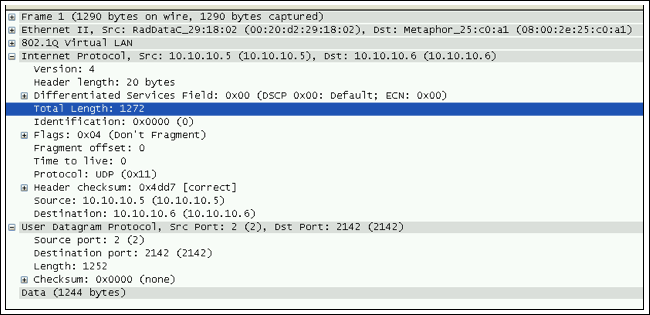
圖15. 捕獲的報文具有不同的報文長度信息
圖15所示為具有不同報文長度信息的報文內容,編號為1。
用戶必須考慮下面的長度:
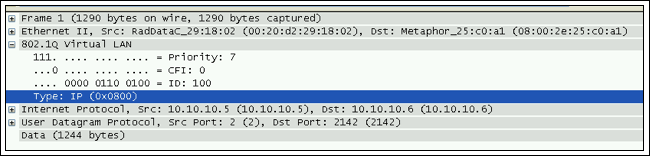
圖16. 以太類型值為0x800,代表著它是IPv4
一旦確定了以太類型,用戶必須將Maxim的TDMoP設備配置成為可以生成同樣的以太類型。每個以太類型可以在Bundle Configuration菜單中通過改變PSN類型進行選擇。Bundle Configuration菜單的部分如下圖所示。
如果您對TDMoP產品或者Maxim的電信產品在使用中有進一步的問題,請通過電子郵件 telecom.support@maxim-ic.com (English only)或電話972-371-6555 (美國)與電信產品應用支持小組聯系
互操作性的要求
互操作性是一個系統與其它廠家的系統共同工作時無需或者只需很少的系統管理員干預的能力。系統具有互操作性就可以提供服務給其它系統或者接受來自其它系統的服務,使得不同廠家的系統可以共同正常工作。本應用筆記介紹Maxim的TDM-over-Packet (TDMoP)設備與其它廠家TDMoP設備共同工作時的一些要求。這篇應用筆記涵蓋的Maxim TDMoP芯片包括:DS34T101,DS34T102,DS34T104,DS34T108,DS34S101,DS34S102,DS34S104和DS34S108。
Maxim的TDMoP設備產生的報文數據也許和其它廠家的TDMoP設備產生的報文數據采用不同的報文頭信息。為了實現Maxim設備的互操作性,用戶需要知道設置類型。設置類型可以是下列選項中的一種:
- IP/UDP/RTP/SAToP
- IP/UDP/RTP/CESoPSN
- MEF/CESoETH-非結構化(比如MEF/SAToP)
- MEF/CESoETH-結構化鎖定(比如MEF/CESoPSN)
TDM-over-Packet (TDMoP)
這一部分將定義TDM-over-Packet模塊的功能描述。TDMoP報文格式
在包交換的網絡上傳輸TDM數據,TDMoP芯片需要將TDM數據如圖1描述的那樣封裝為以太報文。
圖1. TDM-over-Packet封裝進入以太報文
表1. 以太報文結構
| Field | Description |
| Preamble | A sequence of 56 bits (alternating 1 and 0 values) used for synchronization; gives components in the network time to detect the presence of a signal. |
| Start Frame Delimiter | A sequence of 8 bits (10101011) that indicates the start of the packet. |
| Destination and Source Addresses | The Destination Address field identifies the station or stations that are to receive the packet. The Source Address identifies the station that originated the packet. A Destination Address may specify either an individual address destined for a single station, or a multicast address destined for a group of stations. A Destination Address of all 1 bits refers to all stations on the LAN and is called a broadcast address. |
| Type | Ether type |
| Data and Padding | This field contains the data transferred from the source station to the destination station or stations. The maximum size of this field is 1500 bytes. If the size of this field is less than 46 bytes, then padding is used to bring the packet size up to the minimum length. A minimum Ethernet packet size is 64 bytes from the Destination Address field through the Frame Check Sequence. |
| Frame Check Sequence | This field contains a 4-byte cyclical redundancy check (CRC) value used for error checking. When a source station assembles a packet, it performs a CRC calculation on all the bits in the packet from the Destination Address through the Pad fields (that is, all fields except the Preamble, Start Frame Delimiter, and Frame Check Sequence). The source station stores the value in this field and transmits it as part of the packet. When the destination station receives the packet, it performs an identical check. If the calculated value does not match the value in this field, the destination station assumes an error has occurred during transmission and discards the packet. |
VLAN標記
如同IEEE? 802.1q標準規定的一樣,由12位的VLAN標識符標記的報文可以最多構建4096個不同的VLAN。對于那些由于這個限制而數量不夠的應用,VLAN嵌套實現了兩層的VLAN標記結構,它將VLAN的ID空間擴展到1600萬個VLAN。每一個報文在發送時可以沒有VLAN標記,具有一個VLAN標記或者具有兩個VLAN標記(VLAN嵌套)。圖2和圖3所示分別為一個VLAN標記和嵌套的VLAN標記。
圖2. 單一的VLAN標記

圖3. 嵌套的VLAN標記
VLAN標記的協議ID (TPID)用來識別VLAN標記,它可以是0x8100或者是vlan_2nd_tag_identifier配置寄存器中的數值。
- 用戶優先級字段用來給以太報文指定一個優先級的級別
- CFI (規范格式指示符)字段表明有路由信息字段
- VLAN ID字段唯一識別以太報文屬于哪個VLAN
- 圖4所示為UDP/IPv4的報頭結構
- 圖5所示為UDP/IPv6的報頭結構
- 圖6所示為MPLS的報頭結構
- 圖7所示為MEF的報頭結構
- 圖8所示為L2TPv3/IPv4的報頭結構
- 圖9所示為L2TPv3/IPv6的報頭結構
- 圖10所示為Control Word的報頭結構
- 圖11所示為RTP的報頭結構
- 表2描述了IPv4報頭結構的不同字段
- 表3描述了UDP報頭結構的不同字段
- 表4描述了IPv6報頭結構的不同字段
- 表5描述了MPLS報頭結構的不同字段
- 表6描述了MEF報頭結構的不同字段
- 表7描述了L2TPv3/IPv4報頭結構的不同字段
- 表8描述了L2TPv3報頭結構的不同字段
- 表9描述了L2TPv3/IPv6報頭結構的不同字段
- 表10描述了控制字報頭結構的不同字段
- 表11描述了RTP報頭結構的不同字段
UDP/IPv4報頭

圖4. UDP/IPv4報頭
表2. IPv4報頭結構
| Field | Description |
| IPVER | IP version number; for IPv4 IPVER = 4 |
| IHL | Length in 32-bit words of the IP header, IHL = 5 |
| IP TOS | IP type of service |
| Total Length | Length in octets of IP header and data |
| Identification | IP fragmentation identification |
| Flags | IP control flags; must be set to 010 to avoid fragmentation |
| Fragment Offset | Indicates where in the datagram the fragment belongs; not used for TDM-over-packet |
| Time to Live | IP Time-to-Live field; datagrams with zero in this field are to be discarded |
| Protocol | Must be set to 0x11 to signify UDP |
| IP Header Checksum | Checksum for the IP header |
| Source IP Address | IP address of the source |
| Destination IP Address | IP address of the destination |
表3. UDP報頭結構
| Field | Description |
| Source Port Number, Destination Port Number | Either the Source or the Destination Port Number holds the bundle identifier. The unused field can be set to 0x85E (2142), which is the user port number assigned to TDM-over-packet by the Internet Assigned Numbers Authority (IANA). For UDP/IP-specific OAM packets, the bundle identifier is all ones. |
| UDP Length | Length in octets of UDP header and data |
| UDP Checksum | Checksum of UDP/IP header and data; if not computed, it must be set to zero |
UDP/IPv6報頭

圖5. UDP/IPv6報頭
表4. UDP報頭結構
| Field | Description |
| IPVER | IP version number; for IPv6 IPVER = 6 |
| Traffic Class | An 8-bit field similar to the type-of-service (ToS) field in IPv4 |
| Flow Label | The 20-bit Flow Label field can be used to tag packets of a specific flow to differentiate the packets at the network layer. |
| Payload Length | Similar to the Total Length field in IPv4, this field indicates the total length of the IP header and data in octets. |
| Next Header | Similar to the Protocol field in IPv4, this field determines the type of information following the basic IPv6 header. It must be set to 0x11 to signify UDP. |
| Hop Limit | Similar to the Time-to-Live field in IPv4 |
| Source IP Address | Similar to the Source Address field in IPv4, except that this field contains a 128-bit source address for IPv6 instead of a 32-bit source address for IPv4. |
| Destination Address | Similar to the Destination Address field in IPv4, except that this field contains a 128-bit destination address for IPv6 instead of a 32-bit destination address for IPv4. |
MPLS報頭

圖6. MPLS報頭
表5. MPLS報頭結構
| Field | Description |
| Outer Labels | These MPLS labels identify the MPLS LSP used to tunnel the TDMoMPLS packets through the MPLS network. They are also known as tunnel labels or transport labels. The label number can be assigned either manually or via the MPLS control protocol. There can be zero, one, or two outer labels. |
| EXP | Experimental field |
| S | Stacking bit: 1 indicates stack bottom; S = 0 for all outer labels |
| TTL | MPLS time to live |
| Inner Label | The MPLS Inner Label (also known as the PW label or the interworking label) contains the bundle identifier used to multiplex multiple bundles within the same tunnel. It is always at the bottom of the MPLS label stack, and hence its stacking bit is set. |
MEF報頭

圖7. MEF報頭
表6. MEF報頭結構
| Field | Description |
| ECID | The Emulated Circuit Identifier (ECID) contains the bundle identifier. |
L2TPv3/IPv4報頭

圖8. L2TPv3/IPv4報頭
表7. L2TPv3/IPv4報頭結構
| Field | Description |
| IPVER | IP version number; e.g., for IPv4 IPVER = 4 |
| IHL | Length in 32-bit words of the IP header, IHL = 5 |
| IP TOS | IP type of service |
| Total Length | Length in octets of header and data |
| Identification | IP fragmentation identification |
| Flags | IP control flags; must be set to 010 to avoid fragmentation |
| Fragment Offset | Indicates where in the datagram the fragment belongs; not used for TDM-over-packet |
| Time to Live | IP Time-to-Live field; datagrams with zero in this field are to be discarded |
| Protocol | Must be set to 0x73 to signify L2TPv3 |
| IP Header Checksum | Checksum for the IP header |
| Source IP Address | IP address of the source |
| Destination IP Address | IP address of the destination |
表8. L2TPv3報頭結構
| Field | Description |
| Session ID (32 Bits) | Locally significant L2TP session identifier, also contains the bundle identifier; all bundle identifiers are available for use except 0, which is reserved |
| Cookie (32 or 64 Bits) | Optional field that contains a randomly selected value used to validate association of the packet with the expected bundle identifier |
L2TPv3/IPv6報頭

圖9. L2TPv3/IPv6報頭
表9. L2TPv3/IPv6報頭結構
| Field | Description |
| IPVER | See Table 4 |
| Traffic Class | |
| Flow Label | |
| Payload Length | |
| Next Header | Must be set to 0x73 to signify L2TPv3 |
| Hop Limit | See Table 4 |
| Source Address | |
| Destination Address |
L2TPv3報頭結構見表8。
控制字

圖10. 控制字
表10. 控制字結構
| Field | Description |
| RES | Reserved bits—must be set to zero |
| L | Local loss-of-sync (LOS) failure. This bit is set by the CPU. A set L bit indicates that the source has detected, or has been informed of, a TDM physical layer fault that impacts the data to be transmitted. This bit can be used to indicate physical layer LOS that should trigger AIS generation at the far end. Once set, if the TDM fault is rectified, the L bit must be cleared. |
| R | Remote receive failure. This bit is set by the CPU. A set R bit indicates that the source is not receiving packets at the Ethernet port (i.e., there is a failure in the direction of the bidirectional connection). This indication can be used to signal congestion or other network-related faults. A remote failure indication may trigger fallback mechanisms for congestion avoidance. The R bit must be set after a preconfigured number of consecutive packets are not received, and must be cleared once packets are received again. |
| M | Defect modifier failure. These bits are set by the CPU. This field is optional. When used, it supplements the L-bit meaning. |
| FRG | Fragmentation field. This field is used for fragmenting multiframe structures into multiple packets in case of CESoPSN structured with CAS bundles. The field is used as follows: 00 - Indicates that the entire (unfragmented) multiframe structure is carried in a single packet 01 - Indicates the packet carrying the first fragment 10 - Indicates the packet carrying the last fragment 11 - Indicates a packet carrying an intermediate fragment |
| Length | Includes control word, payload, and RTP header (if it exists), unless it is a UDP/IP packet. It is used when this sum is less than 64 bytes. Otherwise, set to zero. |
| Sequence Number | TDM-over-packet sequence number. This value is defined separately for each bundle and incremented by one for each TDMoP packet sent for that bundle. The initial value of the sequence number is random (unpredictable) for security purposes, and the value is incremented in wrap-around manner separately for each bundle. It is used by the receiver to detect packet loss and restore packet sequence. The HDLC payload type machine supports three different modes for this field: always zero, incremented in wrap-around manner, or incremented in wrap-around value, but skips zero value. For OAM packets (see TDM-over-packet payload), it uniquely identifies the message. Its value is unrelated to the sequence number of the TDMoP data packets for the bundle in question. It is incremented in query messages, and replicated without change in replies. |
RTP報頭

圖11. RTP報頭
表11. RTP報頭結構
| Field | Description |
| V | RTP version—must be set to 2 |
| P | Padding bit—must be set to 0 |
| X | Extension bit—must be set to 0 |
| CC | CSRC count—must be set to 0 |
| M | Marker bit—must be set to 0 |
| PT | Payload Type. One PT value MUST be allocated from the range of dynamic values for each direction of the bundle. The same PT value MAY be reused for both directions of the bundle, and also reused between different bundles. |
| SN | The sequence number, identical to the sequence number in the control word |
| TS | Timestamp. The RTP header can be used in conjunction with the following modes of timestamp generation: Absolute mode: the chip sets timestamps using the clock recovered from the incoming TDM circuit. As a consequence, the timestamps are closely correlated with the sequence numbers. The timestamp is incremented by one every 125μs. Differential (common-clock) mode: The two chips at bundle edges have access to the same high-quality clock source, and this clock source is used for timestamp generation. |
| SSRC | Identifies the synchronization source. This identifier should be chosen randomly, with the intent that no two synchronization sources within the same RTP session will have the same SSRC identifier. |
如何獲取其它廠家的TDMoP設備的報文內容
有一些軟件可以用來分析以太網的報文頭。本應用筆記使用Wireshark?軟件。用戶可以從www.wireshark.org/download.html下載這個免費軟件。關于Wireshark的更多信息,請看Wireshark常見問題(English only)。為了確認用戶正確的發送了帶有正確協議的報文,用戶需要保證兩塊來自其它廠家的TDMoP系統板間相互同步。完成此步后,用戶需要利用Wireshark程序來捕捉報文。圖12所示為這個程序的截屏圖。

更詳細的圖片(PDF)
圖12. 用來分析以太報文頭的Wireshark程序截屏圖
為了使系統間能夠互通,必須考慮下面的要求:
- 源端口號和目的端口號
- 報文字節,IP長度,UDP長度和數據字節的總長度
- 以太類型
源端口號和目的端口號
報文分類模塊利用TDMoP端口號來識別TDM-over-Packet的UDP/IP。TDMoIP_Port_Number可以配置為兩個不同的值。雖然Maxim的TDMoP設備有兩個TDMoIP_Port_Number寄存器,但是在很多情況下,兩個寄存器都應該配置為IANA為TDM-over-Packet分配的默認值(0x085E)。源端口號或者目的端口號中含有綁定標識號。未用字段可以設置為0x85E (十進制的2142),它是IANA為TDM-over-Packet分配的用戶端口號。如圖4所示,Maxim的設備首先插入源端口號,然后插入TDMoP目的端口號。圖13所示為用戶數據報協議(UDP)的內容,源端口號被設為2,TDMoP目的端口號被設為0x85E (十進制的2142)。
圖13. UDP源和目的端口號
有些廠家插入0x85E作為UDP的源端口號和UDP的目的端口號。在這種情況下,用戶必須通過preconfiguration菜單來配置系統,Maxim軟件的默認值如下所示:
PreConfig Configuration 1. Link Type E1 2. Bundle Number ID Location Port in DST, Bundle in SRC UDP Port 3. UDP Mask 1FFF 4. VCCV OAM Mask [0 - 4] 0 5. VCCV OAM Value 1FFF 6. MEF Ethernet Type 88D8 7. MEF OAM Type 0 8. TDMoIP Port Number 1 85E 9. Oscillator Type OCXO (Stratum 3E) 10. RTP Clock Source ABSOLUTE 11. Common clock Rate 19440000 12. IP Version IPv4 13. Clock Recovery Smart Statistics Enable 14. One or Two Clock Mode OneMaxim軟件菜單的第二項用來選取所需的Bundle Number ID Location。上面菜單的第二項提供以下可選項:
Bundle Number ID Location 1: Ignore port, Bundle in SRC UDP PORT, 2: Port in DST, Bundle in SRC UDP PORT 3: Port in SRC, Bundle in DST UDP PORT, 4: Ignore Port, Bundle in DST UDP PORT在上面的菜單中,Maxim設備的默認Bundle Number ID Location是選項2: “Port in DST, Bundle in SRC UDP PORT”。為了使得Maxim的設備能夠與其它廠家的設備互通,用戶需要適當地選取選項1、3或者4。比如,某TDMoP廠家的設備在Source (SRS)位置插入Destination端口,在Destination (DST)插入綁定端口號。如果用戶在上面的菜單中選取選項3,那么UDP源端口Bundle Number ID Location就被設置為0x85E (十進制的2142),UDP目的端口就會為2,如圖14所示。這樣就可以匹配那個廠家的TDMoP報文頭,因此,他們可以互操作。

圖14. UDP源和目的端口號與圖13中相反
報文字節,IP長度,UDP長度和數據字節的總長度

圖15. 捕獲的報文具有不同的報文長度信息
圖15所示為具有不同報文長度信息的報文內容,編號為1。
用戶必須考慮下面的長度:
A. 數據字節:圖15所示報文1共有1244個字節。在綁定配置中,我們采用IP/UDP/CESoPSN協議。發送的E1 TDM數據使用31個時隙,每個時隙有40個幀字節,那么總的TDM數據幀字節就是40 × 31 = 1240個幀字節。附加4字節的控制字后就變成了1244個字節。使用Maxim的TDMoP芯片的眾多優點之一就是在自適應時鐘恢復模式下,默認模式的報文里并不使用RTP (實時協議)頭,因此可以為凈荷數據節省一些帶寬。大部分的其它廠家使用12字節的RTP。如果我們在TDMoP數據字節中使用RTP,那么總的數據字節將會是1256 (1244 + 12)。得到TDM數據字節的總數后,本例中為1240字節,用戶需要對Maxim的設備進行編程,使其也生成1240字節的TDM數據,或者是我們在Wireshark程序中得到的數目。互操作要求所有的報文長度都匹配。如果這些長度不同,那么用戶必須利用軟件菜單來配置Maxim的TDMoP設備,使其具有相同的報文長度。
B.UDP長度:圖15所示表明報文1的UDP長度為1252字節,它由1244字節的數據加上8字節的UDP協議組成。
C.IP長度:圖15所示表明報文1的IP長度為1272字節,它由1244字節的數據、20字節的IP報頭加上8字節的UDP協議報頭組成。
D.幀字節的總數目:圖15所示表明報文1共有1290字節。它由1244字節的數據、20字節的IP報頭、8字節的UDP協議報頭、2字節的以太類型、4字節的VLAN標記加上12字節的源和目的MAC地址組成。
以太類型
Maxim的TDMoP設備主要將下列以太類型作為已知的以太類型:- IPv4 (0x800)
- IPv6 (0x86DD)
- MPLS單播(0x8847)
- MPLS多播(0x8848)
- ARP (0x806)
- 配置在Mef_ether_type配置寄存器中的MEF以太類型
- 配置在Mef_oam_ether_type配置寄存器中的MEF OAM以太類型
- 配置在CPU_dest_ether_type配置寄存器中的特定以太類型

圖16. 以太類型值為0x800,代表著它是IPv4
一旦確定了以太類型,用戶必須將Maxim的TDMoP設備配置成為可以生成同樣的以太類型。每個以太類型可以在Bundle Configuration菜單中通過改變PSN類型進行選擇。Bundle Configuration菜單的部分如下圖所示。
Main Menu>Bundle Configuration>CES Bundle Configuration ... (P) 11. VLAN ID 1[1 - 4095] ... (100) 12. VLAN Priority[0 - 7] ... (7) 13. IP Tos[0 - 255] ... (0) 14. IP TTL[0 - 255] ... (128) 15. PSN Type > (IP)上面菜單中的選項15具有下面的內容:
Main Menu>Bundle Configuration>CES Bundle Configuration>PSN Type () 1. IP 2. MPLS 3. L2TPV3 4. Ethernet通過在Bundle Configuration菜單中選擇合適的組合,就可以匹配捕獲報文的以太類型。
總結
互操作性是指不同的設備和組織間可以共同工作(相互操作)。與其它產品可以實現互操作的設備或者遵循公開的接口標準,或者容許改變配置,將一個產品的接口直接的轉換為另一個產品的接口。通過了解其它TDMoP設備生成報文的類型,Maxim的設備可以很容易的實現與其它TDMoP設備的報文配置匹配。如果您對TDMoP產品或者Maxim的電信產品在使用中有進一步的問題,請通過電子郵件 telecom.support@maxim-ic.com (English only)或電話972-371-6555 (美國)與電信產品應用支持小組聯系
IEEE是美國電子和電器工程師協會的注冊服務標志。
Wireshark是Gerald Combs的注冊商標。
 電子發燒友App
電子發燒友App























評論