?
二極管電流公式:

注意的參數(shù):
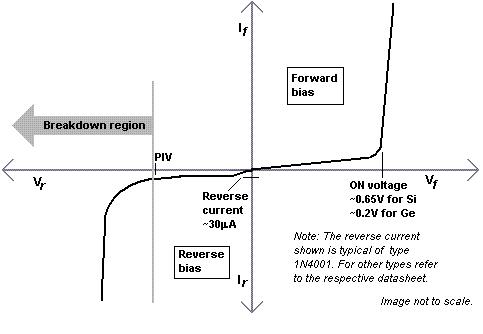
Peak Inverse Voltage(PIV rating) ??? ??? 最大反向電壓(絕對值)
The maximum reverse-bias voltage??? ??? ====>withstand without breaking down
Maximum repetitive reverse voltage[Vrrm]??? 最大反向電壓(重復(fù)脈沖)
the maximum reverse-bias voltage??? ??? ====>withstand in repeated pulses
Maximum DC reverse voltage? [Vr]??? ??? 最大反向電壓(直流)
the maximum reverse-bias voltage??? ??? ====>withstand on a continual basis
Maximum forward voltage [Vf]??? ??? ??? 最大正向電壓
Maximum (average) forward current??? ??? 最大正向電流(平均)
the maximum average current[If]??? ??? ??? ====>conduct in forward bias mode.?
Maximum (peak or surge) forward current ??? 最大正向電流(峰值或者脈沖)
the maximum peak current [If]??? ??? ??? ====>conduct in forward bias mode.
Maximum reverse current leakage current ??? 最大反向泄露電流
the current??? ??? ??? ??? ??? ====>in reverse-bias operation with the maximum rated inverse voltage applied
Maximum total dissipation??? ??? ??? 最大散熱功耗
Operating junction temperature [TJ]???????????? 運行結(jié)溫
maximum allowable temperature for the diode's PN junction
must be kept cool to function properly and give long service life.
Storage temperature range [TSTG]??????????????? 儲存溫度
the range of allowable temperatures for storing a diode (unpowered).
Thermal resistance??? ??? ??? ??? 熱阻
the temperature difference between junction and outside air or between junction and leads for a given power dissipation.
Reverse recovery time [Trr] ??? ??? ??? 反向恢復(fù)時間
the amount of time it takes for a diode to "turn off" when the voltage across it alternates from forward-bias to reverse-bias polarity.
Forward-bias(正向偏置恢復(fù)時間)
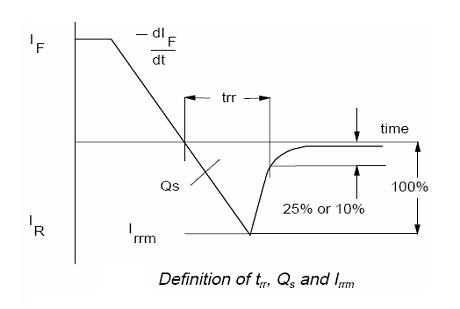
The transition (switching) time from conduction to open circuit when the bias is reversed. the diode bias is switched from forward to reverse.
At the switch time, the current reverses and stays at a constant level for a period of time called the storage time, ts. During this time the diode acts essentially as a short circuit.
Then the current decreases to the reverse leakage current value. This latter time is called the transition time.
The conditions which need to be specified are:(影響條件)
Steady-state forward current (IF); high currents increase recovery time. 正向電流(電流越大反向時間越長)
Reverse bias voltage (VR); low reverse voltage increases recovery time.? 反向電壓(電壓越小反向時間越長)
Rate of fall of anode current (dIF/dt); high rates of fall reduce recovery time, but increase stored charge.(電流變化速度,速度越快減小恢復(fù)時間卻會加長存儲時間)
Junction temperature (Tj); high temperatures increase both recovery time and stored charge.(結(jié)溫越高同時增加恢復(fù)時間和存儲時間)
reverse-bias(反向偏置)
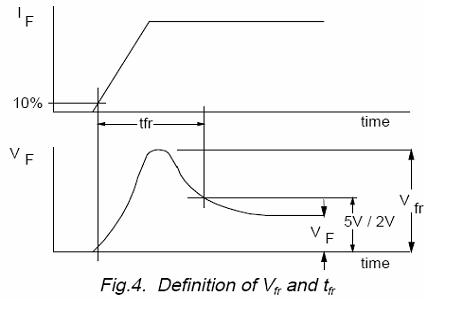
At the instant a semiconductor rectifier diode is switched into forward conduction there are no carriers present at the junction, hence the forward voltage drop may be instantaneously of a high value. As the stored charge builds up, conductivity modulation takes place and the forward voltage rapidly falls to the steady state value. The peak value of forward voltage drop is known as the forward recovery voltage (Vfr). The time from the instant the current reaches 10% of its steady-state value to the time the forward voltage drops below a given value ( usually 5V or 2V)isknown as the forward recovery time (tfr).
The conditions which need to be specified are:
Forward current (IF); high currents give high recovery voltages.正向電流(電流越大正向電壓越大)
Current pulse rise time (tr); short rise times give high recovery voltages.電流脈沖上升時間(脈沖越陡正向電壓越大)
Junction temperature (Tj); The influence of temperature is slight. 溫度影響不大
綜合整個過程
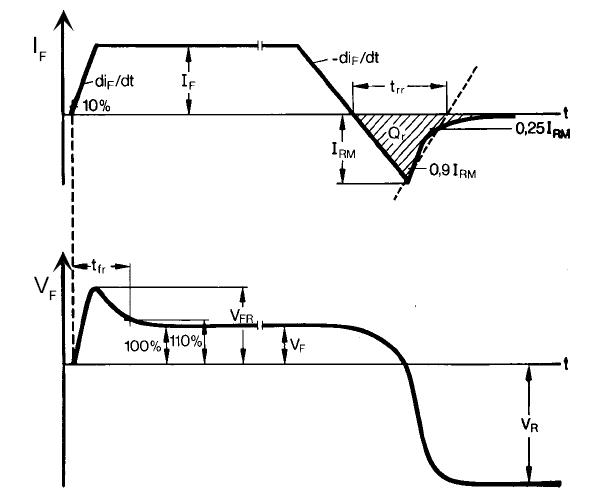
計算結(jié)溫過程(對于脈沖電流的計算方法)
注意的參數(shù):
Peak Inverse Voltage(PIV rating) ??? ??? 最大反向電壓(絕對值)
The maximum reverse-bias voltage??? ??? ====>withstand without breaking down
Maximum repetitive reverse voltage[Vrrm]??? 最大反向電壓(重復(fù)脈沖)
the maximum reverse-bias voltage??? ??? ====>withstand in repeated pulses
Maximum DC reverse voltage? [Vr]??? ??? 最大反向電壓(直流)
the maximum reverse-bias voltage??? ??? ====>withstand on a continual basis
Maximum forward voltage [Vf]??? ??? ??? 最大正向電壓
Maximum (average) forward current??? ??? 最大正向電流(平均)
the maximum average current[If]??? ??? ??? ====>conduct in forward bias mode.?
Maximum (peak or surge) forward current ??? 最大正向電流(峰值或者脈沖)
the maximum peak current [If]??? ??? ??? ====>conduct in forward bias mode.
Maximum reverse current leakage current ??? 最大反向泄露電流
the current??? ??? ??? ??? ??? ====>in reverse-bias operation with the maximum rated inverse voltage applied
Maximum total dissipation??? ??? ??? 最大散熱功耗
Operating junction temperature [TJ]???????????? 運行結(jié)溫
maximum allowable temperature for the diode's PN junction
must be kept cool to function properly and give long service life.
Storage temperature range [TSTG]??????????????? 儲存溫度
the range of allowable temperatures for storing a diode (unpowered).
Thermal resistance??? ??? ??? ??? 熱阻
the temperature difference between junction and outside air or between junction and leads for a given power dissipation.
Reverse recovery time [Trr] ??? ??? ??? 反向恢復(fù)時間
the amount of time it takes for a diode to "turn off" when the voltage across it alternates from forward-bias to reverse-bias polarity.
Forward-bias(正向偏置恢復(fù)時間)
The transition (switching) time from conduction to open circuit when the bias is reversed. the diode bias is switched from forward to reverse.
At the switch time, the current reverses and stays at a constant level for a period of time called the storage time, ts. During this time the diode acts essentially as a short circuit.
Then the current decreases to the reverse leakage current value. This latter time is called the transition time.
The conditions which need to be specified are:(影響條件)
Steady-state forward current (IF); high currents increase recovery time. 正向電流(電流越大反向時間越長)
Reverse bias voltage (VR); low reverse voltage increases recovery time.? 反向電壓(電壓越小反向時間越長)
Rate of fall of anode current (dIF/dt); high rates of fall reduce recovery time, but increase stored charge.(電流變化速度,速度越快減小恢復(fù)時間卻會加長存儲時間)
Junction temperature (Tj); high temperatures increase both recovery time and stored charge.(結(jié)溫越高同時增加恢復(fù)時間和存儲時間)
reverse-bias(反向偏置)
At the instant a semiconductor rectifier diode is switched into forward conduction there are no carriers present at the junction, hence the forward voltage drop may be instantaneously of a high value. As the stored charge builds up, conductivity modulation takes place and the forward voltage rapidly falls to the steady state value. The peak value of forward voltage drop is known as the forward recovery voltage (Vfr). The time from the instant the current reaches 10% of its steady-state value to the time the forward voltage drops below a given value ( usually 5V or 2V)isknown as the forward recovery time (tfr).
The conditions which need to be specified are:
Forward current (IF); high currents give high recovery voltages.正向電流(電流越大正向電壓越大)
Current pulse rise time (tr); short rise times give high recovery voltages.電流脈沖上升時間(脈沖越陡正向電壓越大)
Junction temperature (Tj); The influence of temperature is slight. 溫度影響不大
綜合整個過程
計算結(jié)溫過程(對于脈沖電流的計算方法)
